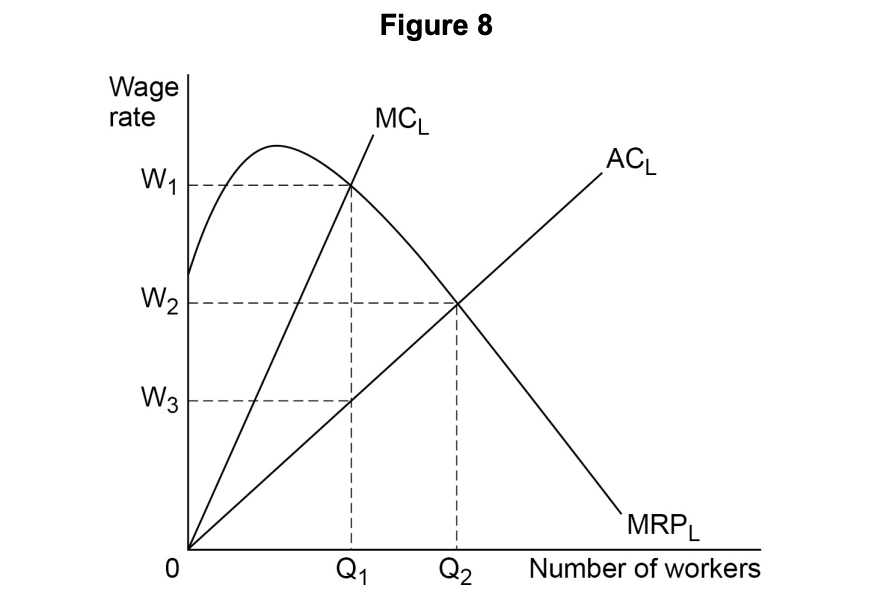
Figure 5 shows the market demand for labour (DL = MRPL), the market supply of labour (SL=ACL), and the marginal cost of labour (MCL), in a particular industry. The employer in this industry is a monopsonist.

From Figure 5, it can be concluded that, in the absence of a trade union or a minimum wage, the firm will employ
OQ1 workers at a wage of OW1.
OQ2 workers at a wage of OW1.
OQ2 workers at a wage of OW2.
OQ2 workers at a wage of OW3.
Was this exam question helpful?