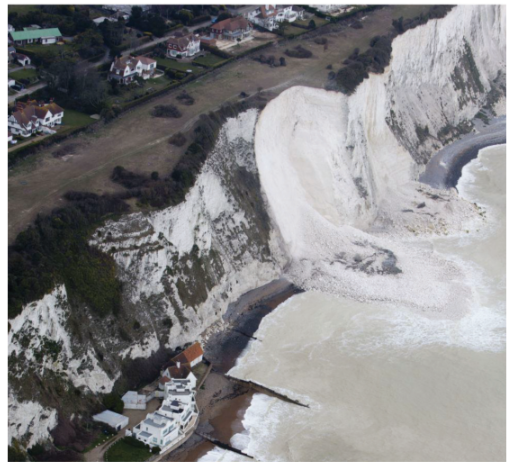
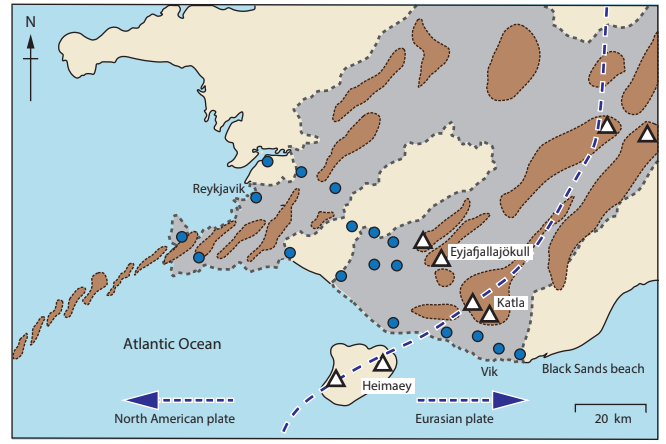
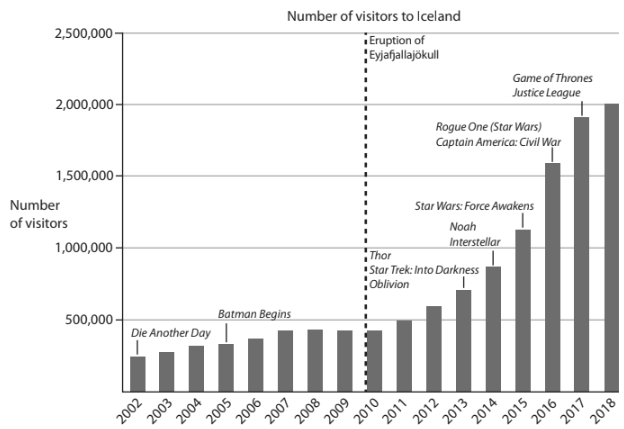
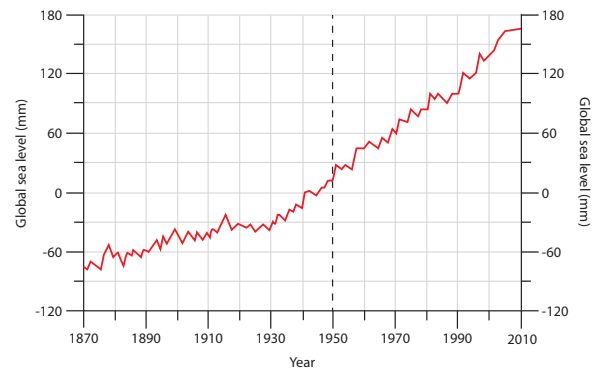
Study Figure 5a below, which shows the measurements taken of the volume of cliff material eroded over a six month period.
Average volume of cliff material eroded (metres3) | |
|---|---|
August | 1 |
September | 3 |
October | 35 |
November | 592 |
December | 994 |
January | 186 |
Figure 5a
Measurements of the volume of eroded cliff material
Calculate the mean volume of cliff material eroded per month.
Show your working.
Give your answer to 2 decimal places.
............................... metres3
Was this exam question helpful?