Displacement-Time Graphs (Edexcel A Level Maths): Revision Note
Exam code: 9MA0
Did this video help you?
Displacement-time graphs
What is a displacement-time graph?
Displacement-time graphs show the displacement of an object from a fixed origin as it moves in a straight line
They show displacement (on the vertical axis) against time (on the horizontal axis)
Displacement-time graphs can go below the horizontal axis whereas distance-time graphs can not
Distance can not be negative whereas displacement can be
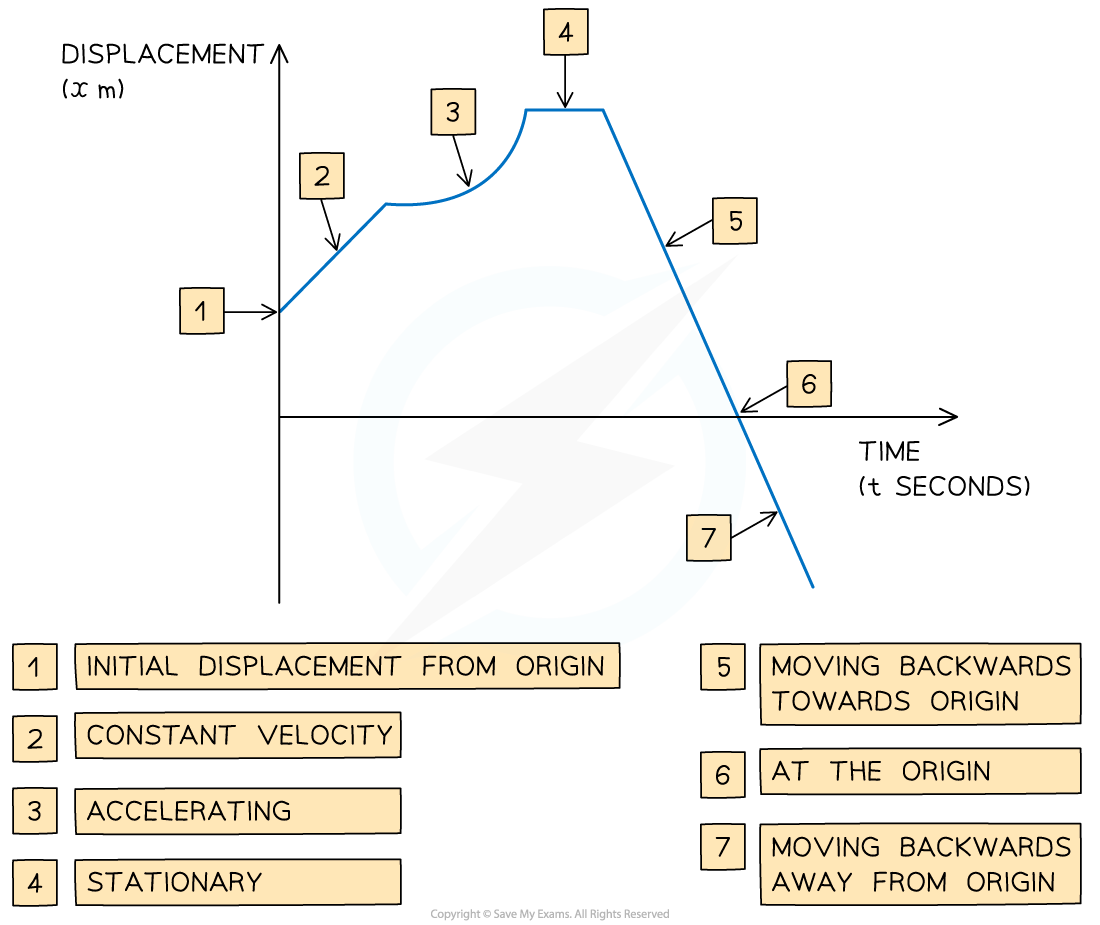
What are the key features of a displacement-time graph?
The gradient of the graph equals the velocity of the object
A positive gradient means the object is travelling forwards
A negative gradient means that the object is travelling backwards
The steeper the line, the greater the speed
A straight line shows that the object is moving at a constant velocity
A curved line shows that the object is accelerating or decelerating
A horizontal line shows that the object is stationary
If the graph touches the x-axis, then the object is at the origin at that time
How do I find the average speed and the average velocity of a journey?
The average speed can not be negative as speed is a scalar quantity and can only take a positive value
The average velocity is a vector quantity and can be positive, zero or negative
Worked Example
An athlete is training by jogging in a straight line.
The displacement-time graph below shows the displacement of the athlete from her starting point throughout her motion.
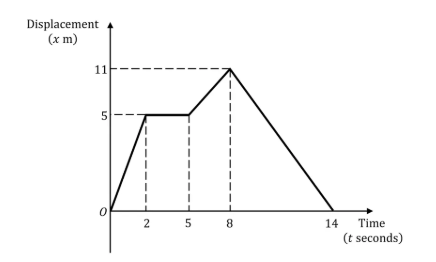
(a) Calculate the velocity of the athlete during the first 2 seconds.
Answer:

(b) Describe the motion of the athlete between the times of 2 seconds and 5 seconds.
Answer:

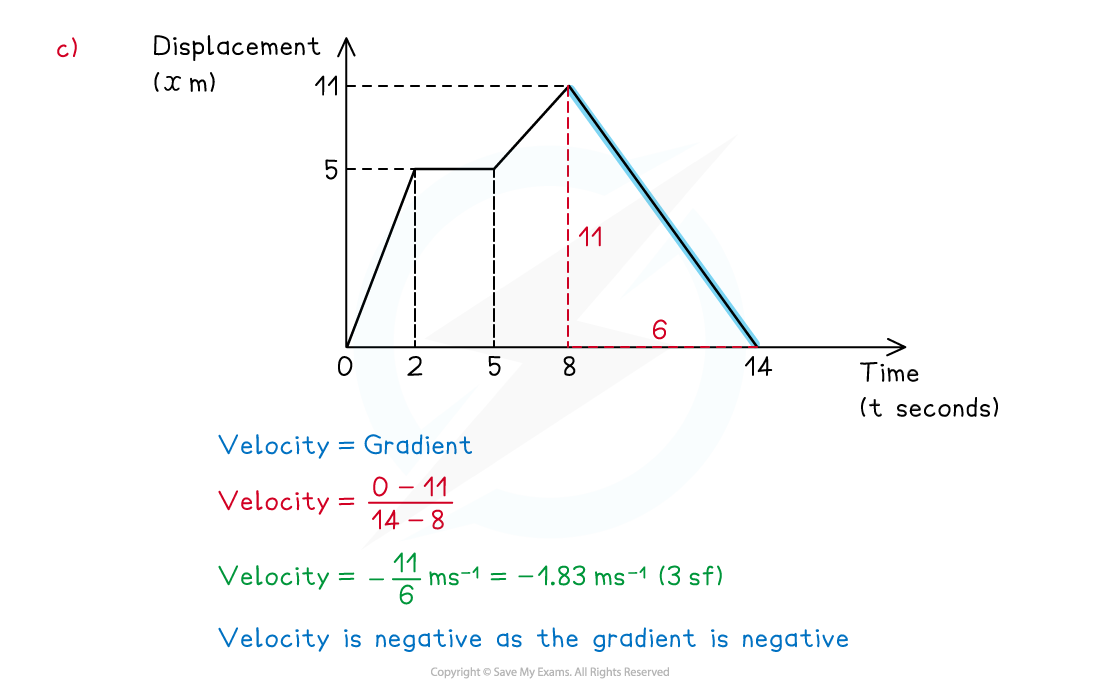
(c) Calculate the velocity of the athlete at 10 seconds.
Answer:
(d) Find the total distanced travelled by the athlete during the 14 seconds.
Answer:
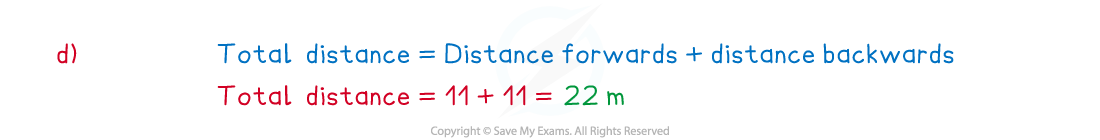
Examiner Tips and Tricks
Be careful to spot if you are working with a displacement-time graph or a velocity-time graph.
Be careful to spot if you are working with a displacement-time graph or a distance-time graph
Check where the graph starts from on the y-axis, the object does not have to start at 0. For example, if the graph starts at 100, the scenario could be a student on a walk starting 100 m from their house.
Distance is a scalar so it can not be negative whereas displacement from a starting point can be.
Think about the units when calculating, make sure they are consistent.

Unlock more, it's free!
Was this revision note helpful?
