Citizens & Local Government (Edexcel GCSE Citizenship Studies): Revision Note
Exam code: 1CS0
What do local councils do?
Local councils operates at a local level, below central government and focuses on issues that directly affect local communities
Local councils help make democracy accessible, as decisions are made closer to the people they affect
They encourages active citizenship, such as voting, volunteering and community involvement
They help balance power between central government and local communities
How local government is structured
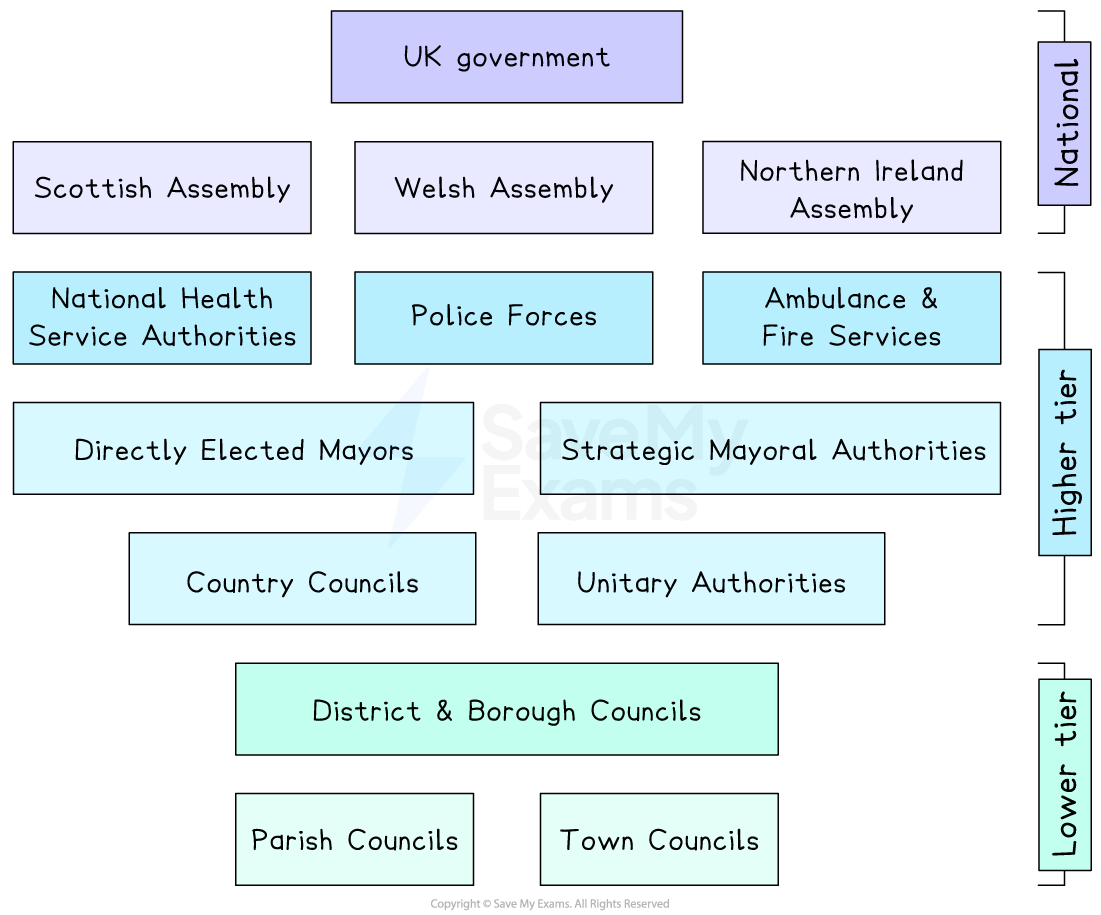
Parish councils
Parish councils represent small villages or rural communities
They deal with very local issues such as footpaths, village halls and community events
Town councils
Town councils are similar to parish councils but operate in larger towns
They focus on local amenities, community projects and representing residents’ views
District and Borough Councils
These councils provide local everyday services, such as housing, waste collection and local planning
They serve individual or groups of towns or cities within a county or larger area
County councils
These are organisations, such as Staffordshire County Council, that provide large-scale services across a wide area, such as education, social care, highways and libraries
They usually work alongside district or borough councils in a two-tier system
Unitary authorities
Unitary authorities, such as Medway Council, combine county and district responsibilities into one council
They provide all local services in their area, making decision-making simpler
Directly Elected Mayors
Directly elected mayors, such as Andy Burnham in Manchester, lead a city or local area and provide visible leadership
They are responsible for setting priorities and representing the area locally and nationally
Councillors and officers
Councillors play a key role in local democracy, representing residents, helping make decisions, and holding the council to account
What do councillors do?
Role | What this involves |
|---|---|
Representing the community |
|
Considering residents’ views |
|
Making local decisions |
|
Committee membership |
|
Specialising in key areas |
|
Dealing with casework |
|
Attending meetings |
|
Civic and community role |
|
Informing the public and media |
|
Councillors are accountable to voters at local elections, which take place every three or four years
Voters can remove councillors who they feel have not represented them effectively
They are held to account by the public, pressure groups and the media
Poor behaviour or controversial decisions can attract public criticism
Councillors must complete declarations of interest so the public can see any financial or employment interests that could influence decisions
Each council has a Code of Conduct for Members
This sets out expected standards of behaviour and includes sanctions for breaches
The role of council officials
Council officials are unelected council staff who turn political decisions into practical action
They ensure services are delivered fairly and legally
They help maintain trust and accountability in local government
The Chief Executive
The Chief Executive is head of the council’s paid staff and the most senior officer in the local council
They are appointed by councillors, not elected by the public
The Chief Executive's role includes:
Managing day-to-day operations
Oversees how council services are run
Ensures decisions made by councillors are put into action
Providing advice to councillors
Gives professional and impartial advice
Helps councillors understand the impact of their decisions
Ensuring the council works effectively
Makes sure the council meets legal duties
Promotes efficiency, good management and value for money
Other senior officers
Directors and department heads
Lead specific services such as education, housing or social care
Responsible for planning and delivering services to the public
Finance officer
Manages the council’s budget and spending
Ensures public money is used responsibly and lawfully
Monitoring officer
Ensures the council follows the law and code of conduct
Investigates complaints about councillor behaviour
Local councils and the community
Local councils play a key role in representing the views and interests of local people
They are the level of government closest to citizens
This means they deal with issues that affect everyday life
Councils help ensure local voices are heard in decision-making
Councillors are elected to speak on behalf of their communities
They represent residents with different needs, opinions and backgrounds
By representing the community, local councils support local democracy
They allow citizens to influence decisions that affect their area
This helps build trust, accountability and participation at a local level

Unlock more, it's free!
Was this revision note helpful?
