Development of Human Rights (Edexcel GCSE Citizenship Studies): Revision Note
Exam code: 1CS0
The Magna Carta
In 1215 the Magna Carta laid the foundations of basic legal rights, including
The right to a fair trial
The right to a trial by jury
Protection from unlawful arrest

The UN Universal Declaration on Human Rights
Human rights are basic freedoms and protections that everyone is entitled to so they can live with dignity, fairness and freedom
The Universal Declaration of Human Rights was agreed by the United Nations in 1948
It is the key document regarding the development of human rights
It comprises 30 ‘articles’ or sections
In short, all states have a duty, regardless of their political, economic and cultural systems, to promote and protect all human rights for everyone without discrimination
The 30 articles of the UNDHR
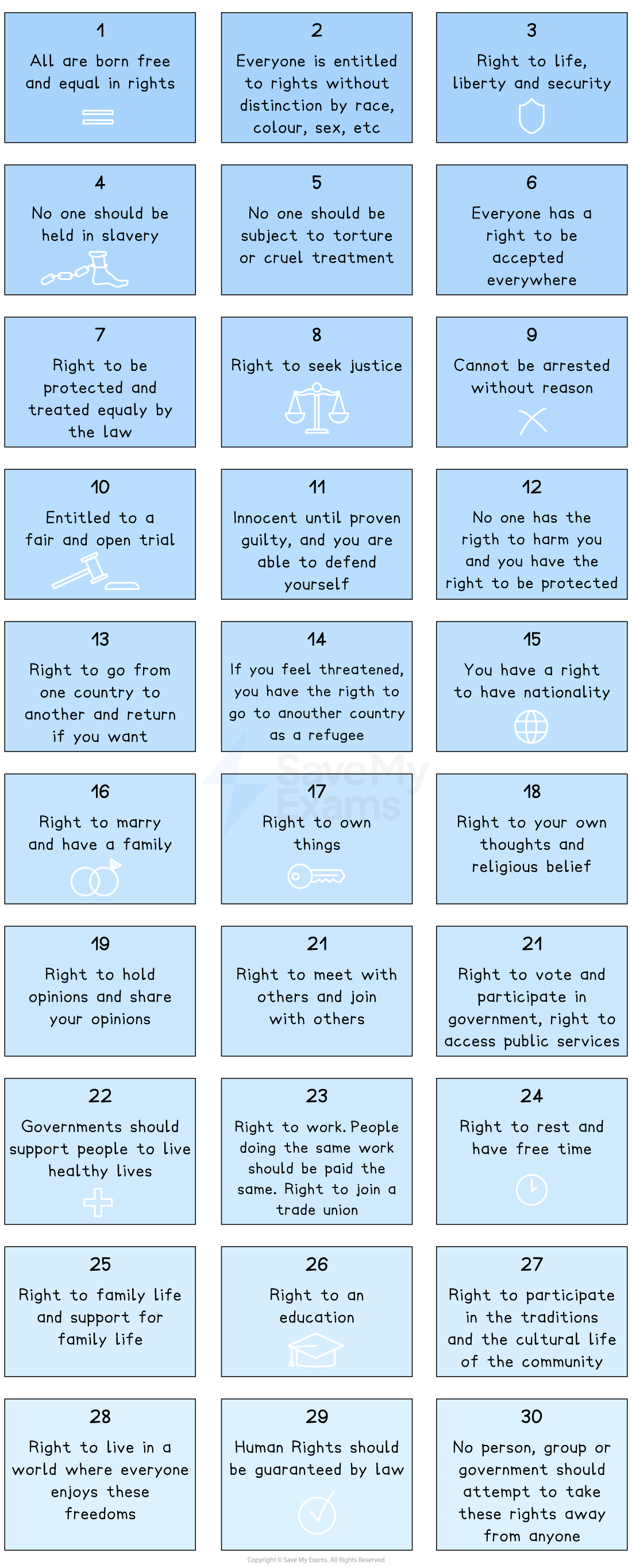
Although the UNDHR is not legally binding, the protection of the rights and freedoms it sets out have been incorporated into many national constitutions and legal frameworks
The European Convention on Human Rights
The European Convention on Human Rights and Fundamental Freedoms (ECHR) was drafted in 1950 by the Council of Europe
The UK played a key role in drafting the original document
The Convention has been updated from time to time
Its articles are enforced by the European Court of Human Rights, which meets in Strasbourg, France
Judges come from member countries and sit as a multinational panel when deciding cases
Its judgments are binding on member states
Citizens in the UK can take cases to the Court after they have exhausted all avenues via UK courts
The ECHR is currently politically contentious in the UK
Some political parties want the UK to leave the Convention, as they feel it limits the power of the UK government to take certain actions
Articles of the ECHR
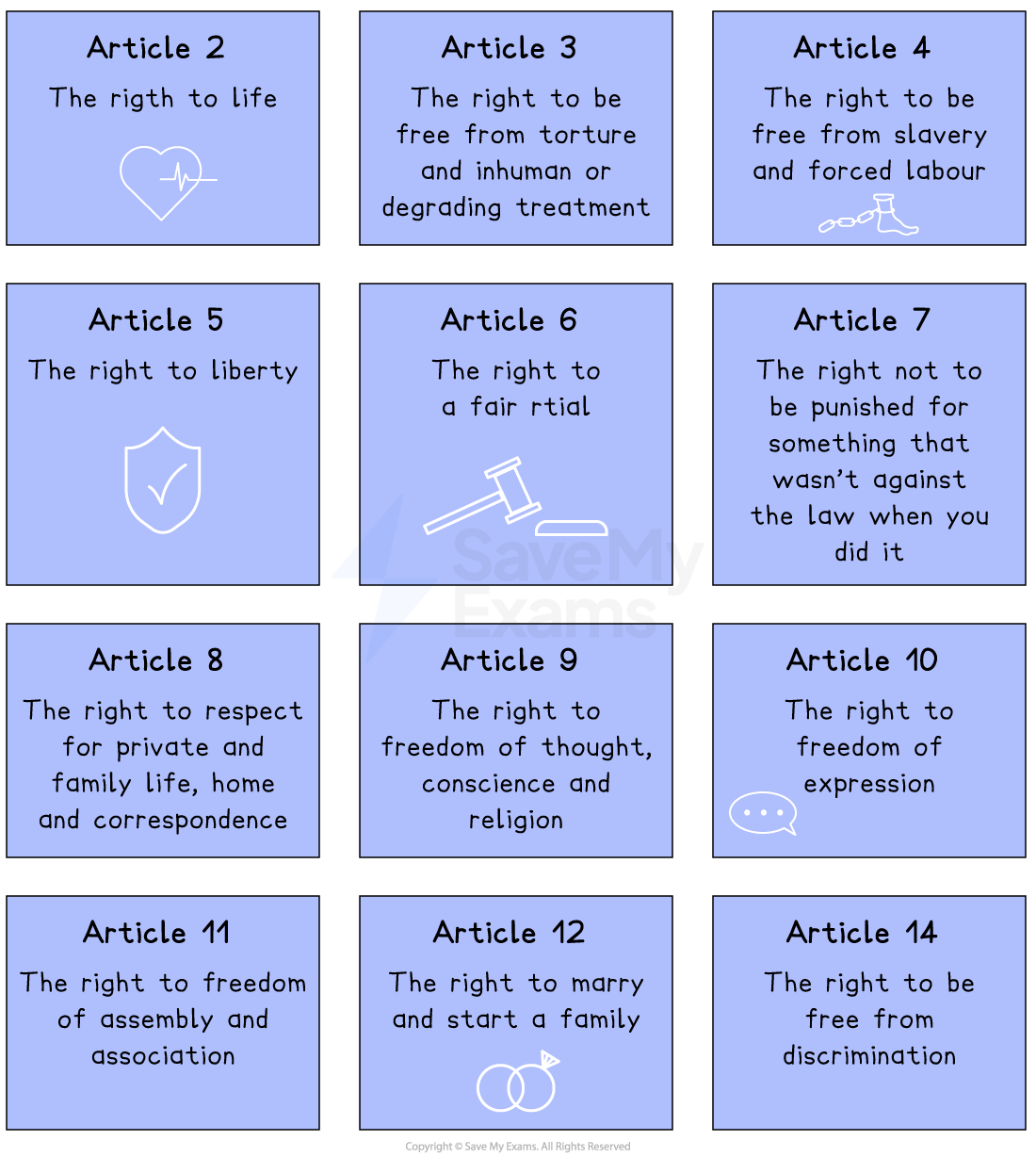
The UK has also agreed to the abolition of the death penalty in all circumstances and the following additions:
The right to free enjoyment of property
The right to education
The right to free and fair elections
The United Nations Convention on the Rights of the Child
The UN Convention on the Rights of the Child was agreed in 1990
It was adopted into UK law in 1992
It is made up of 54 articles or sections
A selection of articles in the UN Convention on the Rights of the Child

Examiner Tips and Tricks
You do not need to memorise every article of the UNDHR, ECHR or UNCRC
Examiners reward understanding, not recall
Focus on knowing what each convention is for, who it protects, and one or two clear examples of rights, rather than trying to list lots of articles
The Human Rights Act 1998
The Human Rights Act 1998 made the ECHR a formal part of UK law
This allows UK courts to deal with issues that before they had to refer to the Strasbourg Court
UK courts and public bodies have to abide by decisions and rulings made by the ECHR
Any new UK law proposed must not contravene any section of the Convention

Unlock more, it's free!
Was this revision note helpful?
