Compound X:
is saturated
is insoluble in water
has two hydrogen atoms for every carbon atom.
Which of the following could be compound X?
Propane
Propan-1-ol
Cyclopropane
Propene
Was this exam question helpful?
Exam code: X813 75
Compound X:
is saturated
is insoluble in water
has two hydrogen atoms for every carbon atom.
Which of the following could be compound X?
Propane
Propan-1-ol
Cyclopropane
Propene
Choose your answer
Was this exam question helpful?
The structures of three members of a homologous series called the dienes are shown.
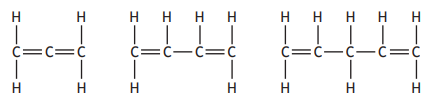
The general formula for the dienes is
CnHn+1
CnHn+2
CnH2n
CnH2n−2
Choose your answer
Was this exam question helpful?
Which of the following formula masses belongs to a hydrocarbon that does not belong to the same homologous series as the others?
16
44
58
70
Choose your answer
Was this exam question helpful?
The shortened structural formula for a compound is shown.
CH3CHC(OH)C(CH3)3
Which of the following is another way of representing this structure?
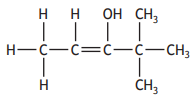
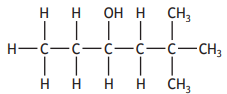
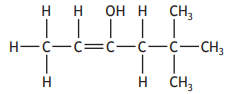
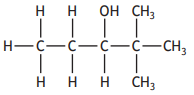
Choose your answer
Was this exam question helpful?
Pent-1-ene reacts with water to form two products.
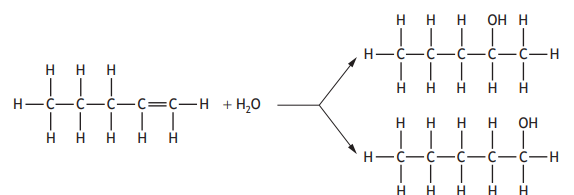
Which of the following alkenes does not form two products on reaction with water?
But-1-ene
But-2-ene
Hex-1-ene
Hex-2-ene
Choose your answer
Was this exam question helpful?
Which of the following is most likely to be a use for alkanes?
Fuels
Soaps
Medicines
Flavourings
Choose your answer
Was this exam question helpful?
The table shows three members of the cycloalkyne family.
Name | Molecular formula |
Cyclooctyne | C8H12 |
Cyclononyne | C9H14 |
Cyclodecyne | C10H16 |
Which of the following is the general formula for the cycloalkyne family?
CnH2n
CnH2n-2
CnH2n-4
CnH2n-6
Choose your answer
Was this exam question helpful?
Which of the following compounds is an isomer of pent-2-ene?
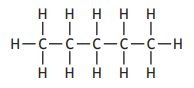
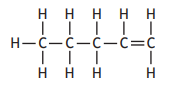
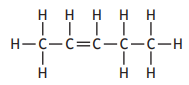
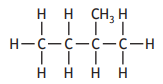
Choose your answer
Was this exam question helpful?
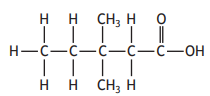
The shortened structural formula for this compound is
CH3CH2CH(C2H5)CH2COOH
CH3CH2C(CH3)2CH2COOH
CH3CH(C2H5)CH2CH2COOH
CH3C(CH3)2CH2CH2COOH
Choose your answer
Was this exam question helpful?
Which bond do ethane, ethene, ethanol and ethanoic acid all contain?
C–C
C–O
C–H
O–H
Choose your answer
Was this exam question helpful?
The table shows how the number of carbon atoms bonded to the nitrogen atom determines the classification of an amine.
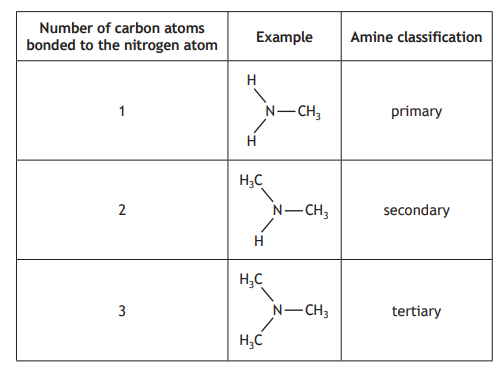
Which of the following is a secondary amine?
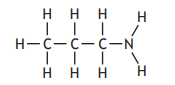
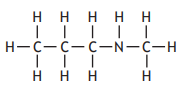
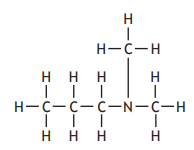
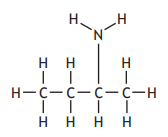
Choose your answer
Was this exam question helpful?
CH3CH(CH3)CH2C(CH3)2CH3
The name of the above compound is
2,2,4-trimethylpentane
2,4,4-trimethylpentane
2,2,4-trimethylpentene
2,4,4-trimethylpentene.
Choose your answer
Was this exam question helpful?
The structure of 2-methylbut-2-ene is
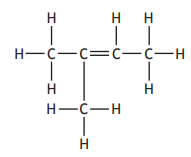
Which of the following represents an isomer of 2-methylbut-2-ene?
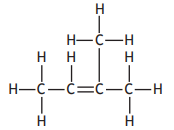
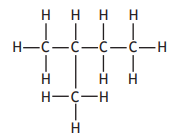
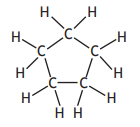
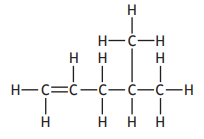
Choose your answer
Was this exam question helpful?
Which of the following would not be produced by an addition reaction of but-2-ene?
CH3CH2CH2CH3
CH3CH2CH2CH2OH
CH3CH(OH)CH2CH3
CH3CHBrCHBrCH3
Choose your answer
Was this exam question helpful?
Which of the following is correct for both of the molecules shown below?
You may wish to use the data booklet to help you.
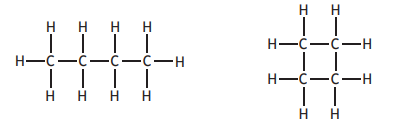
They can be represented by the general formula CnH2n.
They have the same melting point.
They are soluble in water.
They are saturated.
Choose your answer
Was this exam question helpful?
Which of the following molecules will decolourise bromine solution and also form an acidic solution when added to water?
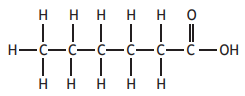
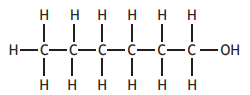
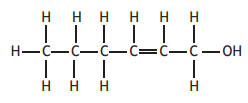
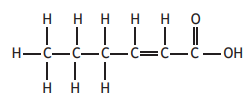
Choose your answer
Was this exam question helpful?
The first three members of the alkanones are
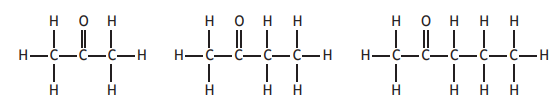
The general formula for the alkanones is:
CnH2n−2O
CnH2nO
CnH2n+1O
CnH2n+2O
Choose your answer
Was this exam question helpful?
Which of the following could be the formula mass of a cycloalkane?
40
42
54
58
Choose your answer
Was this exam question helpful?
Which of the following compounds does not have an isomer?
Cyclopropane
But-1-ene
Pentane
Ethene
Choose your answer
Was this exam question helpful?
The systematic name for CH3CH2C(CH3 )CHCH3 is
3-methylpentane
2-methylpentane
3-methylpent-2-ene
2-methylpent-3-ene.
Choose your answer
Was this exam question helpful?
When pent-1-ene undergoes an addition reaction with water, two products are formed.
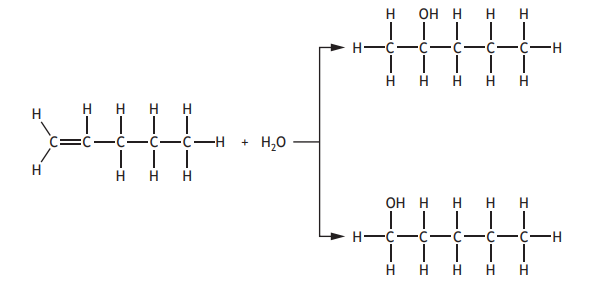
Which of the following alkenes will also produce two products when it undergoes an addition reaction with water?
Oct-2-ene
Hex-3-ene
But-2-ene
Ethene
Choose your answer
Was this exam question helpful?
In the Clemmensen reaction, ketones can be converted to alkanes as shown.
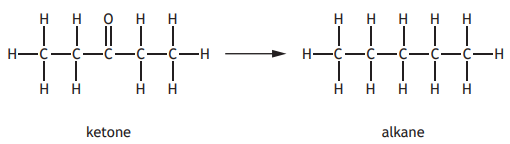
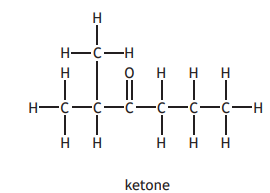
Identify the alkane produced if the following ketone was used in this reaction?
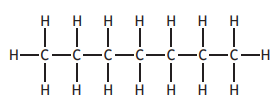
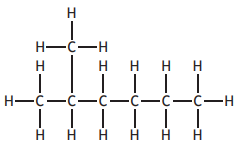
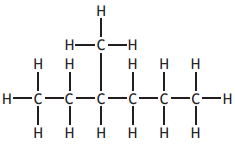
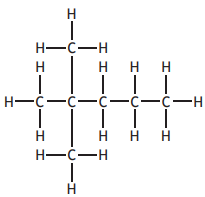
Choose your answer
Was this exam question helpful?
The shortened structural formula for a compound is
CH3CH2CH(CH3 )CH(CH3 )CH2CH2CH3
Which of the following is another way of representing this structure?
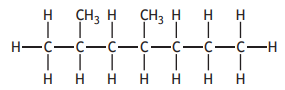
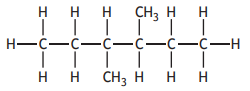
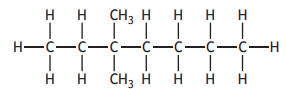
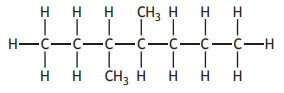
Choose your answer
Was this exam question helpful?
Identify which of the following is an isomer of
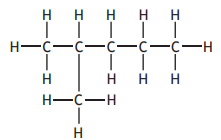
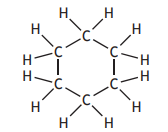
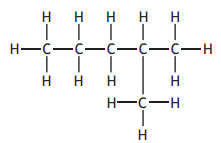
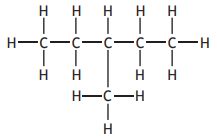
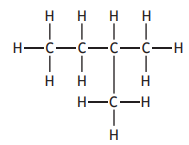
Choose your answer
Was this exam question helpful?
Which of the following reactions takes place when an alcohol is formed from an alkene?
Hydrogenation
Combustion
Hydration
Reduction
Choose your answer
Was this exam question helpful?
The ether, 1-ethoxypropane, can be made by the Williamson reaction.
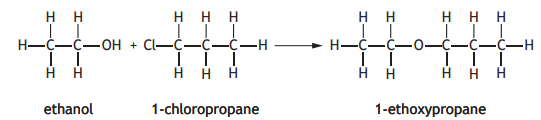
The structural formula for another ether is shown below.
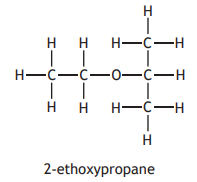
Which of the following pairs of compounds would react together to produce 2-ethoxypropane?
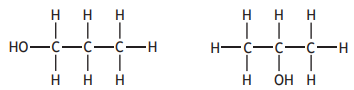
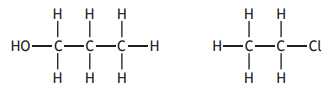
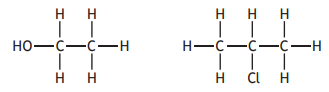
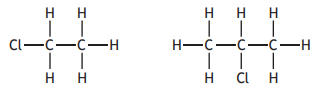
Choose your answer
Was this exam question helpful?