Practical: Limiting Factors (SQA National 5 Biology): Revision Note
Exam code: X807 75
Investigating factors that affect the rate of photosynthesis
Light provides the energy for photosynthesis
Measuring oxygen production from an aquatic plant, such as Elodea, at different light intensities shows how light intensity affects the rate of photosynthesis
Examiner Tips and Tricks
Note that this practical is a 'suggested practical' in the specification, rather than content that all students are expected to learn. Some schools may choose to complete alternative practicals, or may miss out practical work that is not realistic, e.g. due to equipment or time constraints.
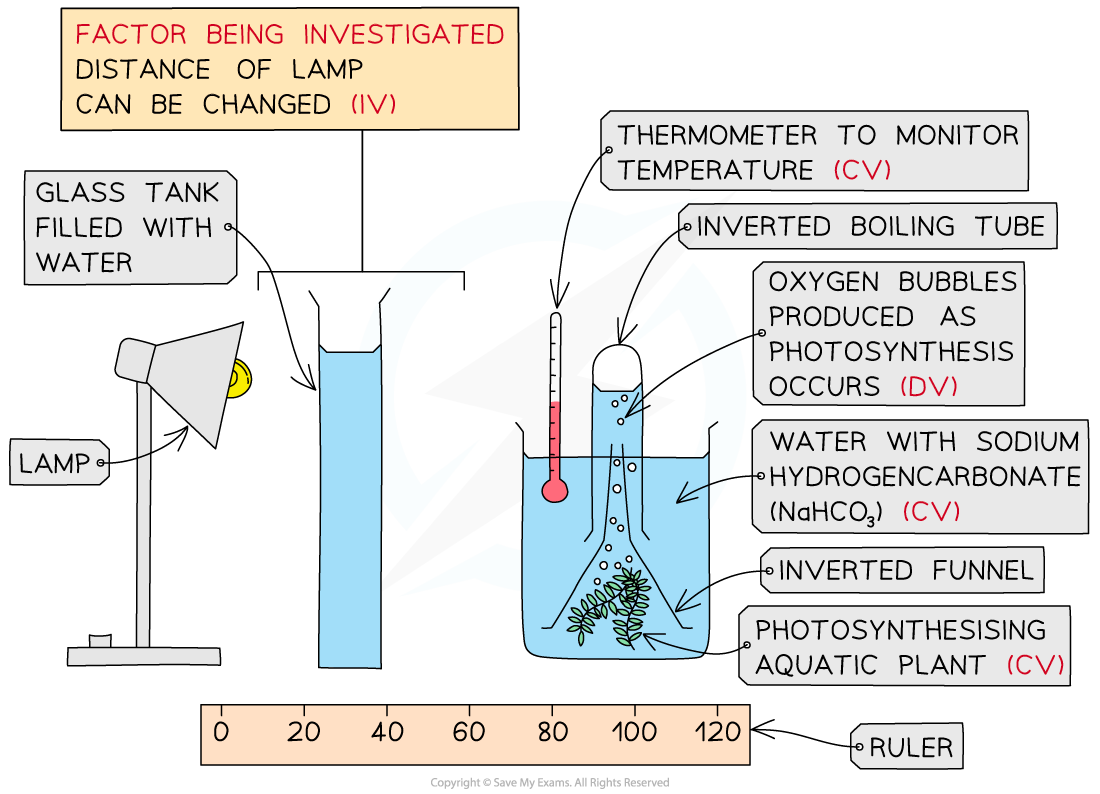
Apparatus
Elodea (or Cabomba) pond weed
Scissors
Beaker
Water (preferably pond water or dechlorinated tap water)
Sodium hydrogencarbonate (NaHCO₃)
Funnel and boiling tube / gas syringe
Thermometer and a glass tank filled with water
Light source, e.g. lamp or LED light
Ruler / measuring tape
Stopwatch
Method
Set up apparatus:
Cut a piece of pond weed using scissors; aim to make the cut at an angle to increase the surface area of the cut stem
Place the pond weed, cut end up, in a beaker of water
Add NaHCO₃ to increase availability of dissolved carbon dioxide in the water
Place an upturned funnel over the pond weed, with a test tube or gas syringe to catch the released gas
Set up a glass tank of water in front of the beaker; this will stop the heat from the lamp from raising the temperature of the water
Set the light intensity:
Set the lamp at a distance of 10 cm from the plant
Optional: measure light intensity at the pondweed with a light meter and record
Allow 5 minutes for the pond weed to equilibrate so that it is photosynthesising at a constant rate
Measure rate of photosynthesis: this can be achieved by, e.g.:
bubble count: count bubbles released from the cut stem for 1 minute
gas syringe: collect oxygen and record volume of gas collected (cm³) over 1 minutes
Repeat: do 3 trials at each light level and calculate a mean
Change the light intensity: move the lamp to a distance of 20, 30, 40 and 50 cm and repeat steps 4-5
Expected results
We would expect the rate of photosynthesis to decrease as the distance between the lamp and the pond weed increases
A graph of the independent variable against the number of bubbles produced per minute can be drawn to see the trend

Limitations
Limitation | Possible solution |
|---|---|
Temperature rises near the lamp | Use LED lamp that does not get hot Set up a water bath to absorb heat |
Bubble size varies | Use a gas syringe and measure total volume of gas released |
CO₂ becomes limiting | Use NaHCO₃ solution and keep concentration constant |
Adaptation time too short so rate of photosynthesis has not stabilised | Allow a 2–5 min acclimation before timing |

Unlock more, it's free!
Was this revision note helpful?
