Figure 2 shows information about average annual sea surface temperatures for 1980 to 2014, compared to the average global sea surface temperature between 1993 and 2012.
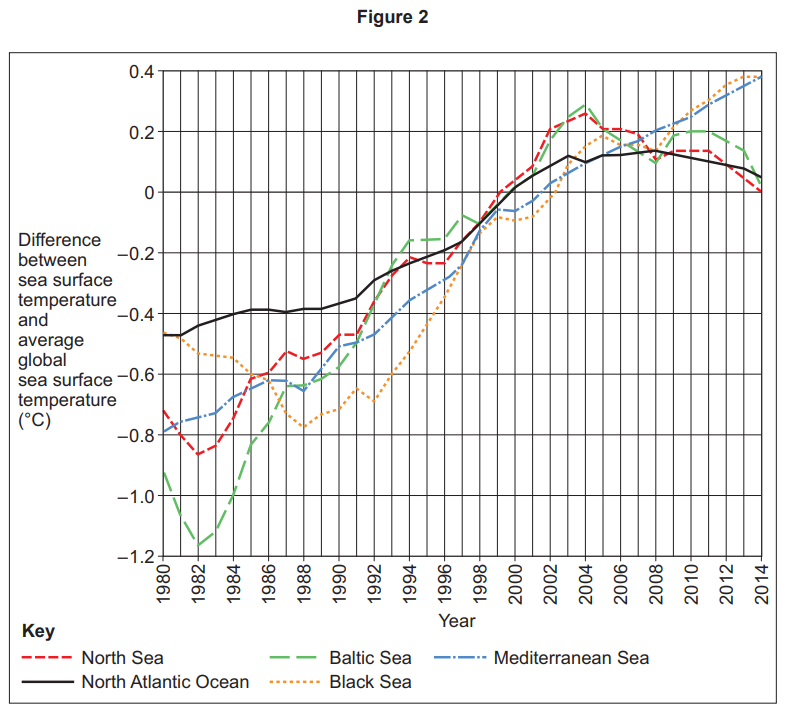
Analyse the information shown in Figure 2.
Was this exam question helpful?
Exam code: 7036
Figure 2 shows information about average annual sea surface temperatures for 1980 to 2014, compared to the average global sea surface temperature between 1993 and 2012.

Analyse the information shown in Figure 2.
How did you do?
Was this exam question helpful?
Which of the following outlines a positive feedback at the coast?
Erosion occurs at the base of a cliff a wave-cut platform begins to form
erosion extends the platform
waves have further to travel and lose energy
erosion decreases.
Vegetation begins to grow in sediments of saltmarshes vegetation traps more sediment
height of the marsh increases
length of time inundated by the sea reduces
vegetation growth increases.
Storms erode sediment from a beach sediment deposited as offshore bars
waves break earlier
erosion reduces
after the storm, waves return sediment to the beach.
Waves erode the base of a cliff undercutting leaves the cliff unsupported
cliff collapses leaving debris at the base
cliff is protected from powerful waves
rates of erosion are reduced.
Choose your answer
Was this exam question helpful?
In systems in physical geography, which of the following correctly defines negative feedback?
Changes in a system amplify, or speed up, the impacts of an initial action.
Changes in a system decrease, or slow down, the impacts of an initial action.
When there is a balance between the inputs and outputs of a system.
When there is a transfer of energy beyond the boundary of the system.
Choose your answer
Was this exam question helpful?
Figure 2 shows information about tidal ranges at coasts around the world.
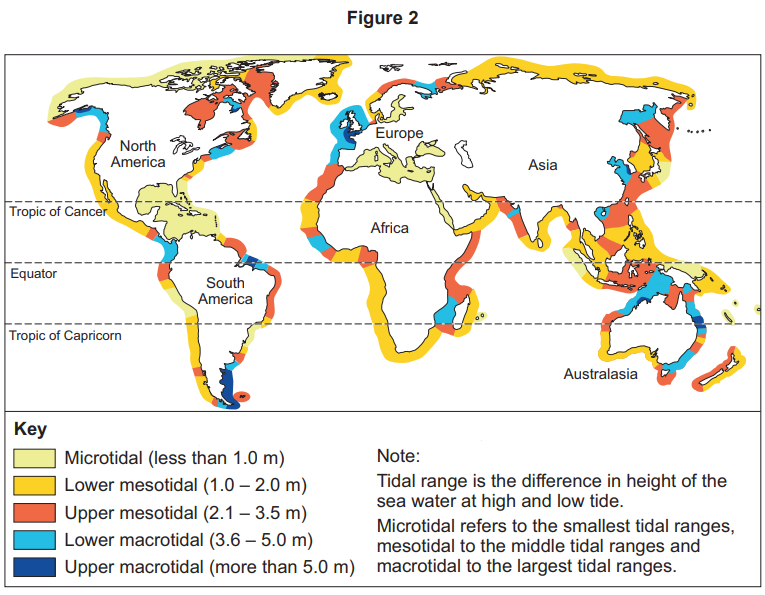
Analyse the information shown in Figure 2.
How did you do?
Was this exam question helpful?