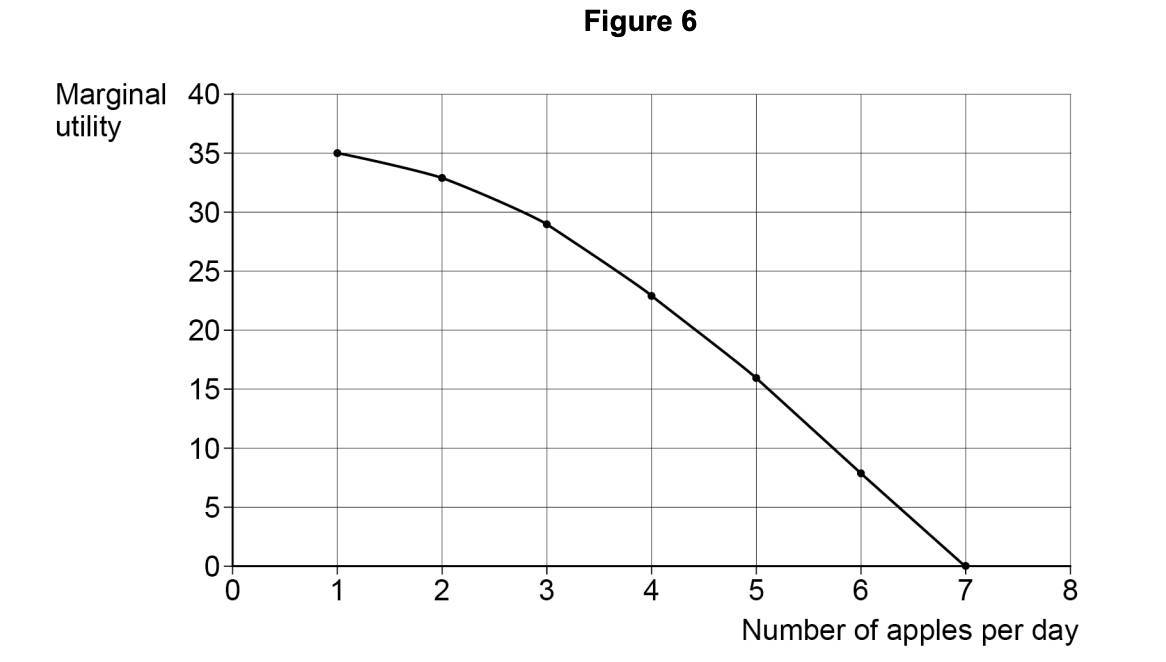
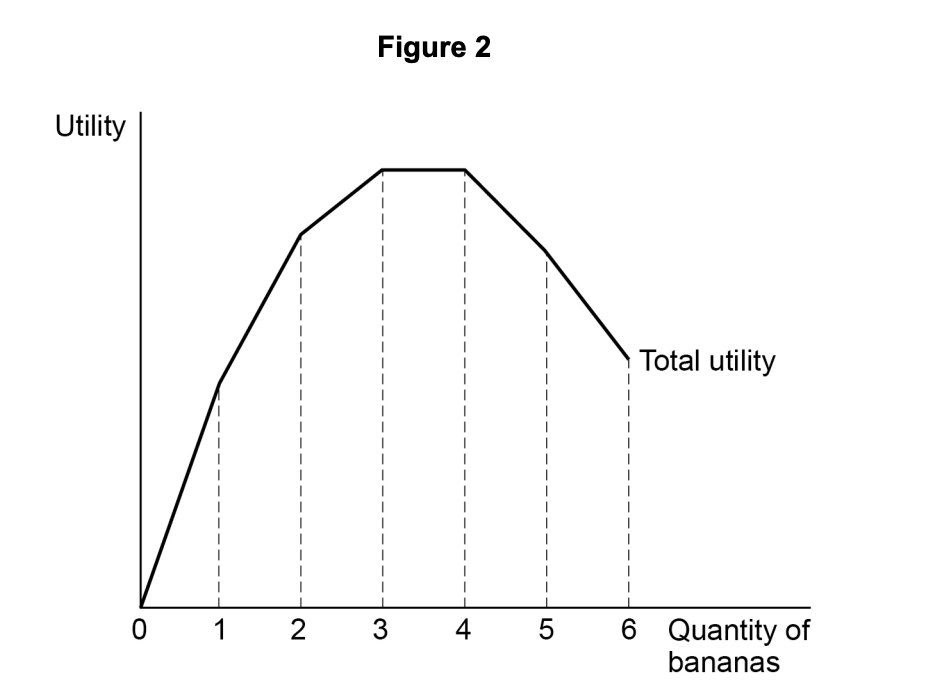
According to the hypothesis of diminishing marginal utility, when marginal utility is zero
average utility is negative
the good is a demerit good.
total utility from consuming the good is maximised.
Total utility will increase by consuming more of the good.
Was this exam question helpful?