Which of the following is not involved in metallic bonding?
Positive ions
Negative ions
Delocalised electrons
Electrostatic attraction
Was this exam question helpful?
Exam code: X813 75
Which of the following is not involved in metallic bonding?
Positive ions
Negative ions
Delocalised electrons
Electrostatic attraction
Choose your answer
Was this exam question helpful?
Four different metals were connected to silver in a cell.
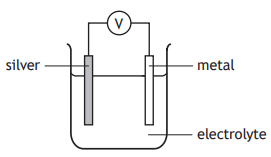
The results obtained were recorded in the table.
Metal | Voltage (V) |
Iron | 0.9 |
Zinc | 1.1 |
Magnesium | 2.7 |
Metal X | 1.5 |
Which of the following could be metal X?
You may wish to use the data booklet to help you.
Aluminium
Sodium
Nickel
Copper
Choose your answer
Was this exam question helpful?
Which of the following is not a redox reaction?
Zn(s) + 2H+ (aq) Zn2+ (aq) + H2(g)
Cu(s) + Cl2(g) Cu2+ (Cl- )2(s)
Br2(aq) + 2Fe2+ (aq) 2Fe3+ (aq) + 2Br- (aq)
Ba2+ (aq) + SO4 2- (aq) Ba2+ SO4 2- (s)
Choose your answer
Was this exam question helpful?
Which of the following substances in the table below would have the following structure?
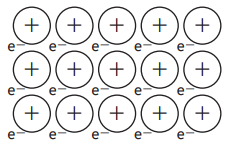
Substance | Melting point (°C) | Boiling point (°C) | Conducts electricity | |
Solid | Liquid | |||
A | 30 | 2229 | yes | yes |
B | -118 | 90 | no | no |
C | 714 | 1412 | no | yes |
D | 2077 | 4000 | no | no |
Choose your answer
Was this exam question helpful?
When magnesium reacts with dilute hydrochloric acid, magnesium chloride is formed.
Name the other substance formed.
Hydrogen chloride
Hydrogen
Chlorine
Water
Choose your answer
Was this exam question helpful?
The ion electron equations for the reactions taking place during the electrolysis of aluminium oxide are given below.
Al3+ + 3e- Al
2O2- O2 + 4e-
The redox equation for the overall reaction is
4Al3+ + 6O2- 4Al + 3O2
3Al3+ + 3O2- 3Al + 3O2
Al3+ + 2O2- Al + O2 + e-
Al3+ + 2O2- + 3e- Al + O2 + 4e-
Choose your answer
Was this exam question helpful?
Which line in the table shows the properties of a metal?
Melting point (°C) | Boiling point (°C) | Conducts electricity | ||
Solid | Liquid | |||
A | 30 | 2229 | yes | yes |
B | -118 | 90 | no | no |
C | 714 | 1412 | no | yes |
D | 2077 | 4000 | no | no |
Choose your answer
Was this exam question helpful?
Information about the reactions of three different metals, X, Y and Z is given in the table.
Reaction with | |||
Metal | Oxygen | Dilute acid | Water |
X | reacts | reacts | no reaction |
Y | reacts | no reaction | no reaction |
Z | reacts | reacts | reacts |
Which of the following correctly shows the metals in order of increasing reactivity?
X, Y, Z
Y, X, Z
Z, X, Y
Z, Y, X
Choose your answer
Was this exam question helpful?
An electrochemical cell was set up by joining two metals, A and B, in an electrolyte as shown.
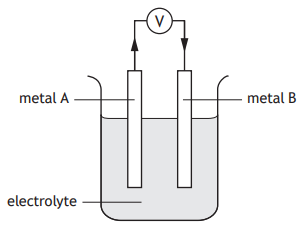
The direction of electron flow is from metal A to metal B.
Which line in the table is correct for this cell?
You may wish to use the data booklet to help you.
Metal A | Metal B | |
A | nickel | zinc |
B | zinc | aluminium |
C | aluminium | magnesium |
D | aluminium | nickel |
Choose your answer
Was this exam question helpful?
The ion-electron equations for the reduction of magnesium ions and silver(I) ions are
Mg2+ (aq) + 2e− Mg(s)
Ag+ (aq) + e− Ag(s)
The redox equation for the overall reaction is
Mg(s) + 2Ag+ (aq) Mg2+ (aq) + 2Ag(s)
Mg2+ (aq) + 2Ag(s) Mg(s) + 2Ag+ (aq)
Mg(s) + Ag+ (aq) + e− Mg2+ (aq) + 2Ag(s) + 2e−
Mg2+ (aq) + 2Ag(s) + 2e− Mg(s) + Ag+ (aq) + e−
Choose your answer
Was this exam question helpful?
Which line in the table shows what would be observed during the electrolysis of copper chloride, using a d.c. supply?
At the positive electrode | At the negative electrode | |
A | gas forms | solid forms |
B | gas forms | gas forms |
C | solid forms | gas forms |
D | solid forms | solid forms |
Choose your answer
Was this exam question helpful?
Metallic bonding is a force of attraction between:
positive ions and delocalised electrons
negative ions and delocalised electrons
negative ions and positive ions
a shared pair of electrons and two nuclei.
Choose your answer
Was this exam question helpful?
Metals used to make aircraft have a density of less than 3 g cm−3 and have to withstand temperatures up to 600 °C.
Which line in the table gives the correct data for a metal used to make aircraft?
Melting point (°C) | Density (g cm−3 ) | |
A | 98 | 0.97 |
B | 660 | 2.70 |
C | 1854 | 6.52 |
D | 1085 | 8.96 |
Choose your answer
Was this exam question helpful?
Which of these metals can only be extracted from its ore by electrolysis and forms an oxide that is insoluble in water?
You may wish to use the data booklet to help you
Aluminium
Calcium
Copper
Lead
Choose your answer
Was this exam question helpful?
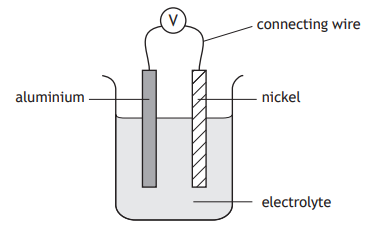
Which statement correctly describes the electron flow in the cell?
You may wish to use the data booklet to help you.
Through the electrolyte from aluminium to nickel.
Through the electrolyte from nickel to aluminium.
Through the connecting wire from nickel to aluminium.
Through the connecting wire from aluminium to nickel.
Choose your answer
Was this exam question helpful?
Which metal, when paired with magnesium in a cell, will produce the highest voltage?
You may wish to use the data booklet to help you.
Iron
Lead
Tin
Zinc
Choose your answer
Was this exam question helpful?
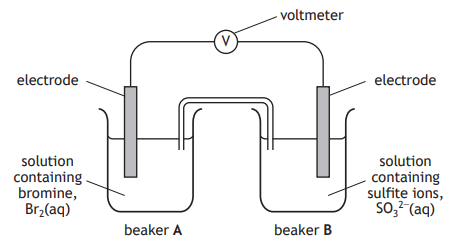
The reactions occurring at each electrode are:
Beaker A Br2(ℓ) + 2e− 2Br− (aq)
Beaker B SO3 2− (aq) + H2O(ℓ) SO4 2− (aq) + 2H+ (aq) + 2e−
Which of the following equations is the overall redox reaction in the cell?
You may wish to use the data booklet to help you.
Br2(ℓ) + SO3 2− (aq) + H2O(ℓ) + 2e− 2Br− (aq) + SO4 2− (aq) + 2H+ (aq) + 2e−
2Br− (aq) + SO4 2− (aq) + 2H+ (aq) Br2(ℓ) + SO3 2− (aq) + H2O(ℓ)
Br2(ℓ) + SO3 2− (aq) + H2O(ℓ) 2Br− (aq) + SO4 2− (aq) + 2H+ (aq)
2Br− (aq) + SO4 2− (aq) Br2(ℓ) + SO3 2− (aq)
Choose your answer
Was this exam question helpful?
Four cells were made by joining silver to different metals.
The cells produced the following voltages 2·7 V, 1·1 V, 0·9 V and 0·5 V
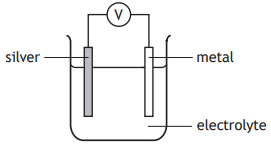
The metals used were copper, zinc, iron and magnesium.
Which voltage was produced in the cell containing silver and copper?
You may wish to use the data booklet to help you.
2·7 V
1·1 V
0·9 V
0·5 V
Choose your answer
Was this exam question helpful?
Information about the reactions of three different metals, X, Y and Z is given in the table.
Metal | Reaction with dilute acid | Reaction with water |
X | reacts | no reaction |
Y | no reaction | no reaction |
Z | reacts | reacts |
Which of the following shows the metals in order of increasing reactivity?
Y, Z, X
Z, X, Y
Y, X, Z
X, Y, Z
Choose your answer
Was this exam question helpful?
Information about the reactions of four different metals, W, X, Y and Z is given in the table.
Metal | Reaction with dilute acid | Reaction with water |
W | moderate reaction | no reaction |
X | fast reaction | slow reaction |
Y | slow reaction | no reaction |
Z | fast reaction | no reaction |
The order of reactivity of the metals, starting with the most reactive is
X, Z, W, Y
Y, W, Z, X
Z, X, W, Y
Y, W, X, Z.
Choose your answer
Was this exam question helpful?
The ion-electron equations for the oxidation and reduction steps in the reaction between hydrogen and oxygen are given below.
H2 (g) 2H+ (aq) + 2e-
2H2O(ℓ) + O2 (g) + 4e- 4OH- (aq)
The redox equation for the overall reaction is
H2 (g) + 2H2O(ℓ) + O2 (g) + 4e- 2H+ (aq) + 4OH- (aq) + 2e-
2H2 (g) + 2H2O(ℓ) + O2 (g) 4H+ (aq) + 4OH- (aq)
H2 (g) + 2H2O(ℓ) + O2 (g) 2H+ (aq) + 4OH- (aq)
2H2 (g) + 2H2O(ℓ) + O2 (g) + 4e- 4H+ (aq) + 4OH- (aq) + 4e-
Choose your answer
Was this exam question helpful?
Which of the following metals, when connected to lead in a cell, would produce the highest reading on the voltmeter?
You may wish to use the data booklet to help you.
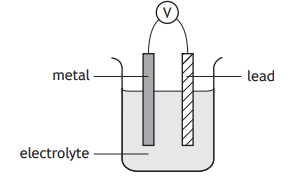
Zinc
Tin
Nickel
Lead
Choose your answer
Was this exam question helpful?
Metallic bonding is a force of attraction between
a shared pair of electrons and two nuclei
negative ions and delocalised electrons
negative ions and positive ions
positive ions and delocalised electrons.
Choose your answer
Was this exam question helpful?