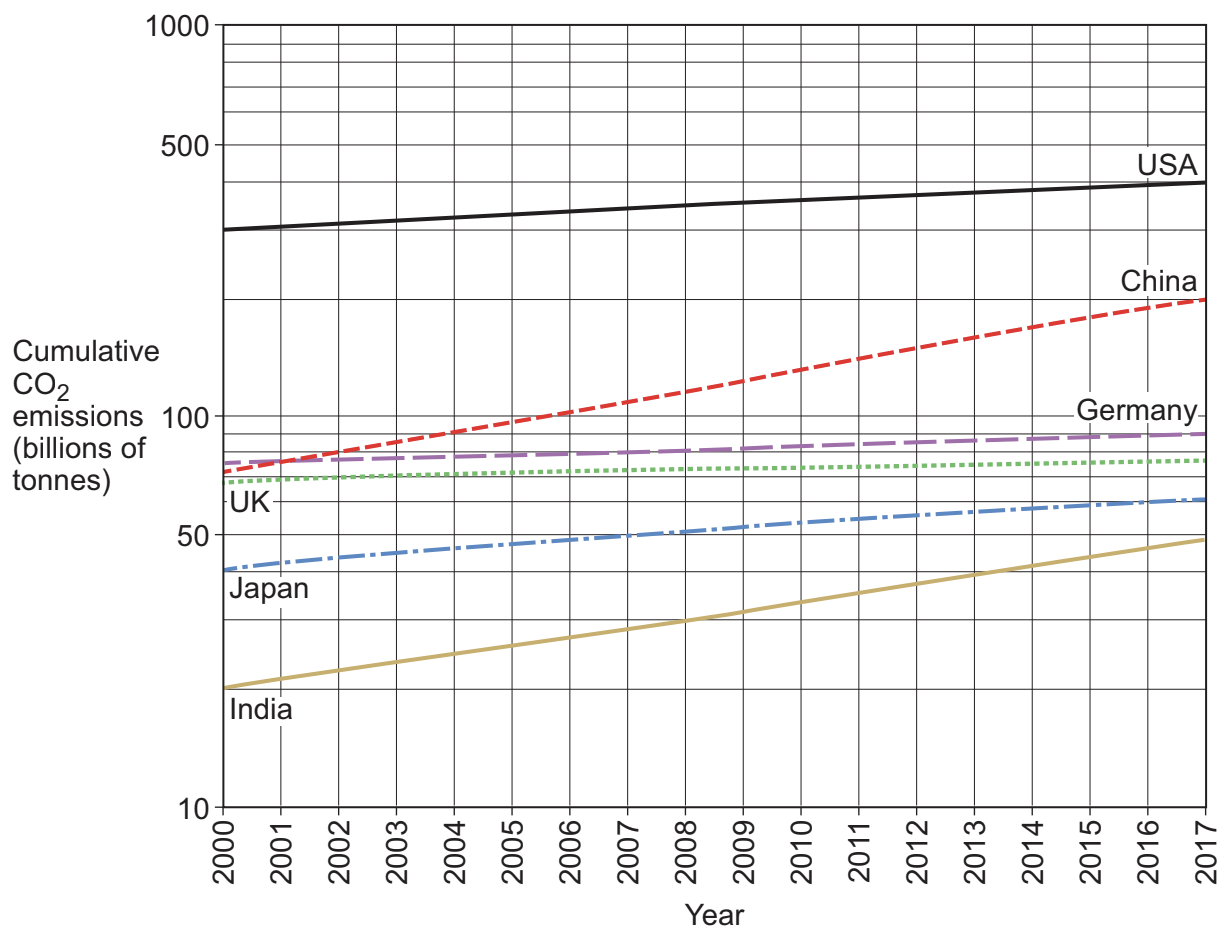
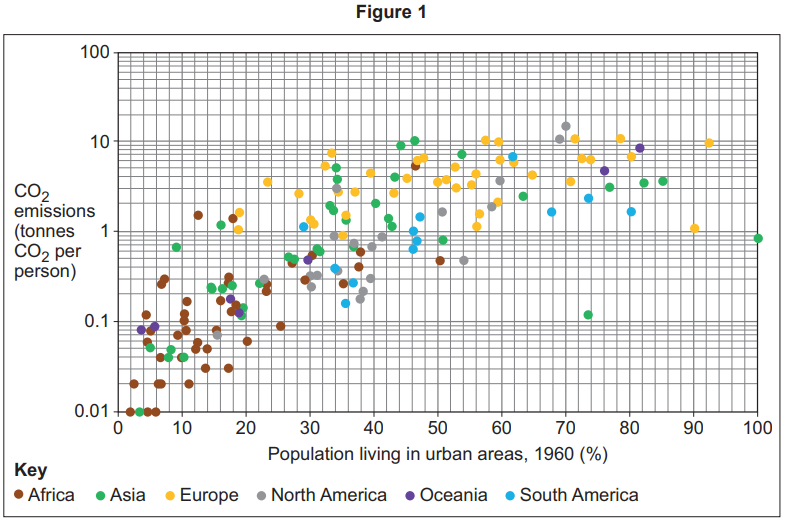
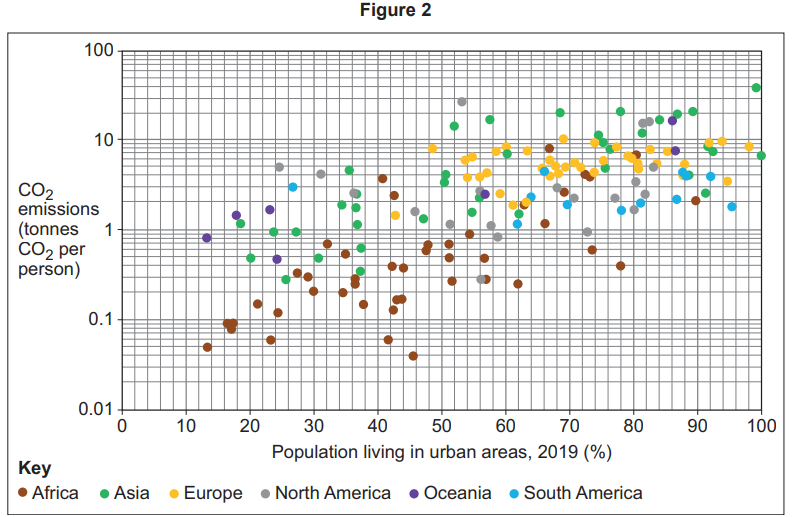
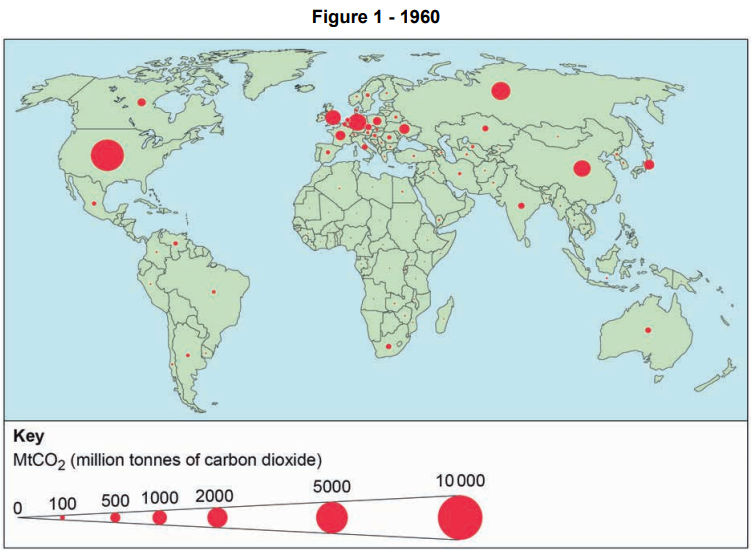
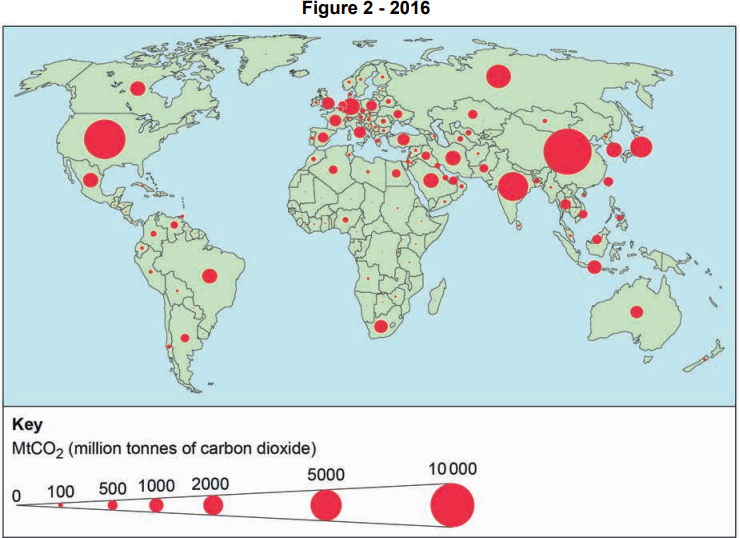
To what does the carbon budget refer?
The amount of carbon in the atmosphere at any one time.
The balance of exchanges between the four major stores of carbon.
The measurement of the quantity of transferred carbon between the land and ocean.
The total quantity of the major stores of carbon.
Was this exam question helpful?