Extraction by Electrolysis (SQA National 5 Chemistry): Revision Note
Exam code: X813 75
Electrolysis of ionic compounds
Electrolysis is the process of breaking down (decomposing) an ionic compound into its elements using electricity
For electrolysis to work, the ionic compound must be in a state where its ions are free to move
This means it must be either molten (melted into a liquid) or dissolved in water (in an aqueous solution)
This conductive liquid or solution is called the electrolyte
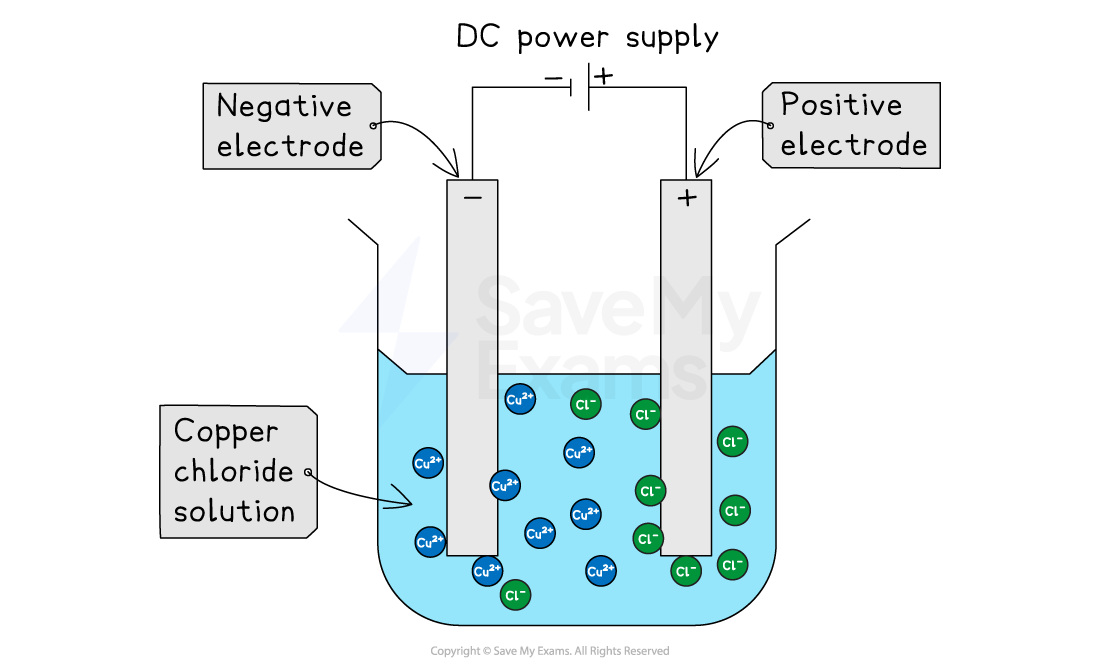
Basic electrolysis set up
The setup requires:
An electrolyte (the molten or dissolved ionic compound)
Two conductive rods called electrodes, which are placed into the electrolyte
A direct current (DC) power supply to connect the electrodes
Ion movement
When the power is switched on, the charged ions in the electrolyte start to move
Positive ions are attracted to the negative electrode
Negative ions are attracted to the positive electrode
Redox at the electrodes
When the ions reach the electrodes, redox reactions occur
At the negative electrode, positive ions gain electrons
This is reduction
At the positive electrode, negative ions lose electrons
This is oxidation
Examiner Tips and Tricks
It can be tricky to remember what happens at each electrode. Use these two mnemonics together:
PANIC:
Positive is Anode, Negative Is Cathode.
OILRIG:
Oxidation Is Loss (of electrons), which happens at the anode.
Reduction Is Gain (of electrons), which happens at the cathode.

Unlock more, it's free!
Was this revision note helpful?
