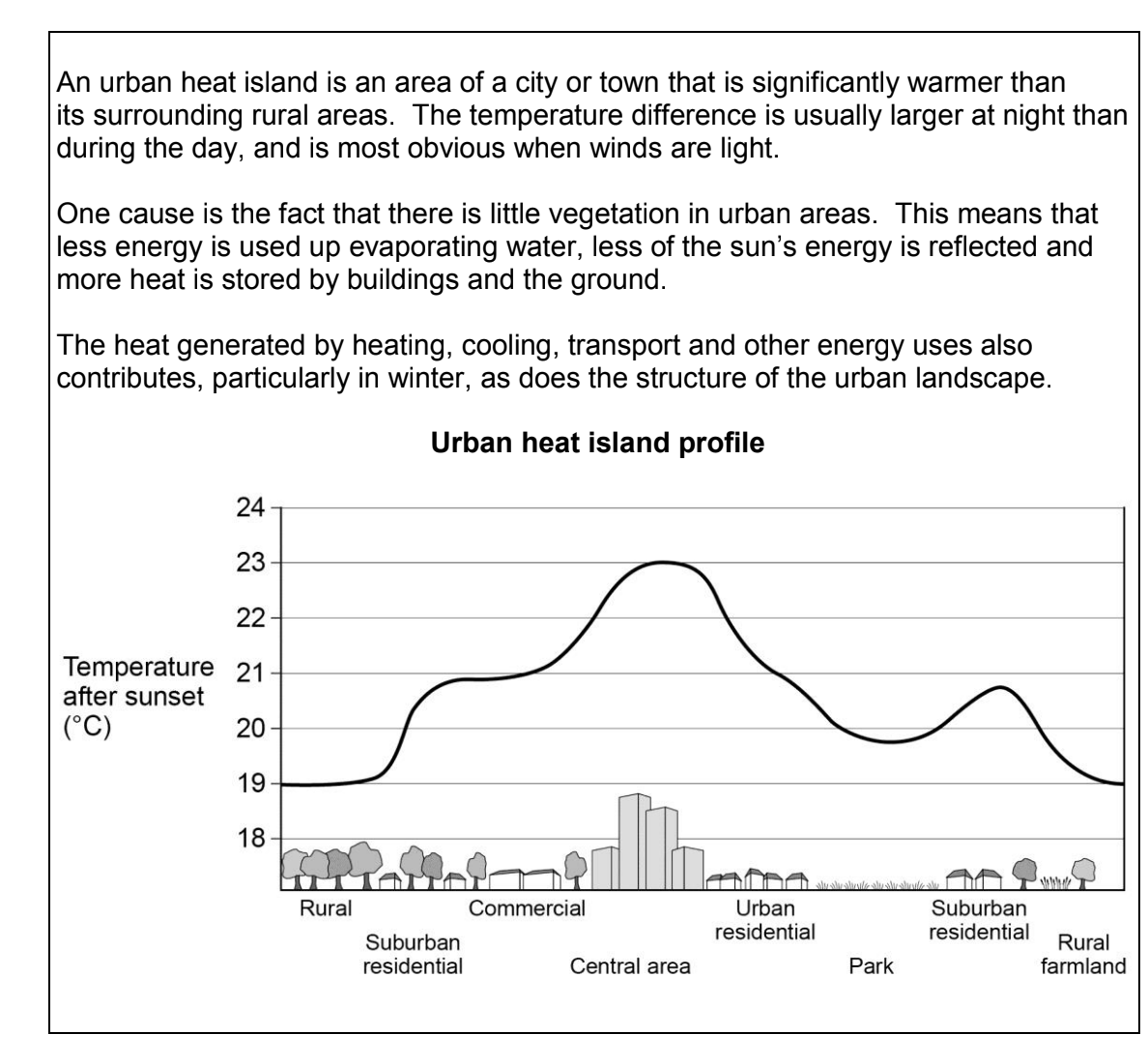
What is the urban heat island effect?
Higher temperatures are found on large developed islands. The temperatures are higher because of the geographical location of the settlements near to the equator.
The physical geography of some cities means that temperatures are higher than the surrounding areas e.g. where they lie on the coast with a warm onshore breeze.
Small villages often have higher temperatures than the surrounding areas in the countryside. This is because of the effect of housing and lighting.
Large cities have higher temperatures than the surrounding areas because of a variety of human activity. Dark surfaces absorb heat during the day and mass heating causes warming.
Was this exam question helpful?