Rights, Duties & Values: Legal Rights (Edexcel GCSE Citizenship Studies): Revision Note
Exam code: 1CS0
What are legal rights?
Legal rights are protected by the law
They apply to everyone and have developed over time through new laws and court decisions
Key legal rights in the UK include:
the presumption of innocence
the right to a fair trial
the right to own property
protection from imprisonment without charge
the right to legal representation
the right to appeal against a conviction or sentence
Legal rights come with legal responsibilities, such as obeying the law and respecting the rights of others
Legal rights at work
The rights of UK citizens at work protect people from unfair treatment and exploitation
They aim to ensure dignity, respect and fairness in the workplace
Workplace rights were won over time, not given automatically
In the past, many workers faced long hours, low pay and unsafe conditions
Trade unions helped secure these rights
Workers acted together to campaign and negotiate for better treatment
Public pressure and protests led to change
Shared moral beliefs about fairness influenced working conditions
Key legal rights at work
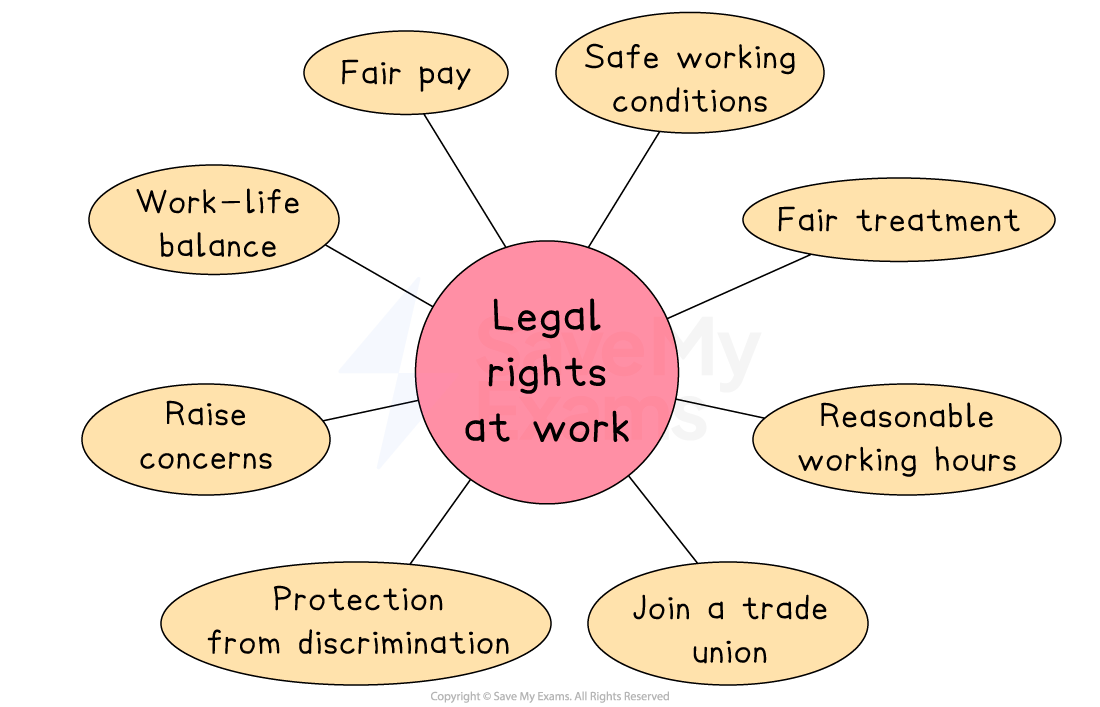
Right to fair pay
Workers should be paid fairly for the work they do
This includes receiving at least the National Minimum Wage or National Living Wage
Fair pay helps prevent exploitation and poverty
Right to safe working conditions
Employers must provide a safe and healthy workplace
This includes training, safety equipment and risk assessments
This protects workers from injury and long-term health problems
Right to fair treatment
Workers should be treated with dignity and respect
Unfair treatment because of protected personal characteristics is against the law
This supports equality and mutual respect in the workplace
Right to reasonable working hours
There are limits on how long people are expected to work
Workers have the right to rest breaks and time off
This protects physical and mental wellbeing
Right to join a trade union
Workers can join together to protect their interests
Trade unions represent workers in disputes and negotiations
This helps balance power between employers and employees
Right to protection from discrimination
Workers should not face unfair treatment at work
This applies to recruitment, pay, promotion and dismissal
It encourages equal opportunities for everyone
Right to raise concerns
Employees can speak up about unsafe or unfair practices
This includes raising complaints or whistleblowing
This helps improve standards and accountability at work
Right to work-life balance
Workers should be able to balance work with family and personal life
It includes rights to leave and flexible working
This supports wellbeing and family life
Case Study
Birmingham City Council equal pay dispute

Birmingham City Council employed many workers in low-paid roles such as cleaners, cooks and care workers
These jobs were mostly done by women
Male-dominated jobs within the council were paid more, even when work was of similar value
How workers’ and employers’ rights came into conflict
Workers argued they had a right to equal pay for work of equal value
Trade unions supported workers to challenge the pay differences
The council argued it had a responsibility to manage public money carefully
Paying backdated compensation and increasing wages created serious financial pressure
The council was concerned about maintaining essential local services
Action taken
Thousands of workers brought equal pay claims over several years
Legal action and negotiations took place between unions and the council
Workers received more than £250 million compensation for unpaid wages
Legal rights for consumers
Consumer rights are legal protections that apply when people buy goods or services
They are designed to protect consumers from unfair treatment and unsafe or poor-quality products
Consumer rights developed over time
In the past, buyers had little protection if things went wrong
Complaints, campaigns and public pressure led to stronger laws
Governments introduced consumer laws to create fairness
Laws help balance power between businesses and consumers
They increase trust and confidence in markets
Key legal rights of consumers in the UK
Consumer right | Explanation |
|---|---|
Right to goods being of satisfactory quality |
|
Right to goods being fit for purpose |
|
Right to goods matching their description |
|
Right to a repair, replacement or refund |
|
Rights when buying services |
|
Protection from unfair practices |
|
Right to complain and seek help |
|
Case Study
Airline refunds and consumer rights during COVID-19

During the COVID-19 pandemic, travel restrictions led to mass flight cancellations
In 2020, over £7 billion was spent by UK consumers on flights that were cancelled
Airlines faced severe financial pressure due to a collapse in travel demand
How consumers’ and businesses’ rights came into conflict
Consumers argued they had the right to a full refund for cancelled flights
Many could not afford to accept vouchers instead of cash refunds
Airlines argued that immediate refunds would threaten their survival
Some airlines faced losses of millions of pounds per day and risked job cuts
Action taken
Large numbers of consumers complained to airlines and advice services
The Civil Aviation Authority reminded airlines they must offer refunds
Millions of consumers eventually received these refunds
Media coverage increased pressure on airlines to comply
Some airlines later changed their refund policies and improved transparency

Unlock more, it's free!
Was this revision note helpful?
