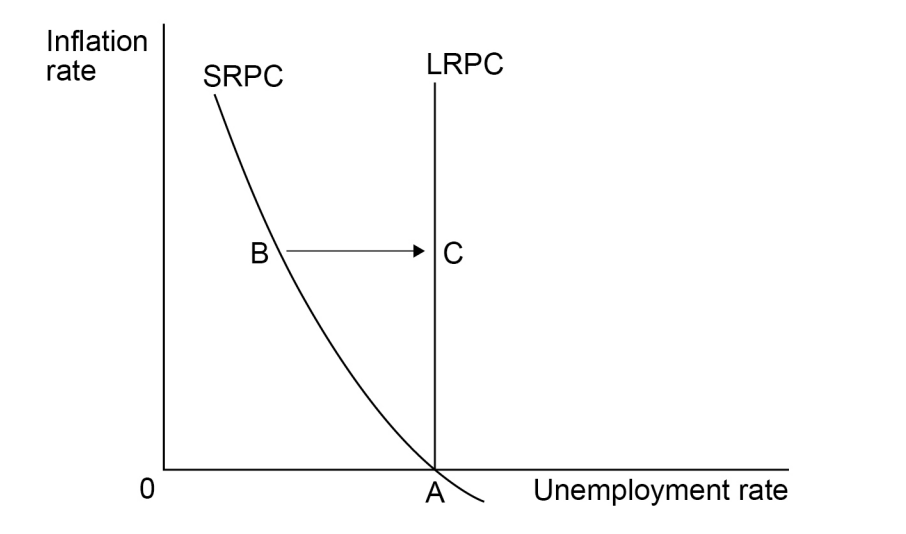
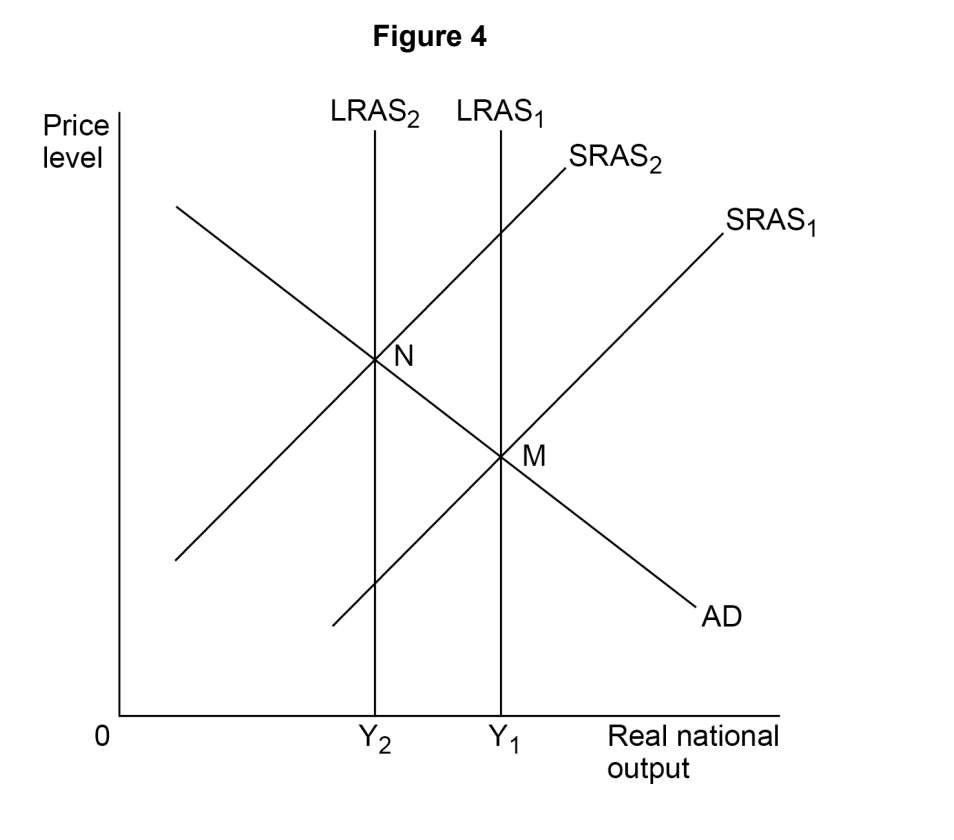
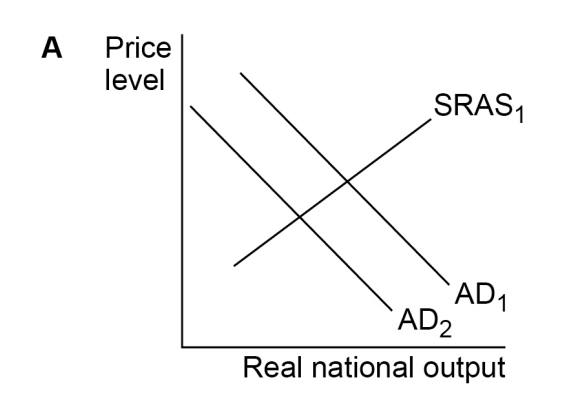
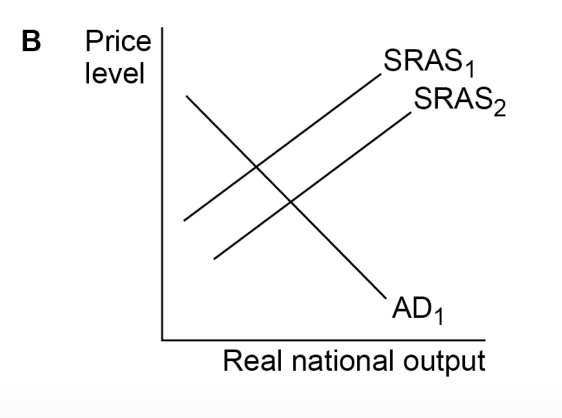
Table 1 contains data for the rates of growth of nominal and real GDP and the rate of inflation for an economy in a given year. Which one of the following combinations,
A, B, C or D, shows the correct relationship between the three variables?
| Nominal GDP growth | Real GDP growth | Inflation |
A | –2% | 0% | +2% |
B | +4% | +3% | –1% |
C | +5% | +5% | +1% |
D | –5% | –2% | –3% |
Was this exam question helpful?