Making & Shaping Law (Edexcel GCSE Citizenship Studies): Revision Note
Exam code: 1CS0
From Bill to Act
Types of legislation
A bill is a proposed law that is debated in Parliament
If it is approved by both the House of Commons and the House of Lords and then given Royal Assent, it becomes an Act of Parliament
Types of Bill
Type of Bill | Explanation |
|---|---|
Public Bills |
|
Private Members’ Bills |
|
Private Bills |
|
Hybrid Bills |
|
Examiner Tips and Tricks
A common mistake is saying all bills are proposed by the government
Remember: Public Bills = government, Private Members’ Bills = backbench MPs or Lords, Private Bills = organisations
In exam answers, name the bill type before explaining it to show clear understanding and secure method marks early
The legislative process in the UK can begin in either the House of Commons or the House of Lords
Most important government bills start in the House of Commons because it is the elected chamber
Legislative stages
Stage | Explanation |
|---|---|
First Reading |
|
Second Reading |
|
Committee Stage |
|
Report Stage |
|
Third Reading |
|
Consideration by the other House |
|
Royal assent
Royal Assent is the final stage of the law-making process in the UK Parliament
It happens after a bill has been debated and approved by both the House of Commons and the House of Lords
Royal Assent involves the monarch formally agreeing to the Bill
This agreement is given on the advice of the government, not as a personal decision by the monarch
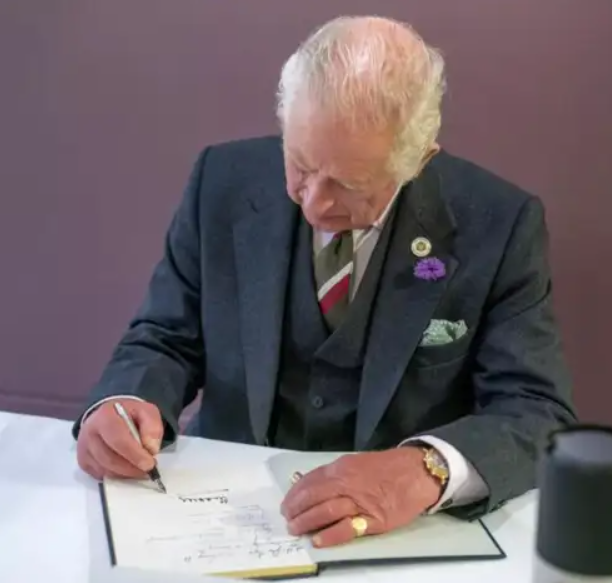

Once Royal Assent is granted, the bill officially becomes an Act of Parliament
The law can then come into force, either immediately or on a specified future date
Royal Assent is largely a formality
No bill has been refused Royal Assent in modern times, as Parliament is sovereign

Unlock more, it's free!
Was this revision note helpful?
