Properties of Alcohols (SQA National 5 Chemistry): Revision Note
Exam code: X813 75
Miscibility of alcohols
Solubility describes how well a solute dissolves in a solvent
For example:
Sugar is soluble in water
Sand is insoluble in water
Miscibility describes how well two liquids mix or dissolve together
It essentially has the same meaning as solubility, but only applies to liquids
For example:
If two liquids are miscible, they will mix completely to form a single solution
If two liquids are immiscible, they will not mix
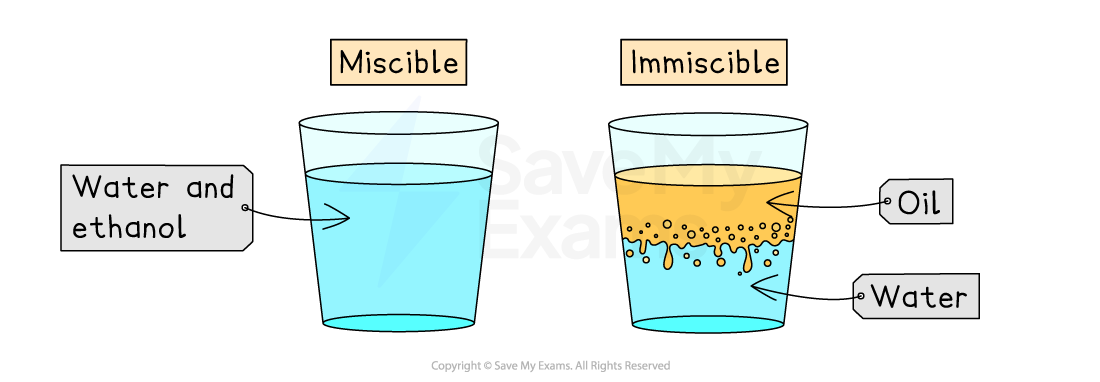
The miscibility / solubility of an alcohol in water changes as its carbon chain gets longer
Miscibility of small alcohols
Methanol, ethanol and propanol are miscible with water
Their small size and -OH group allow them to mix completely with water
Miscibility of larger alcohols
From butanol onwards, the solubility decreases significantly as the carbon chain gets longer
The long hydrocarbon part of the molecule does not mix well with water
This effect becomes more significant as the chain grows
Solubility of alcohols in water
Alcohol | Number of carbons | Solubility (g per 100g of water) |
|---|---|---|
methanol | 1 | miscible |
ethanol | 2 | miscible |
propan-1-ol | 3 | miscible |
butan-1-ol | 4 | 7.3 |
pentan-1-ol | 5 | 2.2 |
hexan-1-ol | 6 | 0.6 |
heptan-1-ol | 7 | 0.1 |
octan-1-ol | 8 | 0.03 |
Melting & boiling points of alcohols
As you go up the alcohol homologous series, the molecules get larger
This has a direct effect on their melting and boiling points
Melting points of alcohols
The melting points of straight-chain alcohols generally increase as the number of carbons in the chain increases
In general, a bigger molecule means a higher melting point
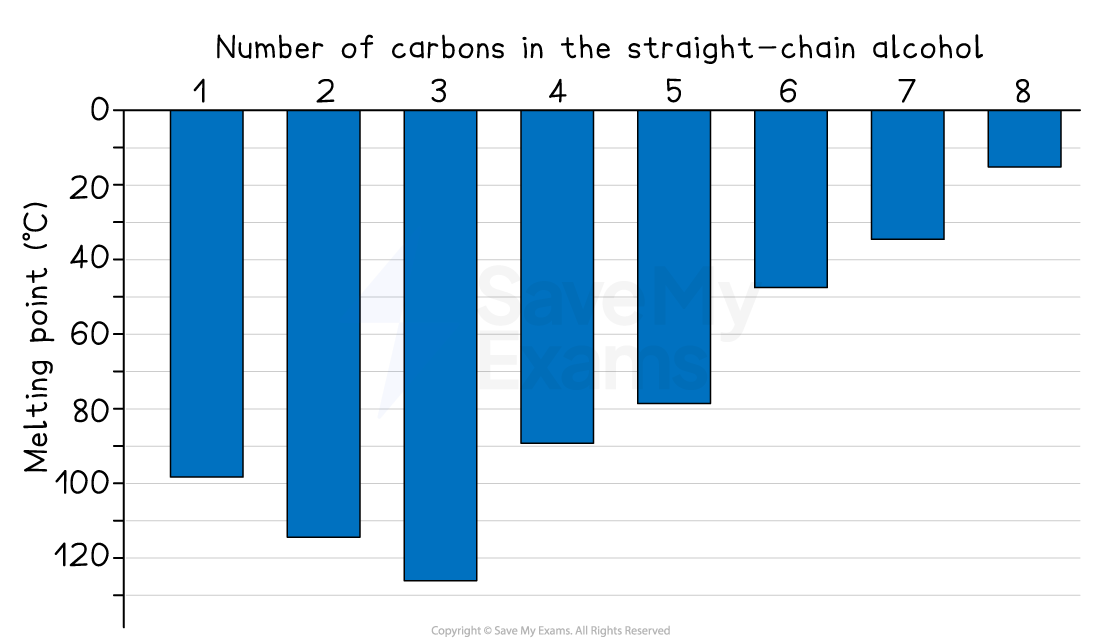
The trend for melting points of alcohols is less regular than boiling points
Boiling points of alcohols
The boiling points of straight-chain alcohols show a much clearer and more predictable trend:
The boiling points increase as the molecule gets bigger
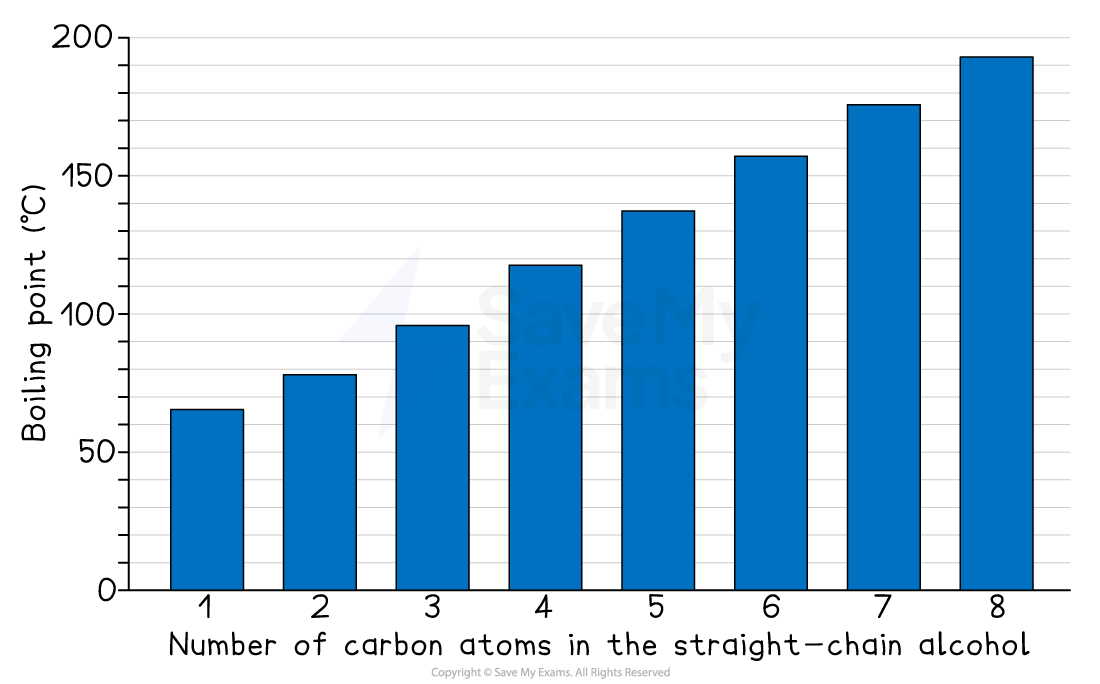
Explaining the general trend
The overall trend for both melting and boiling point is that they increase as the molecule gets bigger
The melting and boiling points increase because:
As alcohol molecules get larger, the strength of the intermolecular forces increases
Intermolecular forces are the weak attractions between molecules
More energy is needed to overcome these stronger forces to allow the substance to melt or boil
Therefore, the melting and boiling points generally increase
Examiner Tips and Tricks
In an exam, you will most likely be asked to explain the boiling point trend as it's more regular
Remember the key reason:
Larger molecules have stronger intermolecular forces, which require more energy to overcome

Unlock more, it's free!
Was this revision note helpful?
