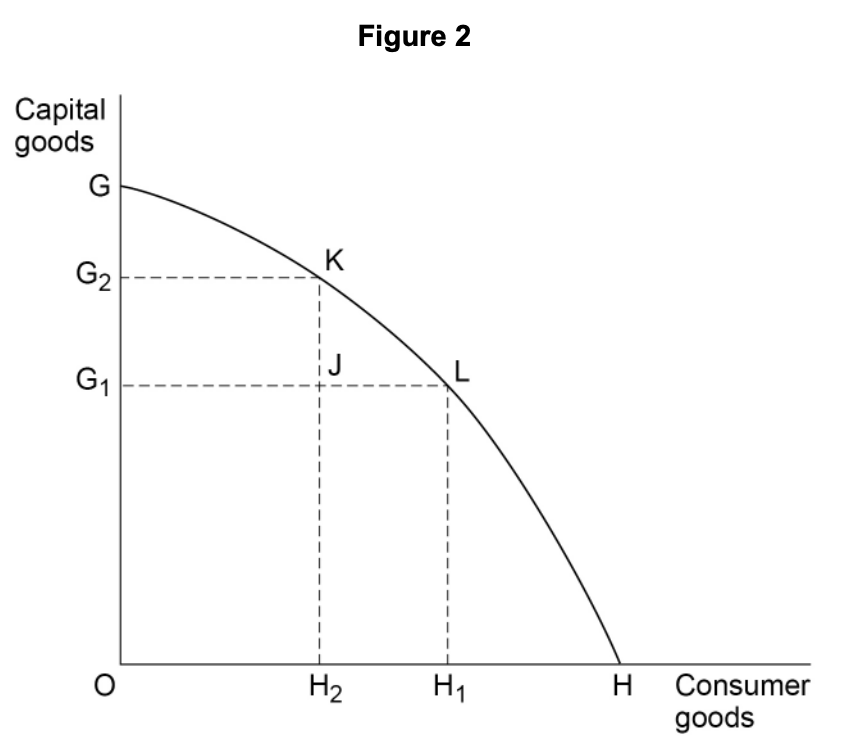
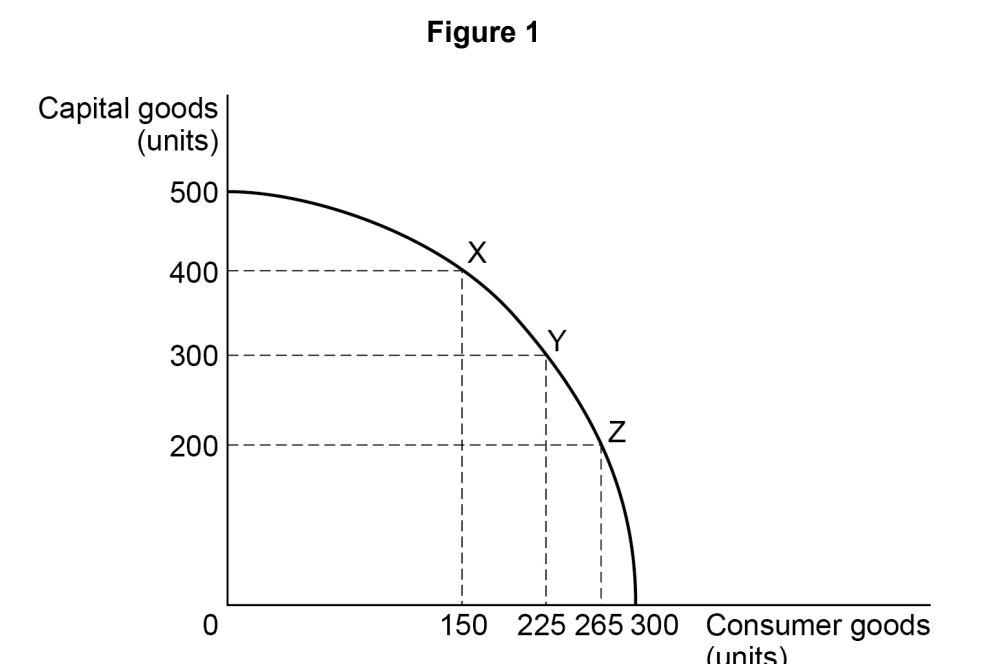
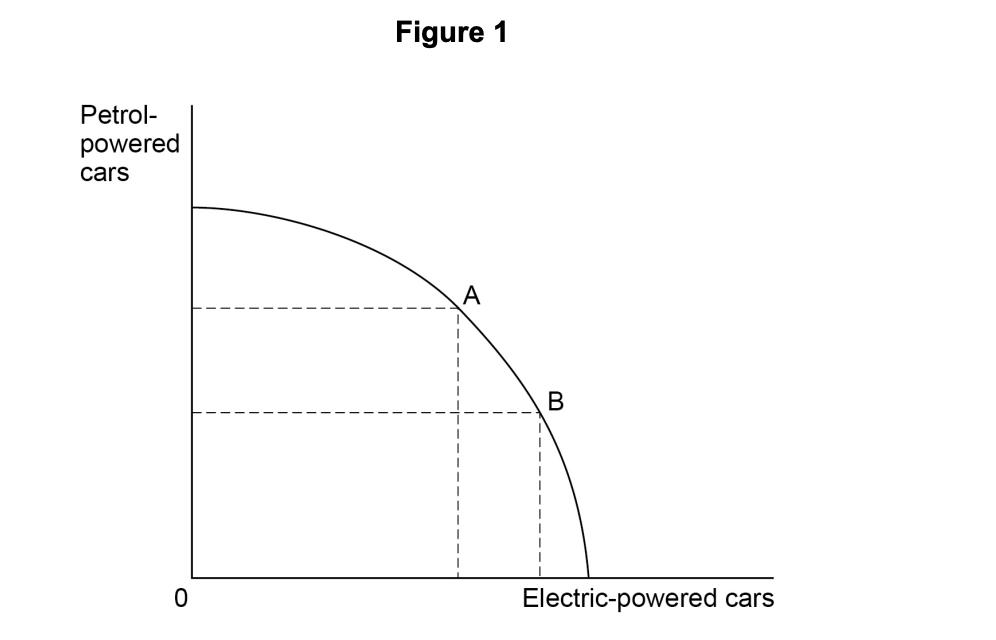
Economics is a social science because
all economic hypotheses are based on value judgements.
economic policies can only be based on positive analysis.
it involves the study of human behaviour and economic decision making.
quantitative data cannot be used to test economic theories.
Was this exam question helpful?