Amending the Constitution (Edexcel A Level Politics): Revision Note
Exam code: 9PL0
Amending the Constitution
The amendment process is the formal method by which the US Constitution can be changed and is outlined in Article V
The process is deliberately difficult
This reflects the desire of the Founding Fathers to protect the Constitution from frequent or partisan change
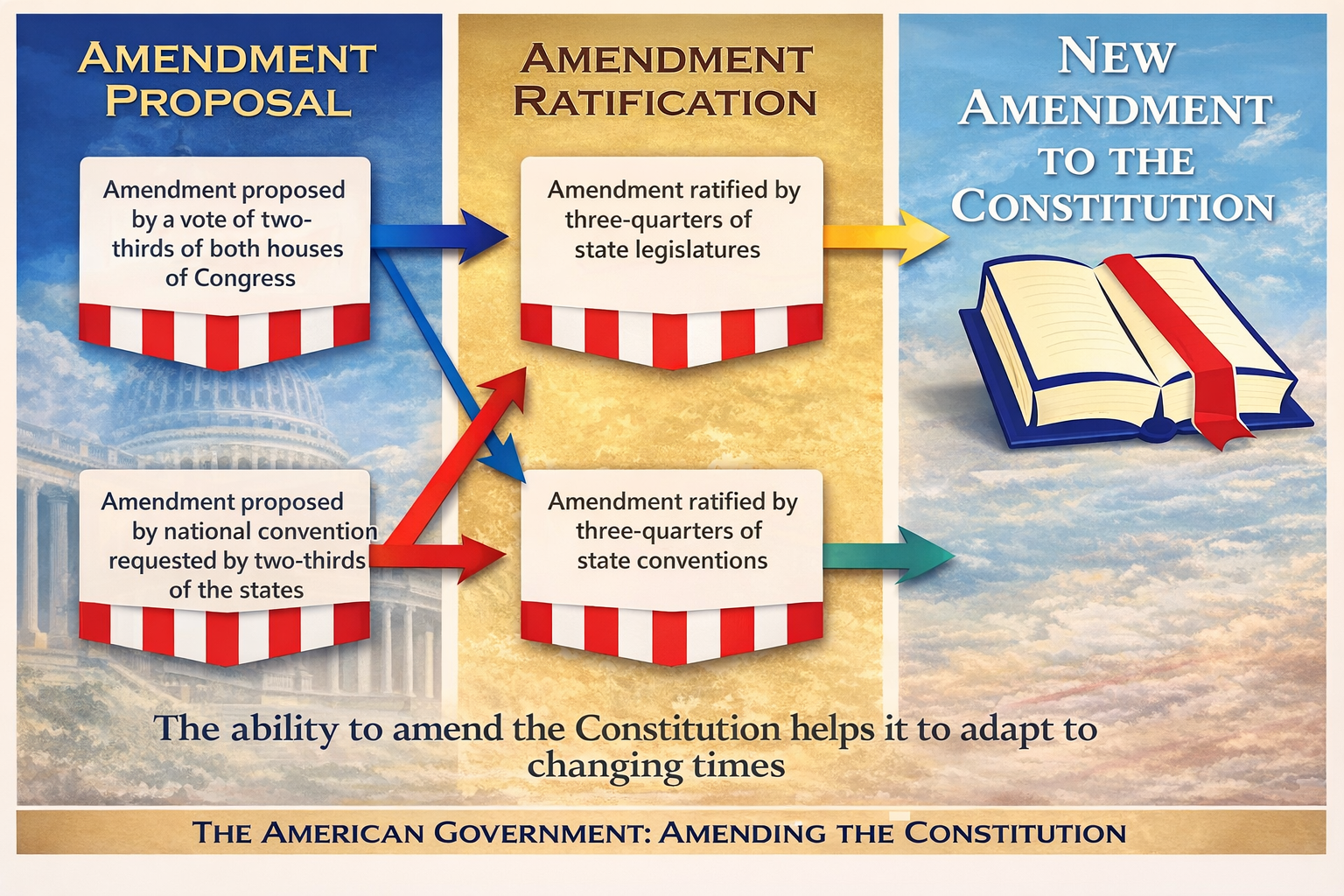
Stage 1: Proposal of an amendment
An amendment must first be proposed before it can be ratified
By Congress | By the states |
|---|---|
A proposed amendment must gain:
|
|
Stage 2: Ratification of an amendment
Once proposed, an amendment must be ratified by the states
Ratification requires approval from three-quarters of the states
This can occur through state legislatures or state constitutional conventions
Case Study
Equal Rights Amendment

The Equal Rights Amendment (ERA) aimed to guarantee gender equality under the Constitution
It was proposed and passed by ⅔ of both Houses of Congress in 1972
It then required ratification by 38 states by an extended deadline of 1979
Actions taken
By the 1979 deadline, the amendment had only received ratification from 35 states
Three additional states signed the ERA in the 21st century
Virginia became the 38th state in 2020
In 2023, the Biden administration supported removing the ratification deadline
Republicans opposed removing the deadline
Outcome
The amendment has not been formally adopted
This is due to disputes over whether ratification after the deadline is valid
Effectiveness of the amendment process today
Why is a complex and difficult amendment process a good thing?
The process ensures broad consensus across the US by requiring supermajorities
This protects against tyranny and rash change made in response to short-term national circumstances
The Constitution can still be interpreted through the judiciary, which is neutral and independent
Why is a complex and difficult amendment process a bad thing?
There have only been 27 amendments over nearly 250 years of US history
This suggests the process is too difficult
Outdated parts of the Constitution can remain in place
For example, the right to bear arms
Because the formal process is so difficult, it allows the Supreme Court to become very powerful
The Court becomes the branch that interprets the Constitution
Supreme Court justices are unelected and unaccountable to the public

Unlock more, it's free!
Was this revision note helpful?
