Product Development (SQA National 5 Business Management): Revision Note
Exam code: X810 75
The process of developing products
Product development is the process a business follows to create a new product or service, or to improve an existing one, to meet customer needs and stay competitive
A successful product development process helps reduce risk, control costs, and ensure the final product appeals to the target market
The product development process
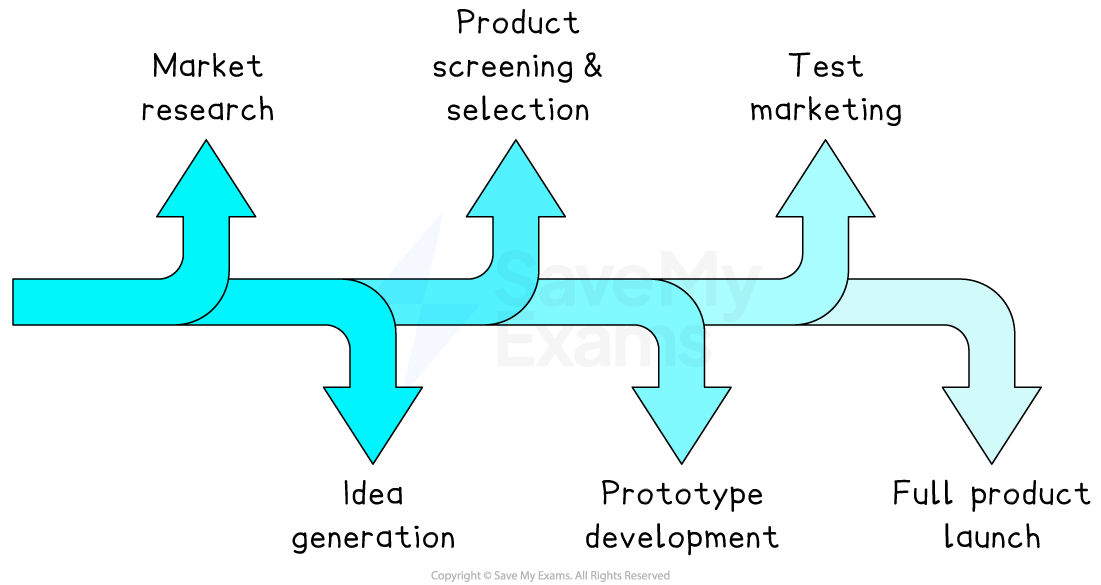
1. Market research
Before any ideas are developed, businesses carry out market research to find out what customers want and what competitors are offering
Research identifies gaps in the market or areas for improvement in existing products
It can include field research, such as surveys, focus groups or interviews and desk research, such as analysing sales data and trends
Decisions made in this stage include
Who the target market will be
What customer needs the new product must meet
What price range and quality level are appropriate
2. Idea generation
Businesses then brainstorm potential product ideas
Ideas can come from employees, customer feedback, competitor analysis or new technology
Decisions made in this stage include
Which ideas are feasible?
Which products fit with the brand image and existing product range?
3. Product screening and selection
Not all ideas are practical or profitable, so the business evaluates and screens them to choose the most promising one
Decisions made in this stage include
Whether there are enough resources and skills to produce it
Whether it will meet legal, safety or ethical standards
4. Prototype development
A prototype (or sample model) is created to test the design, function, and safety of the product before mass production
Prototypes help identify faults or design improvements early in the process
Decisions made in this stage include
Which materials and production methods will be used
How the product will look, feel and perform
Whether to continue with production or redesign
5. Test marketing
The product is launched on a small scale in one area or to a limited group of customers
Feedback is collected on performance, price, packaging and customer satisfaction
Decisions made in this stage include
Whether the product should be modified or improved
What price level and promotion strategy work best
Whether there is enough demand for a full launch
6. Full product launch
Once the business is confident in the product, it is introduced to the wider market
At this stage, all elements of the marketing mix — product, price, place, and promotion — are finalised
Pricing: choose the most suitable pricing strategy (e.g. competitive, skimming, penetration)
Distribution (place): select how and where to sell — e.g. retail stores, online, or direct to customers
Promotion: design an advertising and promotion campaign to create awareness and encourage sales
As well as this, decisions on production approach, such as whether to use job, batch or flow production, depending on demand and cost
Risks of product development
Developing new products can help a business grow, but it also involves significant risks
Poor planning or incorrect decisions at any stage can lead to financial loss and damage to reputation
The main risks of product development
Risk | Explanation |
|---|---|
High development costs |
|
Time delays |
|
Impact on existing products |
|
External Factors |
|
Examiner Tips and Tricks
A common mistake is thinking product development ends once an item is launched. It’s actually a continuous process, from idea to testing, launch and improvement

Unlock more, it's free!
Was this revision note helpful?
