Addition Polymerisation (SQA National 5 Chemistry): Revision Note
Exam code: X813 75
Polymers
Plastics, like PVC and polythene, are examples of materials called polymers
What are polymers & monomers?
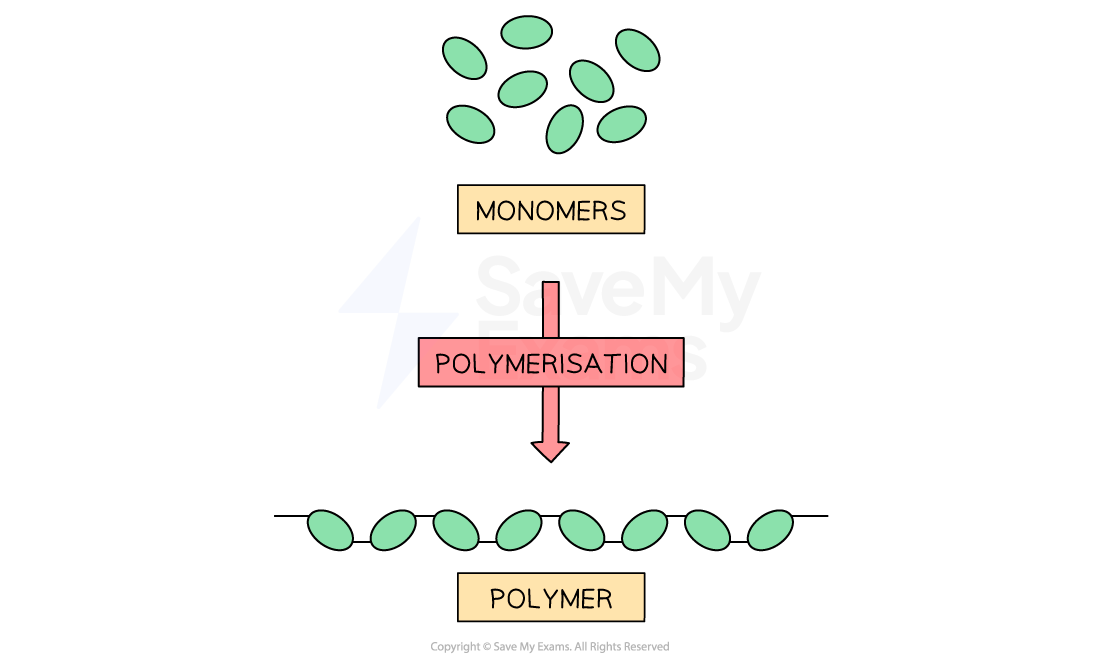
Polymers are very long-chain molecules
They are built by linking together a large number of small, repeating molecules called monomers
The monomers are joined to each other by strong covalent bonds to form the polymer chain
What is addition polymerisation?
Addition polymerisation is the reaction used to make polymers from unsaturated monomers
It is called an addition reaction because the monomer molecules add to each other in a long chain.
Only monomers with a carbon-to-carbon double bond (C=C), like alkenes, can undergo addition polymerisation.
During the reaction:
The double bond in each monomer breaks open
A new single bond forms to link it to the next monomer
Only one product is formed
Example: Poly(ethene)
Many individual ethene monomers react to form one long poly(ethene) chain

Naming addition polymers
The name of an addition polymer is derived directly from the name of its monomer
Simply add the prefix "poly-" to the monomer name
Brackets are often placed around the monomer name for clarity.
Examples of naming polymers
Monomer name | Polymer name |
|---|---|
ethene | poly(ethene) |
propene | poly(propene) |
Worked Example
Many common plastics are known by their historical names, but the systematic naming rule still applies.
For example, the monomer chloroethene is often known by its older name, vinyl chloride. Its polymer is the very common plastic, PVC.
What is the full name of PVC, based on its old monomer name?
What is the systematic name for this polymer, based on its modern monomer name?
[2]
Answer:
Using the old monomer name "vinyl chloride", the polymer is poly(vinyl chloride) [1 mark]
Using the modern monomer name "chloroethene", the polymer is poly(chloroethene)
This shows how the "poly(monomer)" rule applies to any name you are given

Unlock more, it's free!
Was this revision note helpful?
