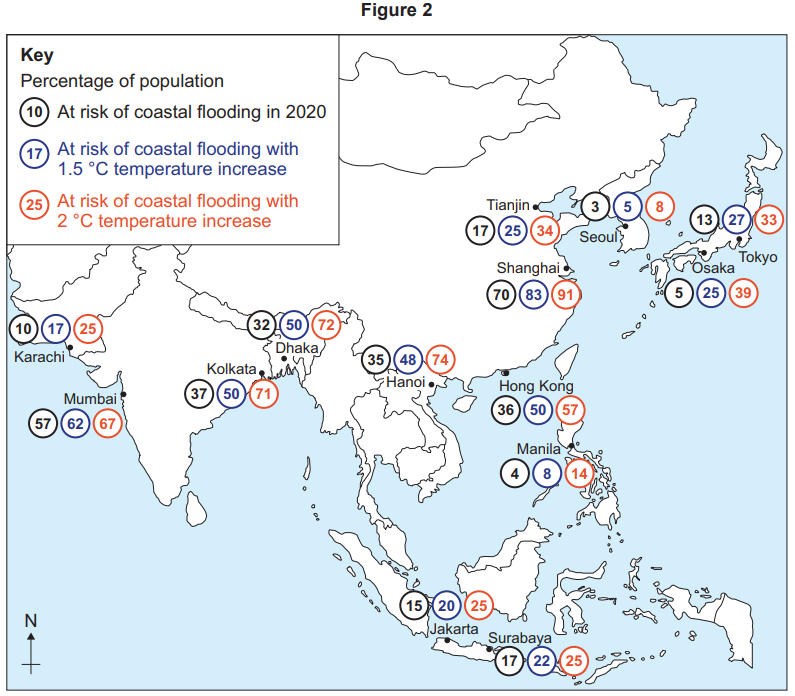
Figures 3 and 4 show information about areas at risk of flooding.
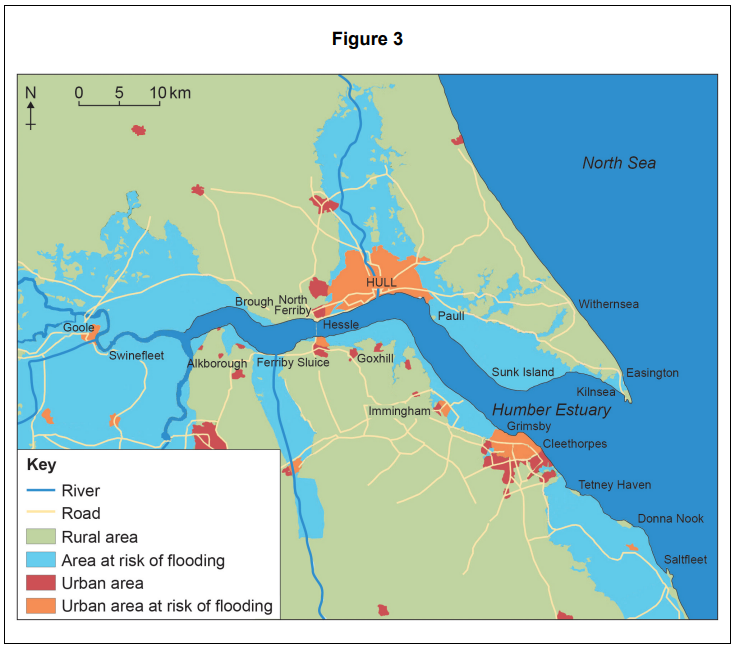
Figure 4
Area | Total population | Number at high risk of flooding | Number at medium risk of flooding | Number at low risk of flooding |
Humber catchment | 11 713 119 | 58 210 | 299 985 | 632 211 |
Grimsby | 275 657 | 3 908 | 16 419 | 22 638 |
Hull | 566 322 | 1 434 | 64 500 | 258 763 |
Using Figure 3 and Figure 4, assess the extent of the flood risk in the area shown.
Was this exam question helpful?