Representation of The Structure of Monomers & Polymers (SQA National 5 Chemistry): Revision Note
Exam code: X813 75
Monomers & repeating units
An addition polymer is often made of the same monomer repeated over and over in a long chain
To simplify this, the polymer can be drawn using repeating units
What is a repeating unit?
A repeating unit is the shortest section of the polymer chain that repeats
A repeating unit:
Is enclosed in brackets
Has bonds that extend out from each side of the brackets to show that the chain continues
These are called continuation or extension bonds
Have a small subscript 'n' at the bottom right to show a large number of repeating units
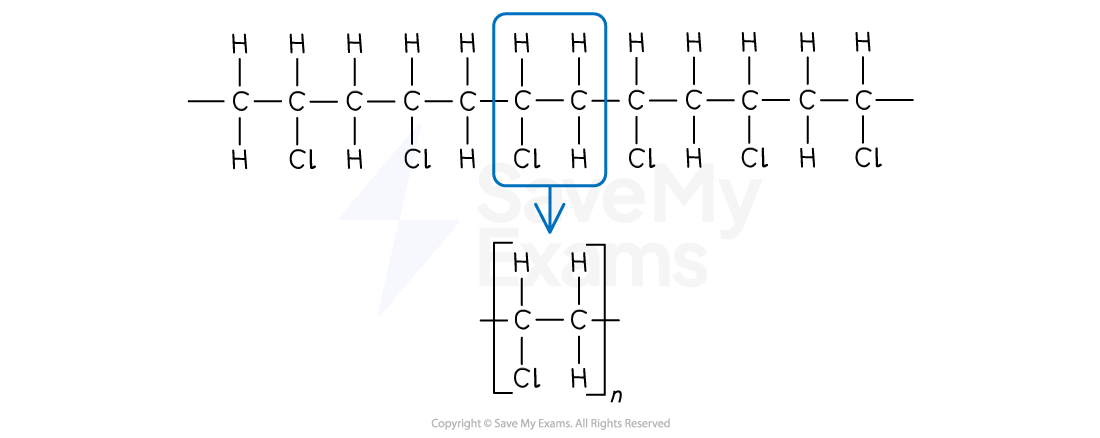
Drawing the polymer from the monomer
Drawing the repeating unit of any polymer from its unsaturated monomer follows these steps:
Identify the C=C double bond in the monomer
Change the double bond to a single bond
Add continuation bonds extending from each of these carbons
Draw the brackets and the subscript 'n'
Worked Example
Propene has the structure shown below.

Draw the repeating unit of poly(propene).
[1]
Answer:
Start with the propene monomer
Change the C=C double bond to a C-C single bond
Identify the atoms or groups of atoms attached to these carbons
Draw these attached to the C-C single bond, above and below
Add the continuation bonds from the C-C carbon atoms
Draw the brackets and the 'n'

[1 mark]
Examiner Tips and Tricks
A common exam mistake relates to the C=C double bond
Never draw a C=C double bond inside the polymer chain or repeating unit
The entire reaction works because this bond breaks
Always check if the question requires the repeating unit to be shown as a full structural formula
This means that all bonds need to be shown
So, the worked example above would need to show the C-H bonds of the CH3 group
Drawing the monomer from the polymer
Working backwards to find the monomer from a polymer structure is a key skill
How you draw the monomer depends on whether you are given:
A portion of the polymer chain
The repeating unit
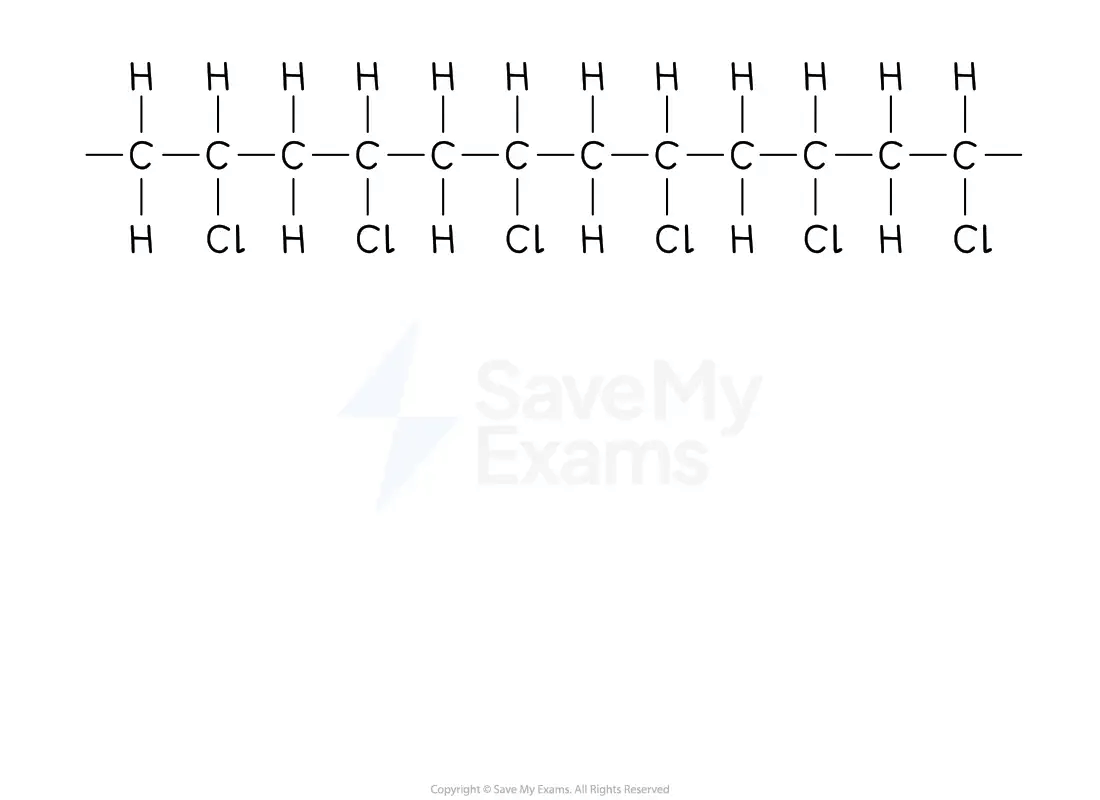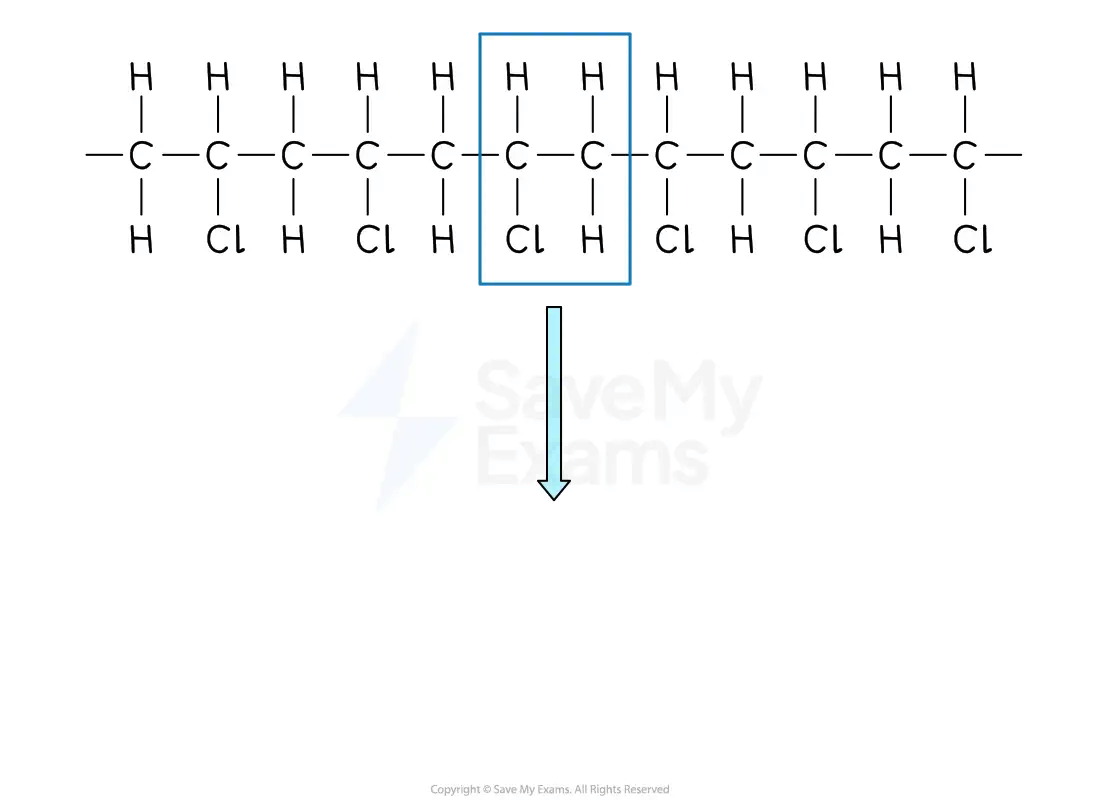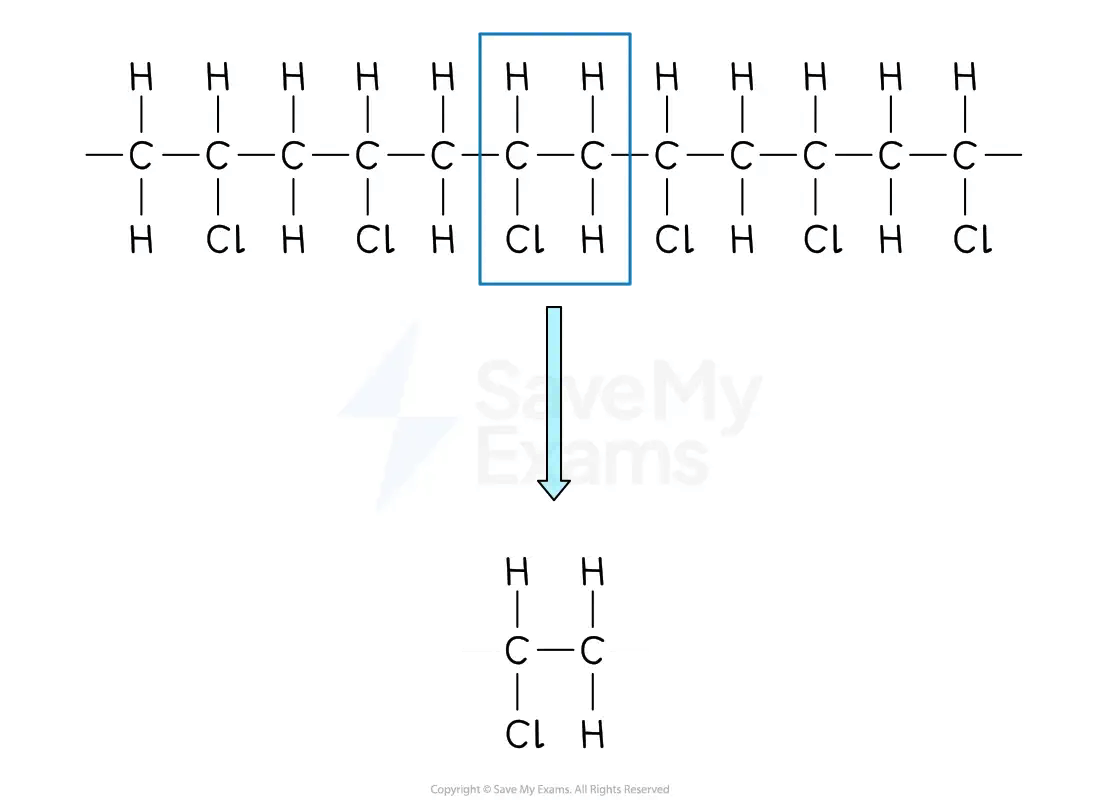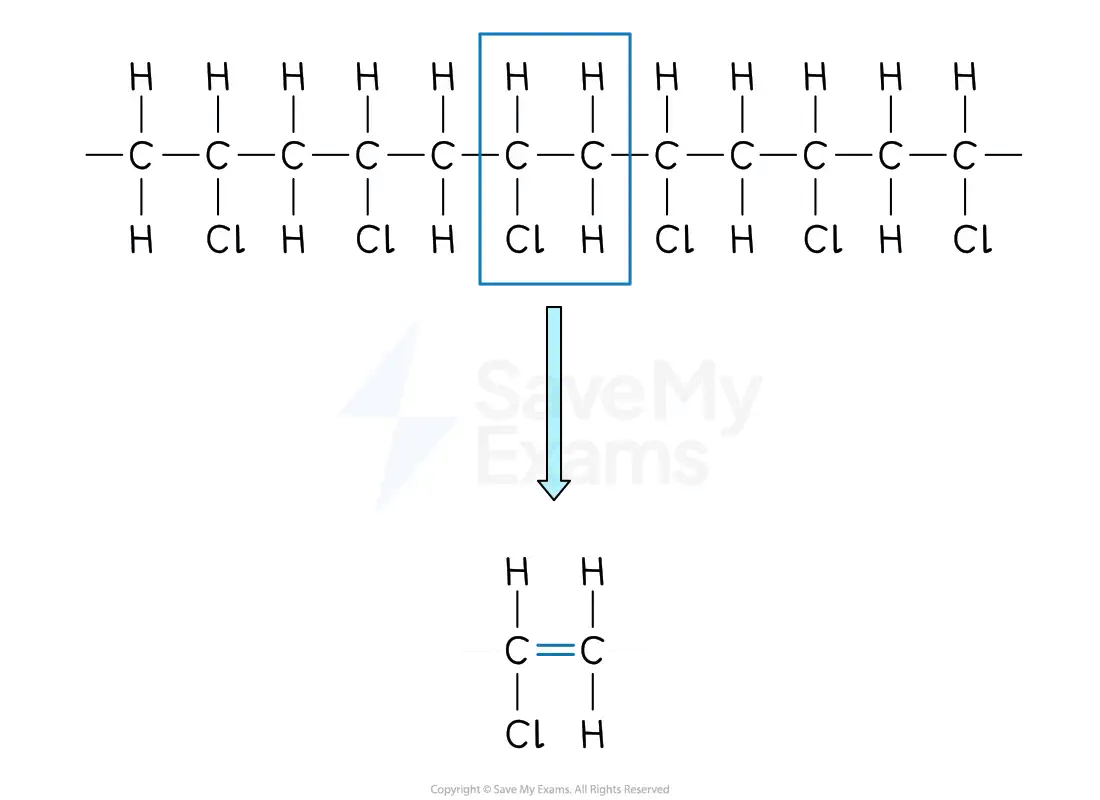
From a section of polymer chain
Identify the repeating two-carbon section inside the polymer chain
Examiner Tips and Tricks
A very common mistake is to identify a monomer that does not contain two carbons
Remember, the monomer is an alkene, so it must have a C=C double bond
This requires at least two carbon atoms
Draw this repeating section
Include the atoms / groups of atoms attached to both carbon atoms
Remove the bonds that form the main chain
Replace the C-C single bond with a C=C double bond
From a repeating unit
Redraw the repeating unit
Remove the continuation bonds, brackets and 'n'
Replace the C-C single bond with a C=C double bond
Worked Example
The repeating unit of poly(chloroethene) is shown below.

Draw the full structural formula of its monomer.
[1]
Answer:
Redraw the structure without the brackets, 'n', or continuation bonds

Replace the C-C single bond with a C=C double bond
So, the full structural formula of the poly(chloroethene) monomer is:

[1 mark]
Drawing a repeating unit from a polymer
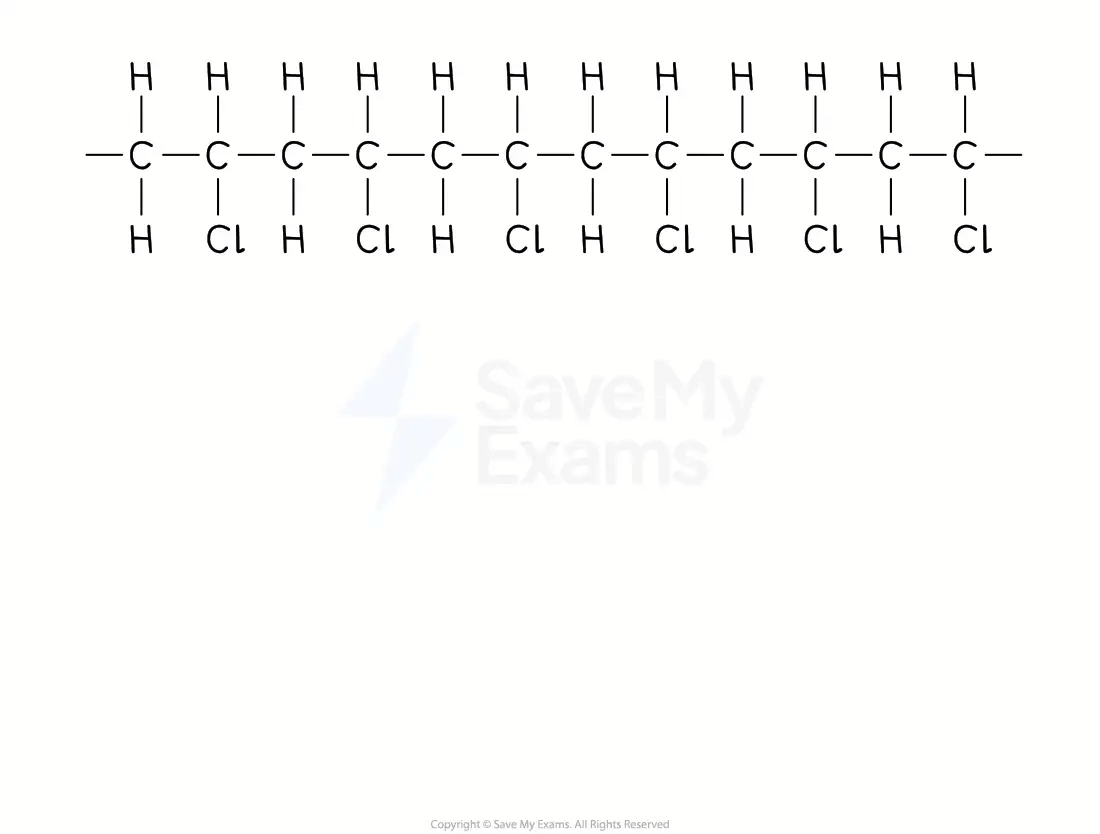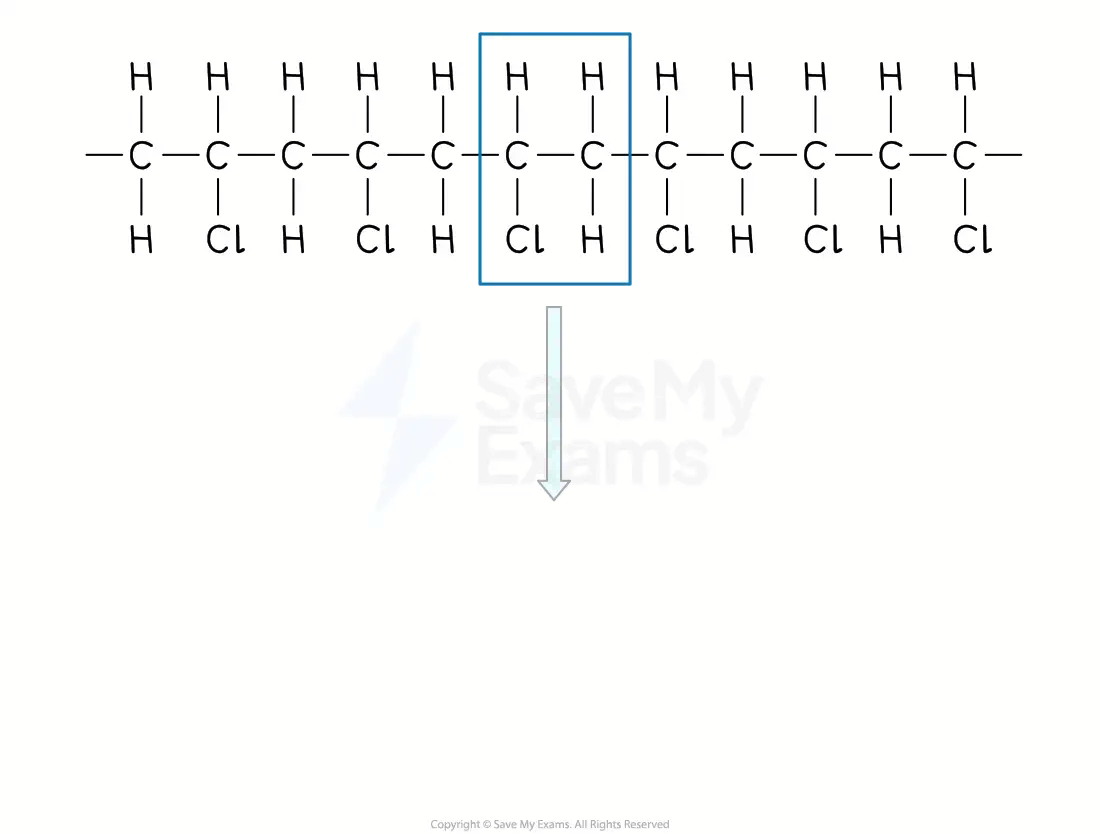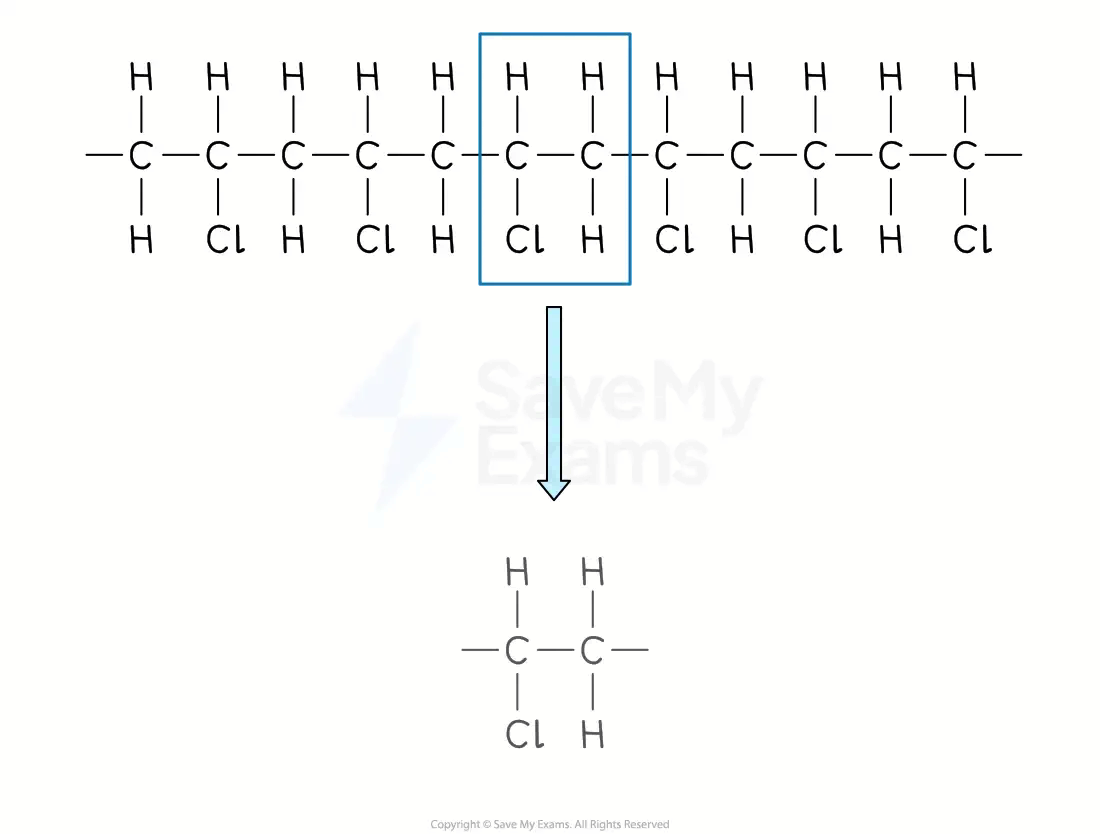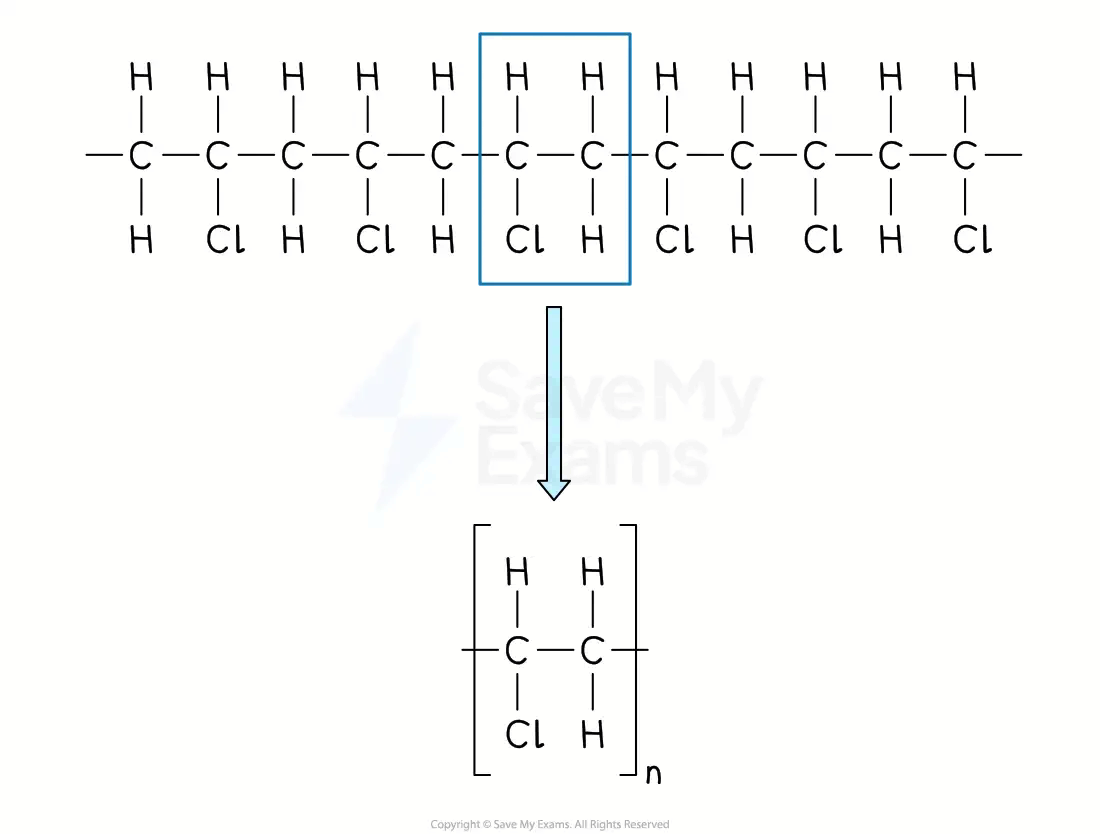
From a section of polymer chain
Identify the repeating two-carbon section inside the polymer chain
Draw this repeating section, including the atoms / groups of atoms attached to both carbon atoms
Add brackets and the subscript 'n'

Unlock more, it's free!
Was this revision note helpful?
