Contemporary Global Issues (Edexcel A Level Politics): Revision Note
Exam code: 9PL0
Human rights and environmental institutions and poverty
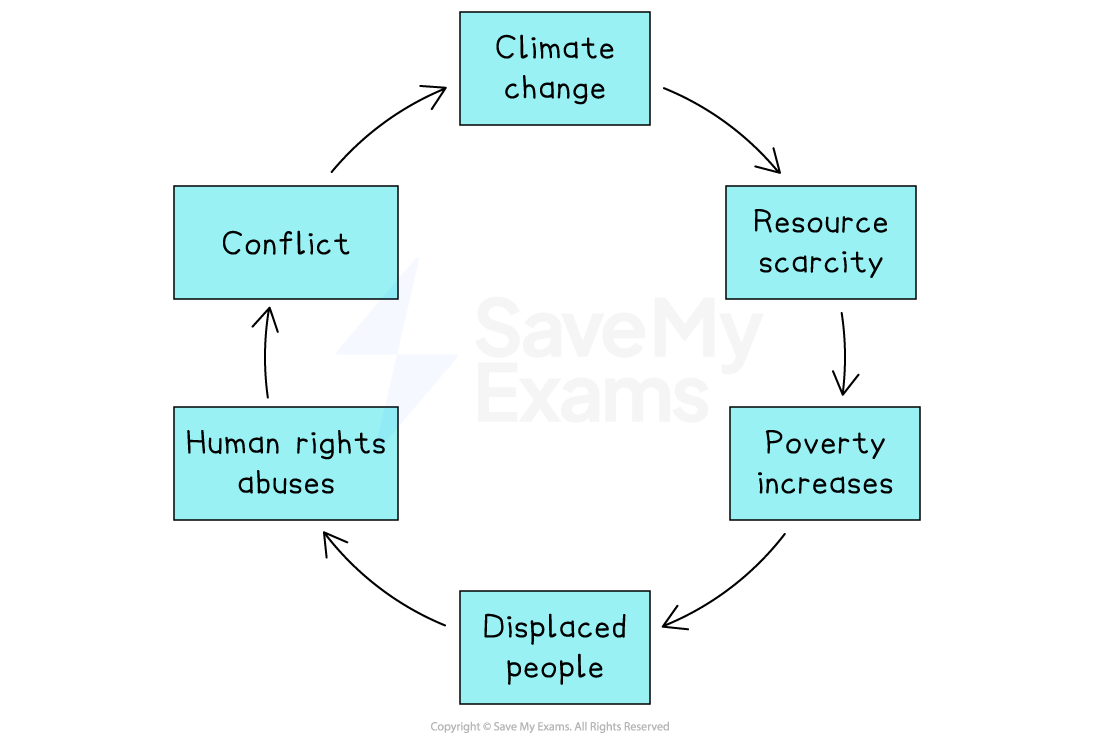
Climate change greatly impacts the poorest and most vulnerable
It intensifies competition for land and water as droughts and floods are making land in many areas of the world less productive
Less productive land means less food is produced and poverty increases
Climate change forces people to move and these displaced people face food insecurity and instability and women are particularly vulnerable to violence as displaced people
Conflict is intensified as vulnerable people compete for limited resources
Conflict brings about further environmental damage, poverty and human rights abuses
There is a deeply interconnected relationship between conflict, poverty, human rights and the environment
Environmental institutions such as the UNFCCC and IPCC were developed by the UN to work toward slowing down climate change and decrease the probability of conflict
Measuring effectiveness
Evidence of ineffectiveness | Evidence of effectiveness |
|---|---|
|
|
An interconnected approach provided by these institutions is considered by many to be the best option
State sovereignty and international law enforcement
It can be argued that state sovereignty supports international law enforcement
The state is the most capable actor to protect and enforce human rights laws
The mechanisms of enforcement, including judicial and policing forces, are all under the control of the state
Only the state can take international human rights laws and codify them into national law
Member states of global governance institutions have the choice to ratify international human rights laws
Although soft power may be used to try to persuade them, they are more likely to protect human rights laws that they have supported
The state has control over its borders
International human rights laws regarding refugees are best enforced by the state
Recent global norms about state sovereignty require that the state has a responsibility to protect its citizens
However, state sovereignty may be considered an obstacle to international law enforcement
All of the arguments that state sovereignty supports international law enforcement are subjected to the basic principle that states control what happens within their borders
States are the greatest abusers of human rights
State sovereignty limits international laws from being enforced by any other actors
Multiple states have ratified human rights laws proposed by global governance and done nothing to enforce them
This has often been due to politicisation (using human rights for political gain)
Governments may change and attitudes toward the enforcement of international laws can change with them
The necessity for global governance to develop Responsibility to Protect (R2P) demonstrates that sovereignty is an obstacle to international law enforcement
Performance of international courts
International courts are designed to apply international laws in order to provide justice at the global/international level
The United Nations courts are:
The International Court of Justice
The International Criminal Court
The performance of international courts is assessed in terms of their ability to provide justice, and this is a hotly debated issue
Case Study
South Africa v Israel (2023– ): The ICJ and Its Limitations
The International Court of Justice (ICJ) settles legal disputes between states using international law
In December 2023, South Africa brought a case against Israel, accusing it of breaching the Genocide Convention in Gaza

The case
South Africa asked the ICJ to rule on whether Israel’s actions amounted to genocide
Israel rejected the claims but agreed to take part in the case and defend itself before the Court
The rulings
January 2024: the ICJ ordered Israel to take all possible steps to prevent genocide
March 2024: the ICJ ordered Israel to ensure humanitarian aid, including food, could reach civilians in Gaza
The Court repeatedly raised concerns about the humanitarian situation
The response
Several states supported South Africa, including Malaysia, Turkey, Jordan, Bolivia and Namibia, as well as members of the Organisation of Islamic Cooperation
The USA defended Israel, while the EU largely remained silent
The significance
The case shows the ICJ’s lack of enforcement power, as rulings rely on state compliance
The process is very slow, with a final judgement not expected until 2027
It highlights limits of international law when powerful states and allies are involved
It demonstrates how the ICJ can raise global attention but struggles to ensure outcomes
Tackling environmental issues
Global governance institutions have a role in finding solutions to environmental challenges by acknowledging the complex and interconnected nature of environmental issues
There are competing views on how best to achieve this
The United Nations addresses the complexity of the environment and firmly links it to poverty and conflict.
It established the UN Environmental Programme (UNEP) to specifically tackle
Climate change
Threats to biodiversity
Pollution
Other threats to environmental stability
The World Bank takes a slightly different approach and claims it tackles environmental issues by promoting
Climate change resilience
Natural resource management
Sustainable development practices
Pollution reduction
The World Health Organisation tackles environmental issues by focusing on the impact they have on human health. They tackle
Access to clean water
Clean air
Stable natural environment, including a stable food supply
There are also competing views by multiple actors and stakeholders regarding these approaches
Shallow green ecology vs deep-green ecology
Many of the approaches taken by global governance fall into the shallow green ecology approach, meaning the purpose is to benefit humanity rather than fostering a deep respect for the environment where all life is equal
Many question the true sustainability of approaches taken by financial global governance
Economic growth and consumerism lead to a greater strain on natural resources and the environment in general
The tragedy of the commons is relevant
Economic development is often prioritised by global governance, particularly in less developed states
This negatively impacts the shared global environment.
International agreements
The United Nations Convention Framework on Climate Change (UNFCCC) has organised several global environmental governance agreements with varying degrees of success
Agreement | Strengths | Weaknesses |
|---|---|---|
Rio Declaration 1992 |
|
|
Kyoto Protocol 1997 |
|
|
Copenhagen Accord 2009 |
|
|
Paris Accord 2015 |
|
|

Unlock more, it's free!
Was this revision note helpful?
