Which process/activity can lead to isostatic sea level change?
A global change in sea level.
Human activity such as road building or mining.
Rotational slumping.
The melting of ice sheets on land areas.
Was this exam question helpful?
Exam code: 7036
Which process/activity can lead to isostatic sea level change?
A global change in sea level.
Human activity such as road building or mining.
Rotational slumping.
The melting of ice sheets on land areas.
Choose your answer
Was this exam question helpful?
Where do salt marshes tend to develop?
At depositional coastlines exposed to longshore drift.
In estuaries with an ample supply of sediment, often on the landward side of spits.
In high-energy environments which bring large waves and lots of sediment pushed into bays.
In places where there has been an isostatic sea level change leading to deep water lagoons in which sediment collects.
Choose your answer
Was this exam question helpful?
Outline processes involved in the development of estuarine mudflat environments.
How did you do?
Was this exam question helpful?
Assess potential impacts of climate change on the physical landforms of a local scale coastal landscape you have studied.
How did you do?
Was this exam question helpful?
Which of the following are all landforms associated with coastal erosion?
Arches, offshore bars, sand dunes
Barrier beaches, caves, compound spits
Beaches, spits, tombolos
Cliffs, stacks, wave cut platforms
Choose your answer
Was this exam question helpful?
Assess the possible impacts of sea level change on estuarine saltmarsh environments.
How did you do?
Was this exam question helpful?
Which of the following are all landforms of coastal deposition?
Beaches, barrier beaches, compound spits, offshore bars.
Beaches, caves, Dalmatian coasts, spits.
Cliffs, offshore bars, spits, tombolos.
Tombolos, rias, sand dunes, wave cut platforms.
Choose your answer
Was this exam question helpful?
‘Submergent coastal landforms will develop faster than emergent features in the future.’
To what extent do you agree with this statement?
How did you do?
Was this exam question helpful?
What is a spit?
A beach that is found higher than the current shoreline formed by a fall in sea level relative to the land.
A gently sloping expanse of eroded rock at the base of a cliff formed by wave erosion.
A horseshoe shaped feature on a beach composed of deposited sand and gravel with seaward facing points.
A long narrow ridge of sand or shingle with one end connected to the shore and the other extending into the sea or estuary.
Choose your answer
Was this exam question helpful?
Which of the following describes a Dalmatian coast?
An emergent coastline of former wave-cut platforms and their beaches at a higher level than the current sea level.
A series of ridges on a beach running parallel to the coast marking successively higher tides between neap and spring tides.
A sheltered area on the landward side of a spit where coastal sediments accumulate and become stabilised by vegetation like marram grass.
A submergent coastline where valleys have been flooded by a rise in sea level leaving a series of islands parallel to the coastline.
Choose your answer
Was this exam question helpful?
Outline the concept of eustatic sea level change.
How did you do?
Was this exam question helpful?
Figure 3 and Figure 4 provide information about the changes in coastal landforms in the Kuala Baram region of Sarawak, East Malaysia.
Figure 3
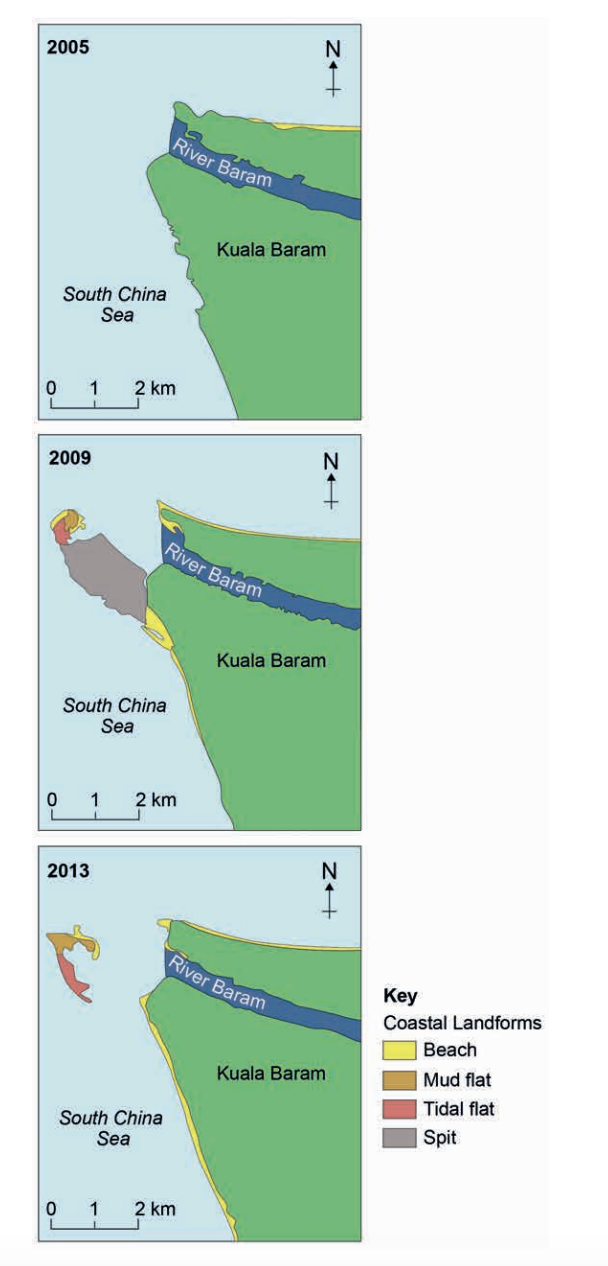
Figure 4
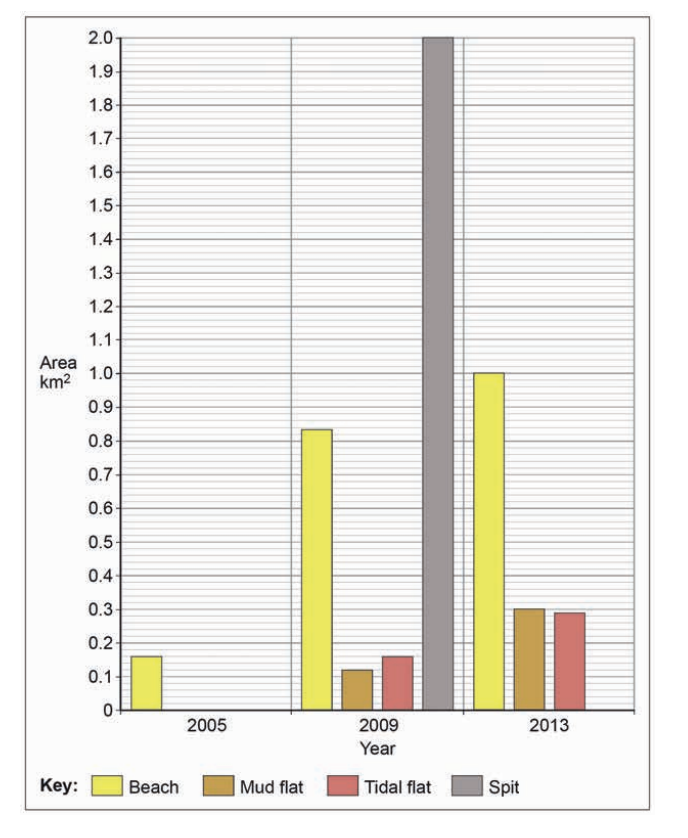
Analyse the data shown in Figure 3 and Figure 4.
How did you do?
Was this exam question helpful?