Reactions of Alkenes (SQA National 5 Chemistry): Revision Note
Exam code: X813 75
Addition reactions of alkenes
Alkenes undergo addition reactions
This is where the double bond breaks open and the atoms of another molecule are "added across" it
In an addition reaction:
The C=C double bond becomes a C-C single bond
The product is always a saturated compound
Only one product is formed
There are several important types of addition reactions
The three most common involve adding small molecules like:
Hydrogen, H2
Halogens, e.g. Cl2, Br2
Water, H2O
1. Addition of hydrogen
This reaction is:
alkene + hydrogen → alkane
The process: Adding hydrogen to an alkene is called hydrogenation
The hydrogen atoms "add across" the double bond
This turns the unsaturated alkene into a saturated alkane
Conditions: This reaction requires a nickel catalyst and heat
Example hydrogenation reaction
ethene + hydrogen → ethane
C2H4 + H2 → C2H6

2. Addition of halogens
This reaction is:
alkene + halogen → dihaloalkane
The process: Adding a halogen to an alkene is called halogenation
The halogen atoms "add across" the double bond
This turns the unsaturated alkene into a saturated dihaloalkane
A dihaloalkane is an alkane molecule that has two halogen atoms attached to it
There are specific types of halogenation reaction:
Chlorination is the addition of chlorine, Cl2
Bromination is the addition of bromine, Br2
The addition of bromine to an alkene is the standard
Example halogenation reaction
ethene + bromine → 1,2-dibromoethane
C2H4 + Br2 → C2H4Br2
This is the reaction that happens in the test for unsaturation, where the orange-brown bromine solution is decolourised

Examiner Tips and Tricks
You are not required to name the dihaloalkane product of a halogenation reaction as part of this course.
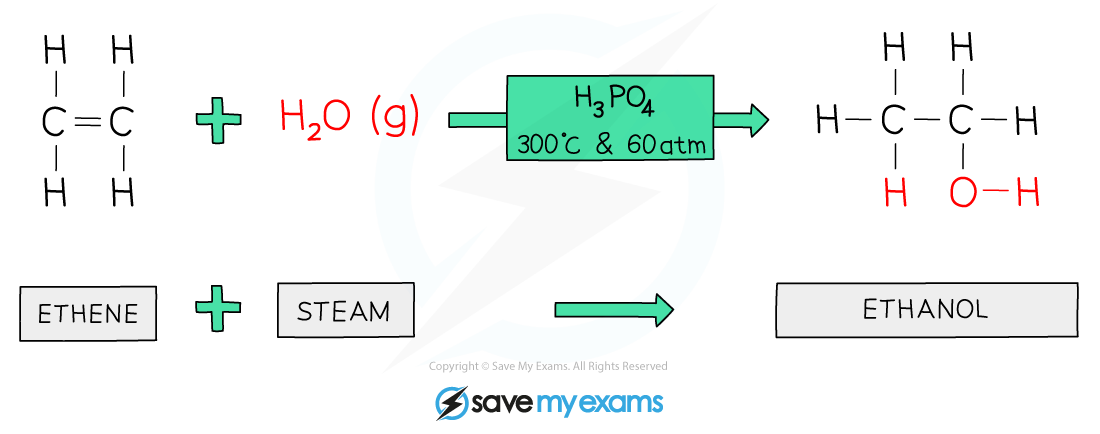
3. Addition of water (steam)
This reaction is:
alkene + water (steam) → alcohol
The process: Adding water to an alkene is called hydration
The water "adds across" the double bond
This turns the unsaturated alkene into an alcohol
Hydration is a key industrial method for making alcohols
Conditions: This reaction requires:
High temperature
High pressure
An acid catalyst, such as phosphoric acid
Example hydration reaction
ethene + water (steam) → ethanol
C2H4 + H2O → C2H5OH
Examiner Tips and Tricks
To draw the product of any addition reaction:
Redraw the alkene
But, change the C=C double bond to a C-C single bond
This gives the two carbon atoms "spare" bonds
"Add" the atoms from the other molecule to these two spare bonds:
For hydrogenation, add H and H
For halogenation with bromine, add Br and Br
For hydration, add H to one bond and OH to the other bond
A special type of addition: Polymerisation
Addition reactions can also happen between many alkene molecules themselves
This process is called addition polymerisation, which is how plastics are made

Unlock more, it's free!
Was this revision note helpful?
