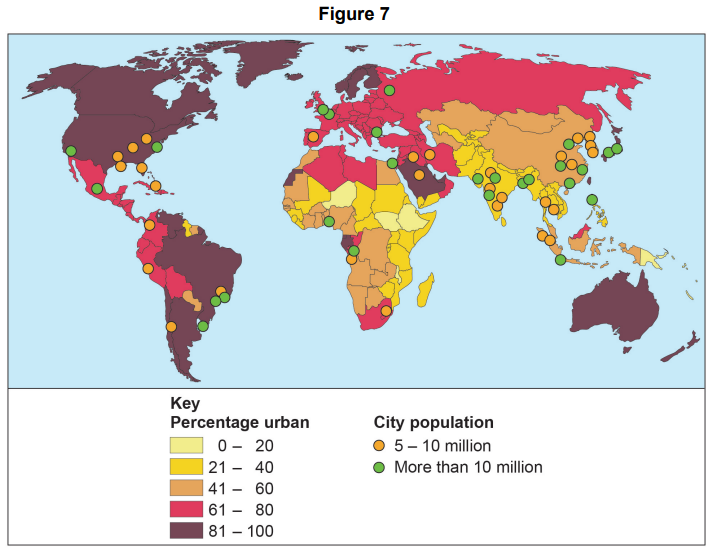
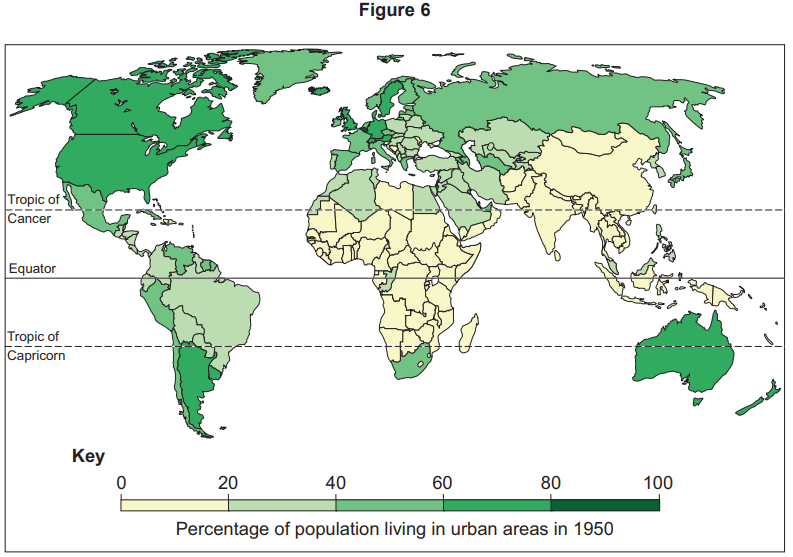
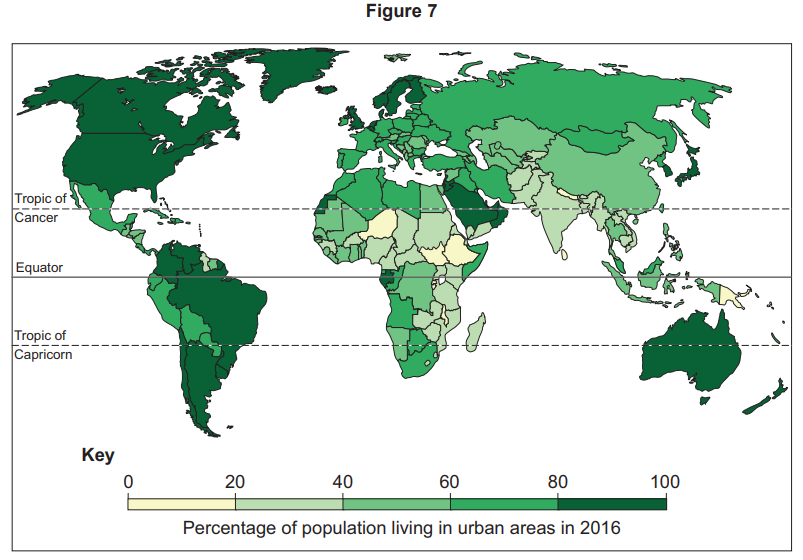
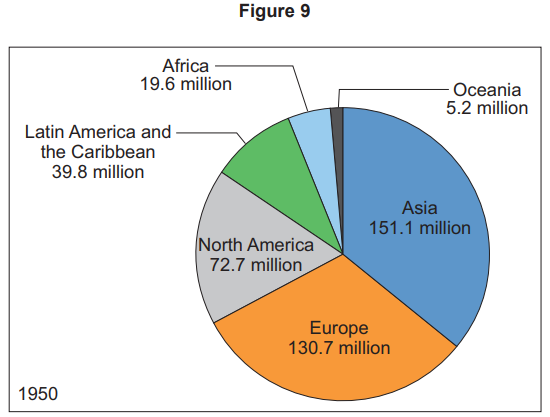
Counter-urbanisation is:
Caused when the poor are pushed out of an area by gentrification.
Movement of people back into a regenerated urban area.
Movement of people from urban areas into surrounding rural areas.
The flow of commuters into city in the morning then back to the suburbs in the evening.
Was this exam question helpful?