Key Features of the US Constitution (Edexcel A Level Politics): Revision Note
Exam code: 9PL0
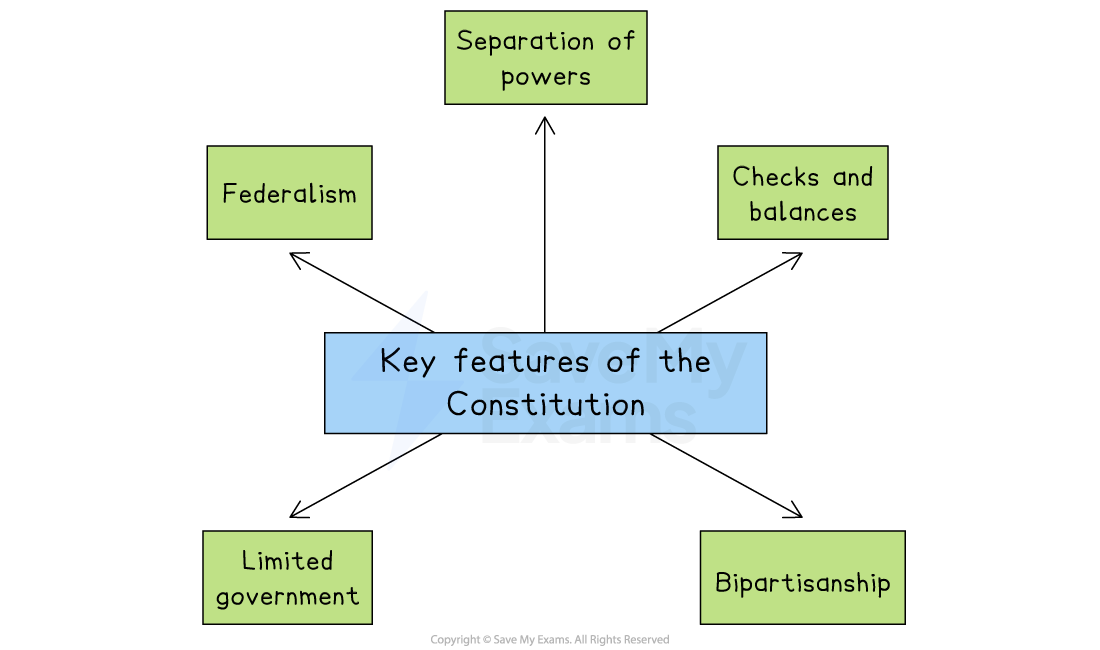
An introduction to the key features
The US Constitution is underpinned by a number of key principles
Although these terms are not always explicitly written into the Constitution, they can be identified in its structure, wording and operation
Federalism
Federalism is the principle of shared sovereignty, meaning power is divided between the federal (national) government and state governments
The powers of the federal government are enumerated in Articles I–III of the US Constitution
Powers not given to the federal government are reserved to the states under Amendment X, which states:
“The powers not delegated to the United States by the Constitution, nor prohibited by it to the States, are reserved to the States respectively, or to the people.”
The Supreme Court has the power to interpret the Constitution
In Dobbs v Jackson (2022), the Court ruled that the power to decide over abortion should be returned to the states
Effectiveness of federalism
Effective | Not effective |
|---|---|
|
|
Separation of powers
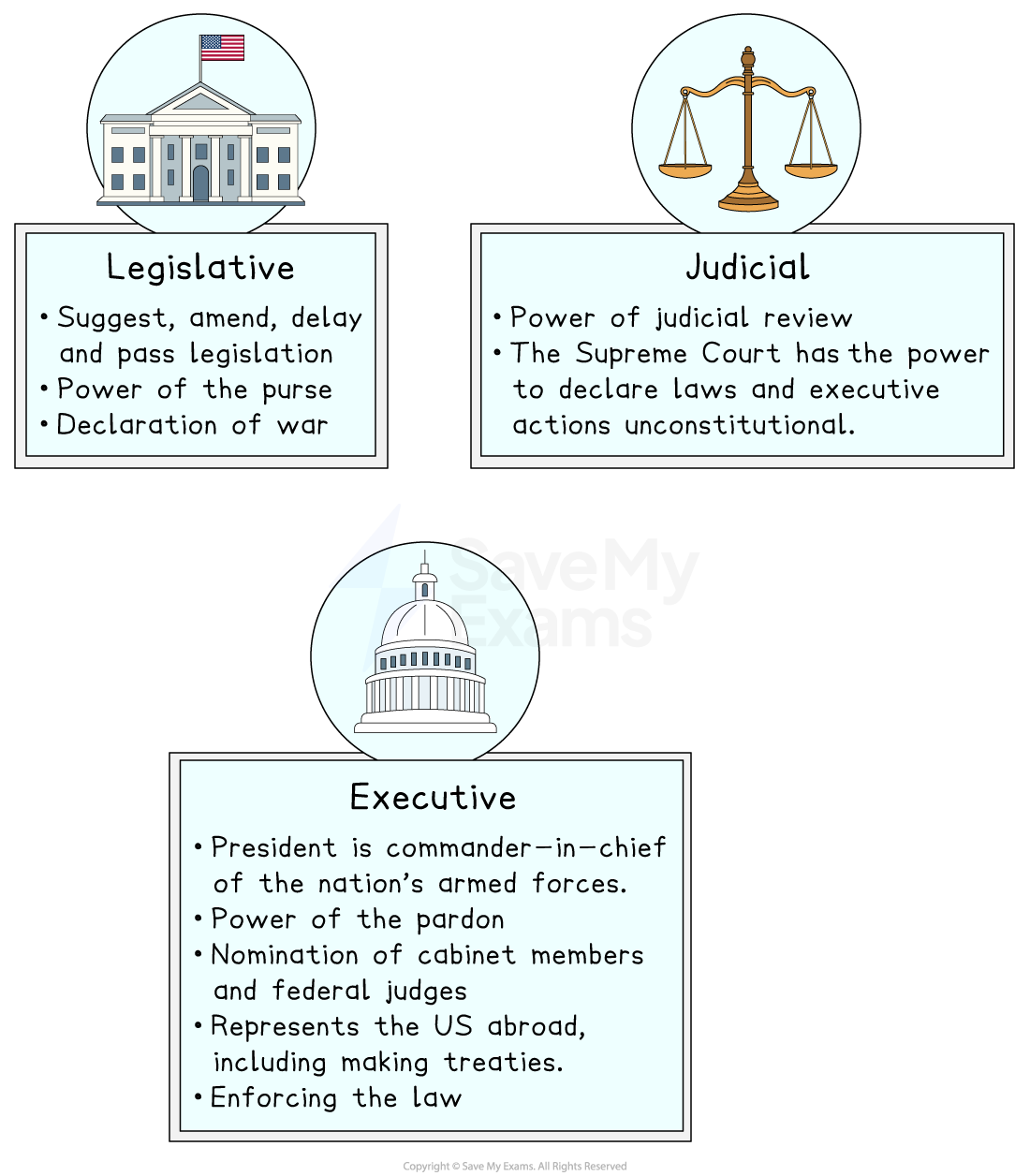
Separation of powers means that the three branches of the federal government each have their own powers, personnel and buildings
The three branches are:
Congress (legislative)
President (executive)
Supreme Court (judicial)
Individuals can only sit in one branch of government at a time
The President is given the power of the pardon in the Constitution
President Trump pardoned nearly 1,600 individuals in 2025 for their role in the January 6 insurrection
Effectiveness of separation of powers
Effective | Not effective |
|---|---|
|
|
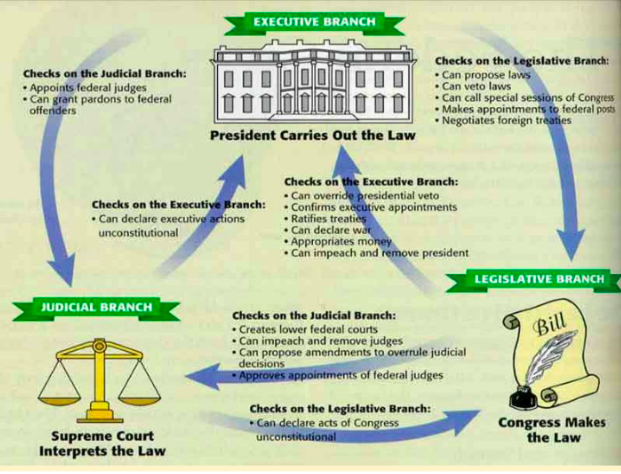
Checks and balances
Checks and balances means that each branch of the federal government has the power to scrutinise and limit the actions of the other branches
If one branch oversteps its powers, the other branches can prevent it from acting
Congress, as the representative body of the people and taxpayers, has the power of the purse
Effectiveness of checks and balances
Effective | Not effective |
|---|---|
|
|
Bipartisanship
The Founding Fathers were sceptical about political parties but anticipated their impact
As a result, they included requirements for bipartisanship throughout the Constitution
This is achieved through the use of super-majorities
Certain actions require a two-thirds majority in both Houses of Congress, including:
proposing constitutional amendments
overriding a presidential veto
Effectiveness of bipartisanship
Effective | Not effective |
|---|---|
|
|
Limited government
A limited government is one that operates with restraints on its power, preventing it from becoming tyrannical
Federalism limits power by dividing it between federal and state governments
Separation of powers limits power by dividing it between the three branches
The Supreme Court plays a key role in enforcing limited government
Case Study
Shelby County v Holder (2013): Voting Rights in the USA

The Voting Rights Act (1965) forced some states with a history of racism in voting to get federal approval before changing election laws
Shelby County argued this rule was unfair and no longer needed.
The case
Shelby County said that Section 4(b) of the Act was outdated and treated some states differently, which went against state equality and states’ rights
The ruling
In a 5–4 decision, the Supreme Court struck down Section 4(b). This meant Section 5, which required federal approval, could no longer be used.
The significance
Reduced protection for minority voters
Allowed states to change voting laws more easily
Showed the Supreme Court limiting the power of Congress
Highlighted the importance of states’ rights in US politics
Effectiveness of limited government
Effective | Not effective |
|---|---|
|
|

Unlock more, it's free!
Was this revision note helpful?
