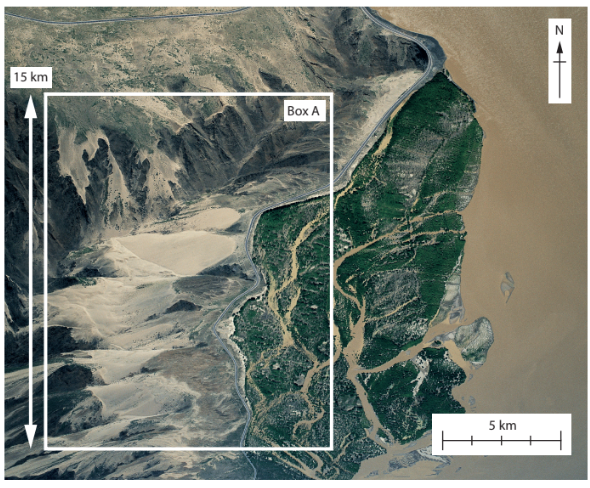
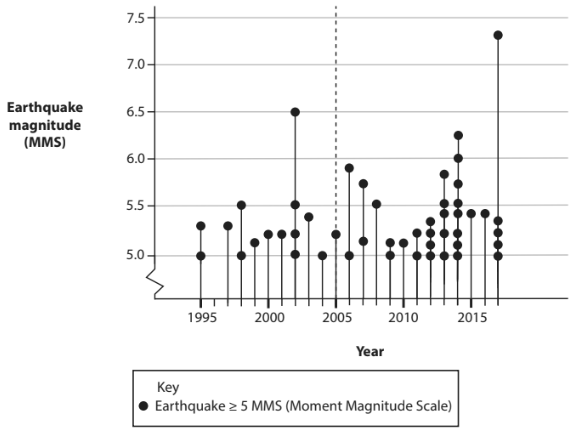
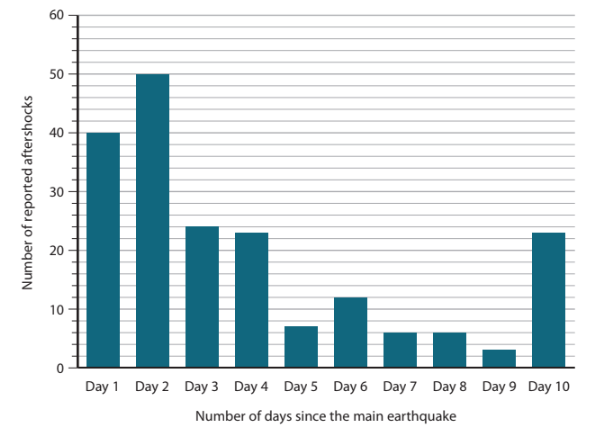
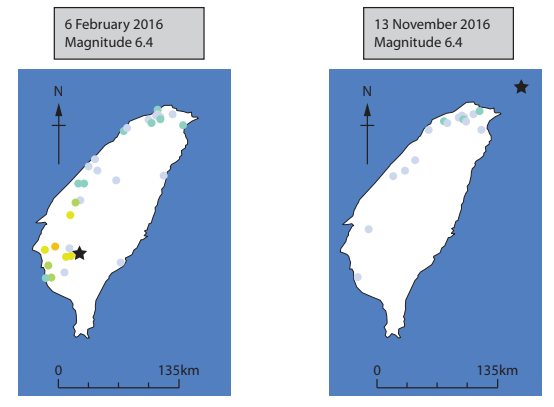
Study Figure 1
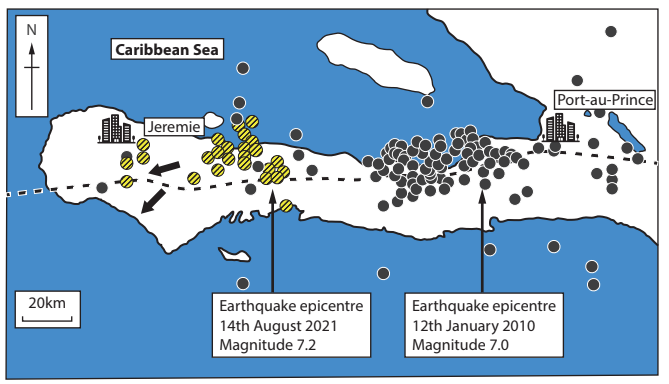

Figure 1
Aftershocks reported following two earthquakes in Haiti, 2010 and 2021
Compare the distribution of aftershocks between the two earthquakes.
Suggest one reason for the different pattern of aftershocks shown in 2021.
Was this exam question helpful?