Chromosome Structure (Cambridge (CIE) A Level Biology): Revision Note
Exam code: 9700
Chromosome structure
Chromosomes are made of one very long, condensed DNA molecule associated with proteins (in eukaryotic cells)
The main proteins present are the large positively charged globular proteins called histones
Their role is to organise and condense the DNA tightly so that it fits into the nucleus
The tightly coiled combination of DNA and proteins is called chromatin—this is what chromatids, and therefore chromosomes, are made of
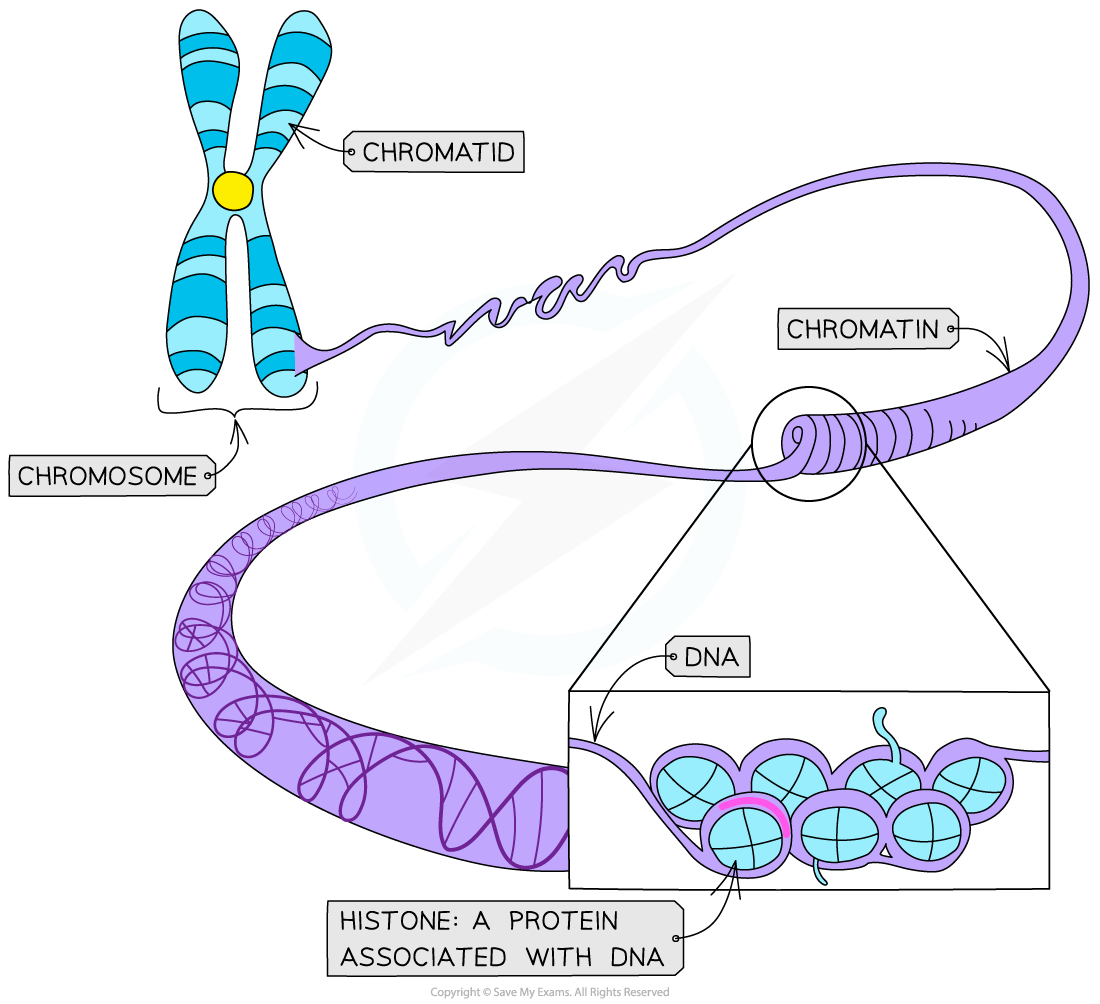
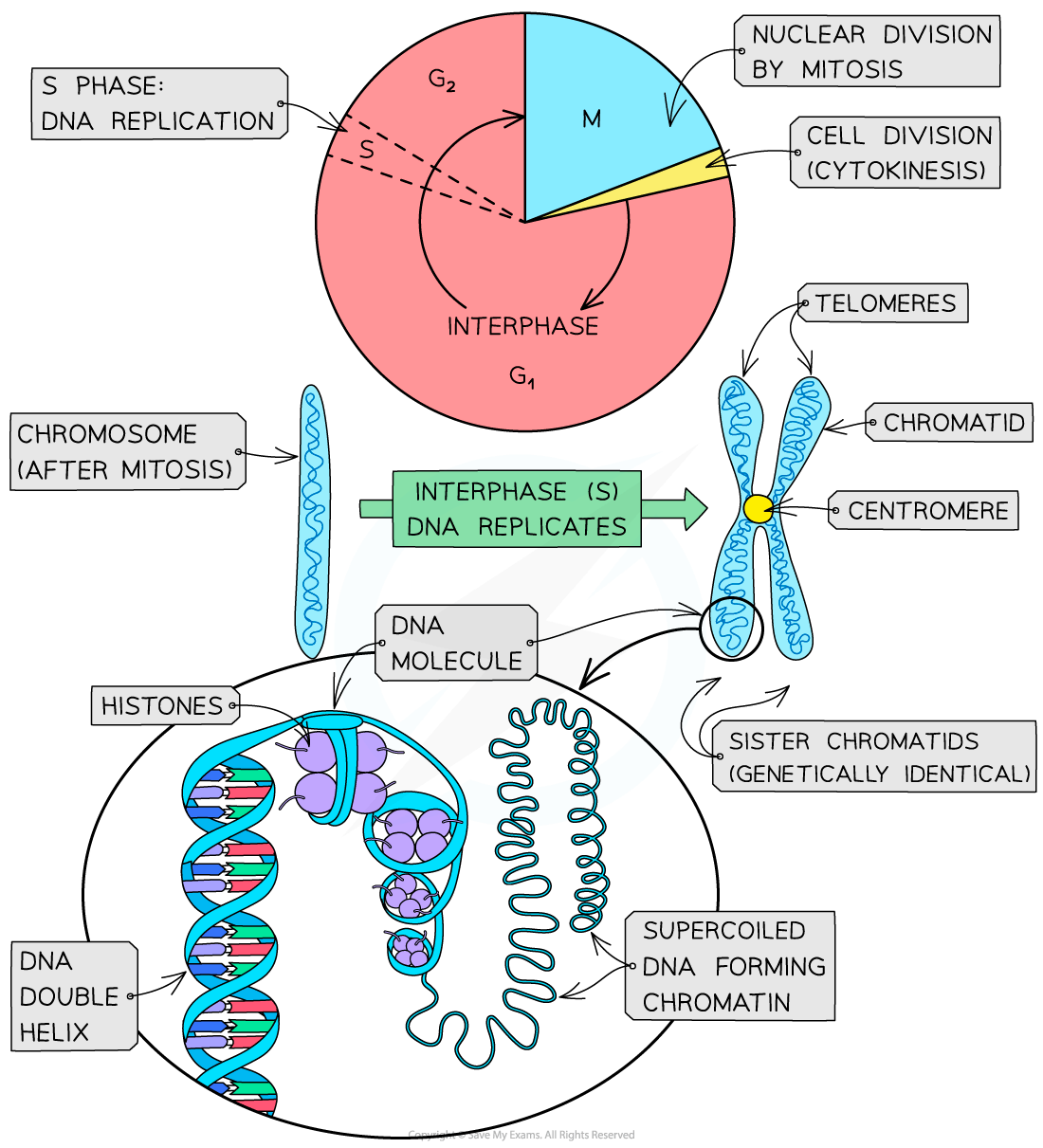
During interphase (S phase) the DNA replicates to create two identical strands of DNA called chromatids
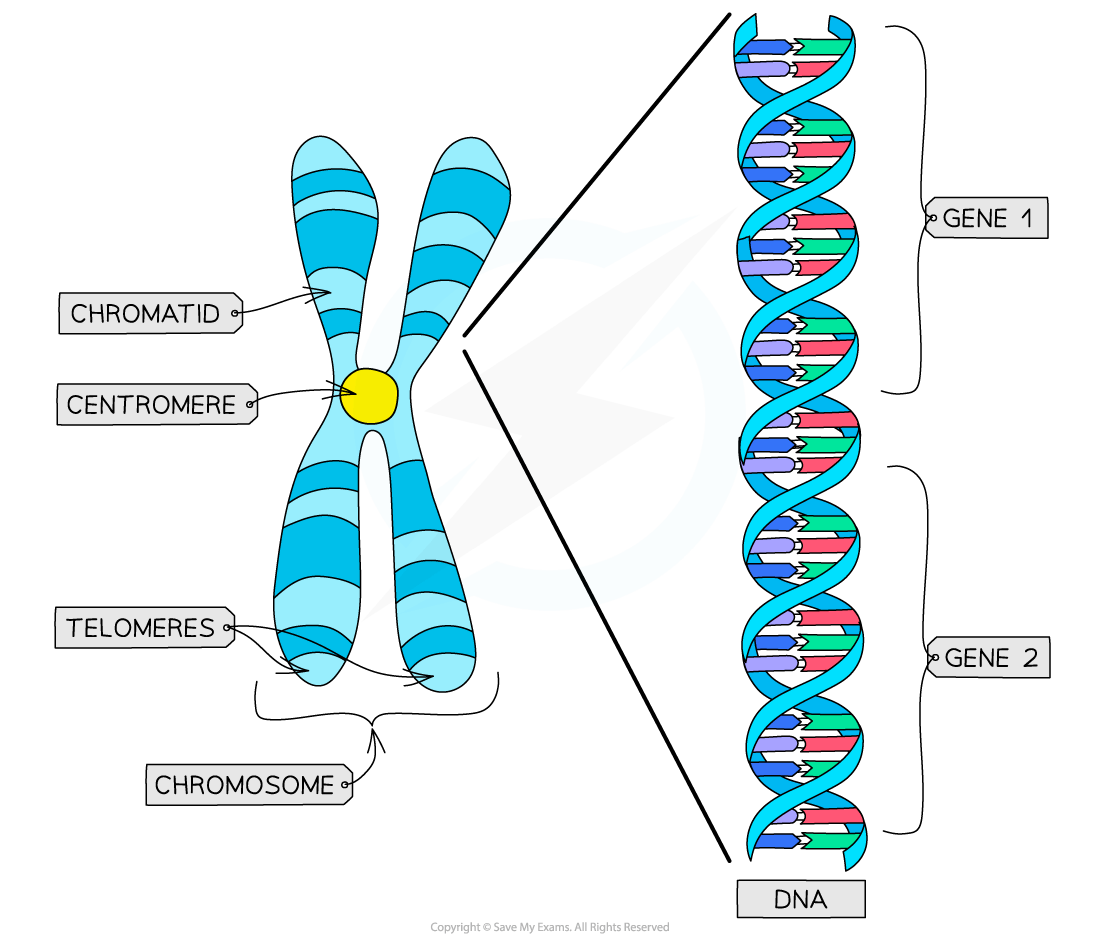
These chromatids are joined together by a narrow region called the centromere
The two chromatids that make up the double structure of a chromosome are known as ‘sister chromatids’
It is important that the sister chromatids are identical (contain the same genes) because this is key to cell division
One chromatid goes into one daughter cell and one goes into the other daughter cell during mitosis, ensuring the daughter cells are genetically identical
Each chromatid is made up of one very long, condensed DNA molecule, which is made up of a series of genes
The ends of the chromatids in chromosomes are ‘sealed’ with protective structures called telomeres
Examiner Tips and Tricks
It is important that you are able to distinguish when the terms chromatid, sister chromatids and chromosomes are used.

Unlock more, it's free!
Was this revision note helpful?
