Haber & Ostwald Processes (SQA National 5 Chemistry): Revision Note
Exam code: X813 75
The Haber process
The Haber process is an industrial process
It is used to manufacture the ammonia (NH3) required for fertiliser production
The reaction
The process is a reversible reaction between nitrogen gas (from the air) and hydrogen gas:
nitrogen + hydrogen ⇌ ammonia
N2 (g) + 3H2 (g) ⇌ 2NH3 (g)
The ⇌ symbol shows that the reaction is reversible
This means that the reaction can go in both directions
The forward direction makes ammonia
The backward direction breaks ammonia down
The conditions
Choosing the right conditions for the Haber process involves a compromise between:
The rate / speed of the reaction
The amount of product you get (the yield)
Temperature
At low temperatures:
The forward reaction is favoured
This gives a high yield of ammonia
However, the reaction is too slow to be economical
At high temperatures:
The rate of reaction increases
This is because particles have more energy, leading to more frequent and successful collisions
However, the backward reaction becomes more dominant
This leads to a low yield of ammonia
This means that a compromise temperature is used to get a reasonable rate and a reasonable yield
Catalyst
An iron catalyst is used to increase the rate of reaction
The catalyst speeds up both the forward and backward reactions equally
This allows the process to become fast enough to be economical at the compromise temperature
Examiner Tips and Tricks
You must know the catalyst for this process
Remember: Making fertilisers is a tough, industrial job, and you need a tough metal like iron to get it done
The Ostwald process
The Ostwald process is the industrial method for producing the nitric acid (HNO3) needed to make fertilisers
The reaction
Ammonia, made in the Haber process, is the essential starting material
In the Ostwald process:
Ammonia reacts with oxygen (from the air)
Water is also used in the process
The final product is nitric acid
Examiner Tips and Tricks
The Ostwald process involves several steps, but you only need to know:
The overall reactants: ammonia, oxygen and water
The final product: nitric acid
The catalyst
A platinum catalyst is used to speed up the reaction between ammonia and oxygen
Like all catalysts, the platinum is not used up and can be recovered at the end of the reaction
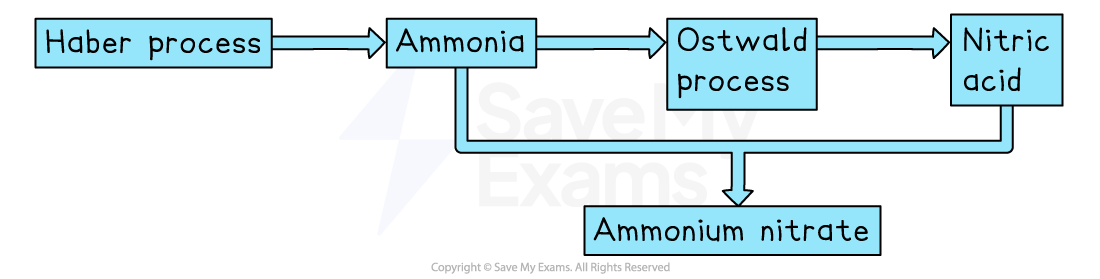
Linking the processes
The Haber and Ostwald processes are linked together in the production of ammonium nitrate, a key fertiliser
The Haber process produces ammonia
The Ostwald process uses some of the ammonia to produce nitric acid
Ammonia (from the Haber process) and nitric acid (from the Ostwald process) are used to make ammonium nitrate
Examiner Tips and Tricks
You must know the catalysts for both processes. Don't get them mixed up
Haber process = iron (Fe)
Ostwald process = platinum (Pt)

Unlock more, it's free!
Was this revision note helpful?
