In nuclear equations a proton is represented as
Was this exam question helpful?
Exam code: X813 75
In nuclear equations a proton is represented as
Choose your answer
Was this exam question helpful?
Identify the radioisotope, S, that is formed when radium-228 decays by emission of two beta particles and an alpha particle.
Choose your answer
Was this exam question helpful?
An atom of 227Th decays by a series of alpha emissions to form an atom of 211Pb.
How many alpha particles are released in this decay process?
2
3
4
5
Choose your answer
Was this exam question helpful?
Radon-222 is a radioisotope present in the Earth’s atmosphere. Plants can absorb radon-222 through their roots.
Compared with radon-222 in the atmosphere, the half-life of the radon-222 in the plant cells will be:
shorter
longer
the same
dependent on the size of the plant.
Choose your answer
Was this exam question helpful?
A radioisotope is used to monitor blood flow around the body. In order to prevent damage to the body the radiation emitted must be able to escape through the skin.
Which line in the table describes the type of radiation emitted and half-life that would make a radioisotope suitable for this use?
Type of radiation emitted | Half-life | |
A | alpha | long |
B | beta | long |
C | alpha | short |
D | beta | short |
Choose your answer
Was this exam question helpful?
The diagram shows the path of two different types of radiation as they pass through an electric field.
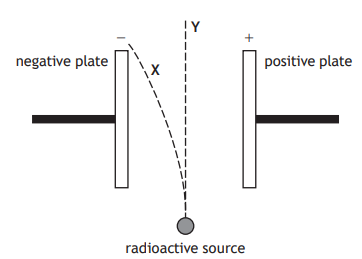
Which line in the table correctly identifies the types of radiation which follow paths X and Y?
Path X | Path Y | |
A | alpha | beta |
B | beta | alpha |
C | beta | gamma |
D | alpha | gamma |
Choose your answer
Was this exam question helpful?