Contemporary Global Issues (Edexcel A Level Politics): Revision Note
Exam code: 9PL0
The UN Security Council and global issues
The Security Council's primary purpose under the UN Charter is to maintain peace and global security
It addresses poverty, human rights and environmental issues when they directly threaten peace and security
Permanent members of the UN Security Council
The Security Council has five permanent members, all of whom have veto power
This can be an obstacle to addressing contemporary global issues
The relationships between the five permanent members is often strained
This contributes to a lack of consensus in tackling global peace and security
Case Study
The UN Security Council’s failure to act in the 2023 Israel–Gaza conflict
In 2023, Hamas, an Islamic militant group controlling the occupied Gaza Strip, launched an attack on Israel after decades of hostility
More than 1,000 Israelis were killed, and hostages were taken
Israel retaliated with military action in Gaza, which many international observers considered disproportionate due to its impact on civilians
The UN Security Council’s role
There were widespread calls for the UN Security Council to act to end the conflict
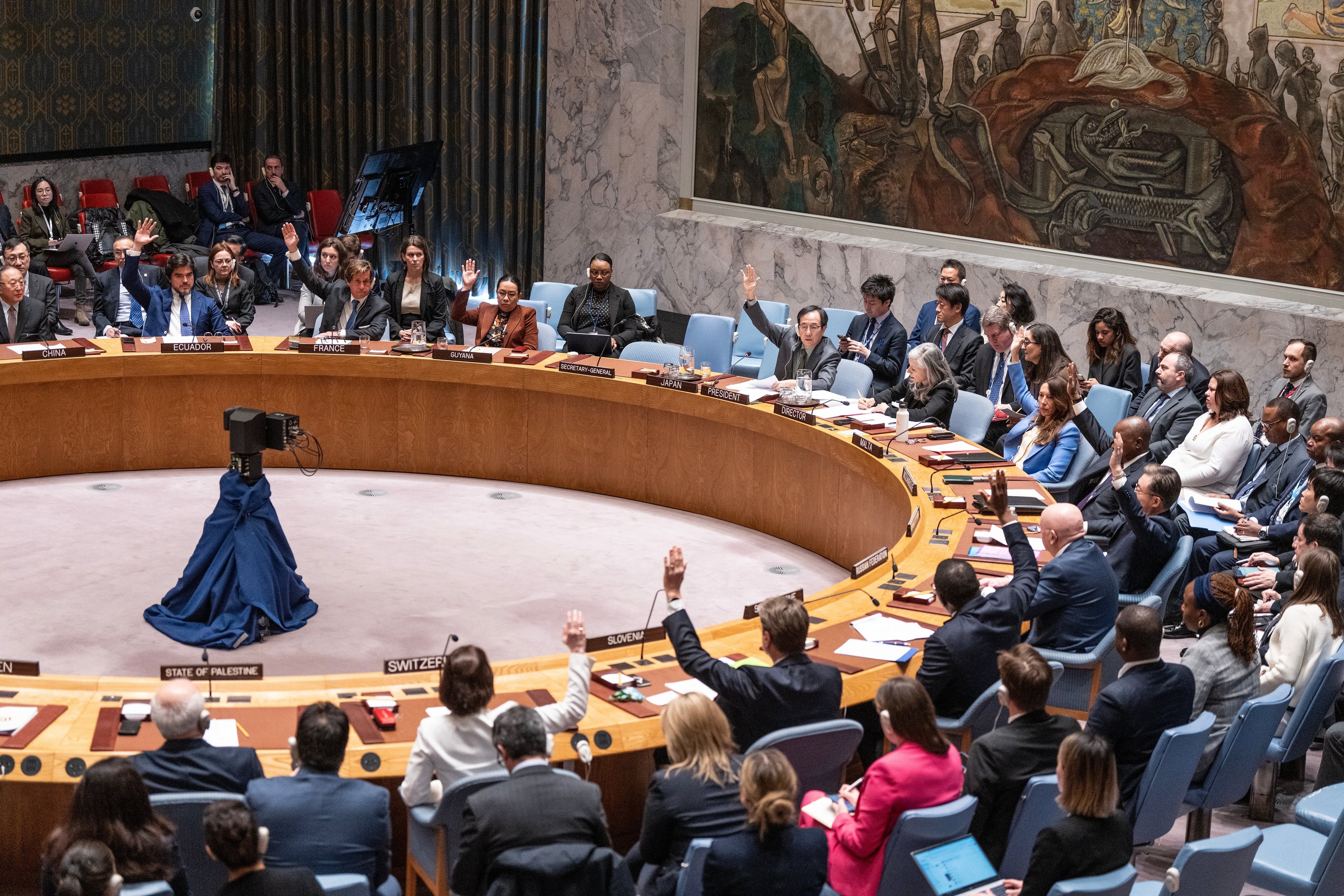

Thirteen draft resolutions were proposed at the Security Council
The USA used its veto power six times, China and Russia each used their veto twice on different resolutions, and the UK used its veto once in support of the USA
The ten non-permanent members could vote but did not have veto power
A resolution can pass if it receives at least nine votes and no permanent member uses its veto
The outcome
Only four resolutions were passed, and the conflict continued
UN Secretary-General António Guterres described the Security Council as an “outdated, unfair and ineffective” system that damaged the global reputation and trust of the United Nations
The IMF, World Bank and global issues
Both the IMF and World Bank are global institutions focused on global economic stability and development
However, their impact and effectiveness is widely criticised, especially in relation to Structural Adjustment Programs (SAPs)
They recognise that conflict, poverty, human rights abuses and environmental destruction are threats to global economic stability and development
SAPs go beyond simply loaning money to nation states
They often require that states implement policies to address these concerns
SAPs have left many developing countries with enormous debt
In 2025 the UN Conference on Trade and Development (UNCTAD) found that 3.4 billion people worldwide live in countries that spend more on debt-interest payments than on health or education
Many argue that the IMF and World Bank have increased the probability of poverty, human rights abuses and environmental destruction in the global south
SAPs to Ghana, Kenya, Malawi, Nigeria, Senegal, Sierra Leone, Tanzania, Uganda, Zambia and Zimbabwe required these states to cut or freeze public spending
This has negatively impacted the health and education of citizens
Many criticise the fact that wealthier nations have more power within these organisations and prioritise their own economic stability
Calls for reform
The purpose and mandate of the IMF and World Bank are widely questioned
At the Summit for the Future in 2024, UN Secretary Antonio Guterres argued that the IMF and World Bank are outdated, ineffective and unequipped to tackle emerging issues
The USA, the most powerful state in these organisations, argued that the World Bank and IMF should return to driving economic growth and stop interfering with human rights and environmental issues
Many argue that SAPs are mostly ineffective and often harmful and should be restructured or abolished
As economically developed states dominate decision-making, there are calls to give all members equal opportunity to vote
Global civil society and global issues
Civil society is a broad term that covers groups of people or organisations who unite because they have a common goal and have ideas of what action needs to be taken to improve society
Examples of civil society
Non-governmental organisations (NGOs) | Charitable organisations | Social movements |
|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Characteristics of civil society
They work independently from governments, are funded by private donations and usually focus on:
poverty reduction
empowering people who face discrimination
environmental protection
demanding government or corporate accountability
ending conflict
They use a range of methods to try to bring about awareness and change, such as:
organising protests
sharing information on social media
publishing detailed reports and sharing them with all media
Civil society groups and organisations are important features of life in most democratic states
For example they can be effective in raising awareness of social problems, delivering educational and medical support or challenging governments to change policies
Non-state actors and global issues
Non-state actors include any group or organisation that works independently from government control but plays some kind of role in global politics
Examples include
Political parties not currently in power
Civil society, including NGOs
Private citizens
Private companies and businesses
Social movements
Pressure groups
Resistance movements, both peaceful and violent
The media
Case Study
Greenpeace and global climate change
Greenpeace is an international non-governmental organisation (NGO) that operates independently of governments
It campaigns on global environmental issues, particularly climate change, deforestation and fossil fuel use

The global issue
Climate change is a global issue that requires international cooperation to reduce greenhouse gas emissions
Many governments have been criticised for failing to take sufficient action to meet climate targets
Actions taken
In recent years, Greenpeace has used protests, media campaigns and legal action to pressure governments and multinational companies to reduce fossil fuel use
In 2023–24, Greenpeace campaigns targeted oil and gas companies in Europe and pressured governments to block new fossil fuel projects
Greenpeace also uses reports and scientific evidence to influence public opinion and policy debate
Impact
Greenpeace has helped raise global awareness of climate change and increased political pressure on governments and corporations
Its actions have influenced public debate and, in some cases, contributed to delays or cancellations of fossil fuel projects
However, Greenpeace has no formal decision-making power, meaning its influence depends on public support and media attention

Unlock more, it's free!
Was this revision note helpful?
