Carboxylic Acids (SQA National 5 Chemistry): Revision Note
Exam code: X813 75
The carboxylic acids
What are carboxylic acids?
Carboxylic acids are a family of organic compounds
Like alcohols, they are not hydrocarbons because they contain oxygen
For a full table of the first carboxylic acids and their structures, see the full & shortened structural formulae
Carboxylic acids are a homologous series with four key facts:
1. They contain the -COOH (carboxyl) functional group
All carboxylic acids contain a carboxyl group
This is a carbon atom double-bonded to one oxygen atom and single-bonded to an -OH group
This is the functional group that gives this family its characteristic acidic properties.
2. They are represented by a general formula
The general formula for the carboxylic acids homologous series is CnH2n+1COOH
This formula applies to saturated, straight-chain carboxylic acids
Examiner Tips and Tricks
In the general formula of a carboxylic acid, n represents the number of cabron atoms before the COOH group
For example:
Propanoic acid has 3 carbons in total
But, one carbon is in the -COOH group
This means there are 2 carbons in the CnH2n+1 part of the chain, so n = 2
The formula is C2H(2 x 2) + 1COOH = C2H5COOH
3. They are used to make preservatives, soaps, and medicines
Carboxylic acids are important in manufacturing
They are used as building blocks for:
Preservatives (to stop food from spoiling)
Soaps
A variety of medicines
4. A key example is ethanoic acid (vinegar)
Vinegar is a dilute solution of ethanoic acid (CH3COOH).
It is a non-toxic acid
This is why it is used safely in food (as a preservative) and in household cleaning products
Names & formulae of carboxylic acids
Like other organic compounds, carboxylic acids are named systematically
There are three skills for carboxylic acids:
Naming carboxylic acids from their structure
Drawing carboxylic acids from their name
Determining the formula of a carboxylic acid
1. Naming carboxylic acids
Naming carboxylic acids is straightforward as the functional group is always at the end of the chain
The name of a straight-chain carboxylic acid is made of two parts:
A prefix to show the number of carbon atoms
The ending "-oic acid" to show it is a carboxylic acid
The rules for naming carboxylic acids:
Find the longest continuous chain of carbon atoms
This chain must contain the -COOH group
The carbon of the -COOH group must be included in the count
Add the ending "-oic acid"
No number is needed because the carboxyl group is always on carbon 1
If there are branches, you name the branches in the same way as alkanes
Worked Example
Name the following molecule.

[1]
Answer:
Main chain:
The main chain containing the -COOH group has 6 carbon atoms
So, the name starts with hexan-
The -COOH group:
The ending for a carboxylic acid is -oic acid
Combine the parts:
The full name is hexanoic acid [1 mark]
2. Drawing carboxylic acids
You can work backwards from the name to draw the structure of a carboxylic acid
The rules for drawing carboxylic acids:
The -COOH functional group
"-oic acid" means one of the end carbons is a -COOH group
Draw this group first, showing the C=O and O-H bonds
Identify the longest carbon chain
Identify the number of carbons in the longest chain
For example, "pent" means a 5-carbon chain
Add the main carbon chain
Make sure to include the COOH carbon as one of the atoms counted in the chain
Add the hydrogens to complete the structure
Make sure every carbon atom has exactly four bonds
Worked Example
Draw the full structural formula for pentanoic acid.
[1]
Answer:
The -COOH group:
"-oic acid" means one of the end carbons is a -COOH group
Main Chain:
"Pentan-" means a chain of 5 carbons in total
So, the full structural formula for pentanoic acid is:

[1 mark]
Examiner Tips and Tricks
When drawing the full structural formula of a carboxylic acid, you must show all the bonds in the carboxyl (-COOH) group
The carbon is:
Double-bonded to one oxygen
Single-bonded to the other oxygen
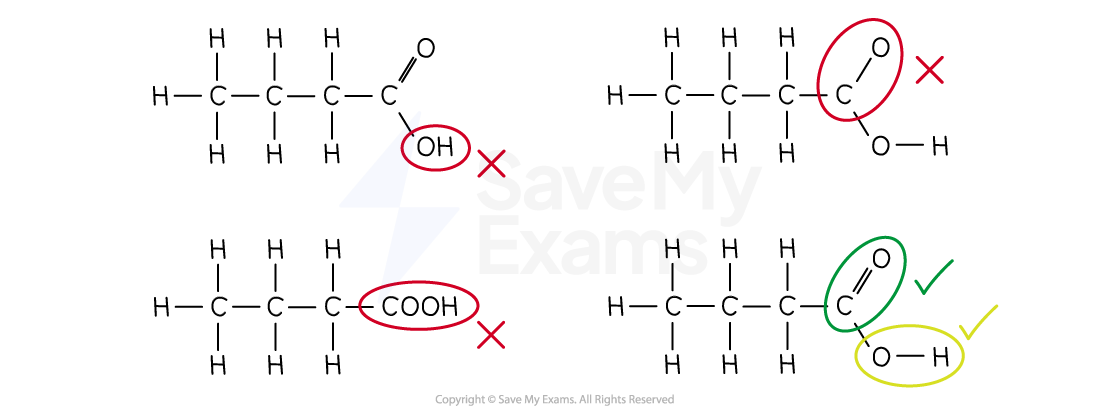
SQA National 5 will expect you to draw all of the bonds, but they may give you condensed versions (like the first worked example) in exam questions
3. The molecular formula of carboxylic acids
The general formula of carboxylic acids can be used to determine the molecular formula
Worked Example
State the formula of octanoic acid.
[1]
Answer:
The general formula of a carboxylic acid is CnH2n+1COOH
Oct means a chain of 8 carbons
But, one carbon is in the -COOH group
This means that the remainder of the chain has 7 carbons
So, n = 7
So, the formula of octanoic acid is C7H(2 x 7) + 1COOH = C7H15COOH [1 mark]

Unlock more, it's free!
Was this revision note helpful?
