Integrating Trigonometric, Exponential & Reciprocal Functions (DP IB Analysis & Approaches (AA)): Revision Note
Did this video help you?
Integrating trig functions
How do I integrate sin, cos and sec^2?
The antiderivatives for sine and cosine are
where is the constant of integration
Also, from the derivative of
Examiner Tips and Tricks
The standard integrals of and
are both in the exam formula booklet.
The integral for is not in the formula booklet. However the derivative result
is in the formula booklet, so that can be used 'the other way round' to deduce the antiderivative.
For the linear function
, where
and
are constants,
For calculus with trigonometric functions angles must be measured in radians
Ensure you know how to change the angle mode on your GDC
Examiner Tips and Tricks
Make sure you are familiar with the calculus formulas that are in the exam formula booklet. Many standard integrals are included, but remember that you can also use the standard derivatives in the booklet to help you find antiderivatives.
Just remember to add '+c', the constant of integration, for any indefinite integrals you solve.
Worked Example
a) Find, in the form, an expression for each integral
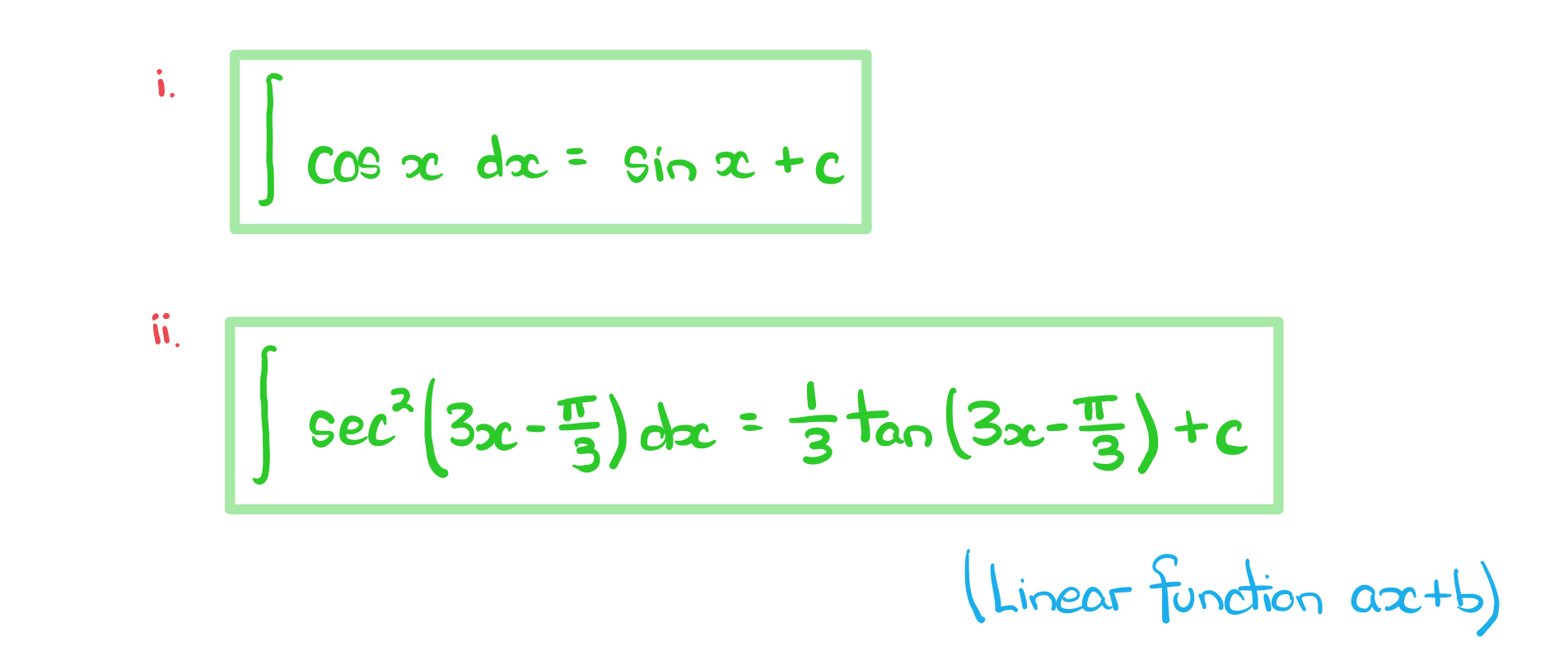
b) A curve has equation.
The curve passes through the point with coordinates.
Find an expression for.
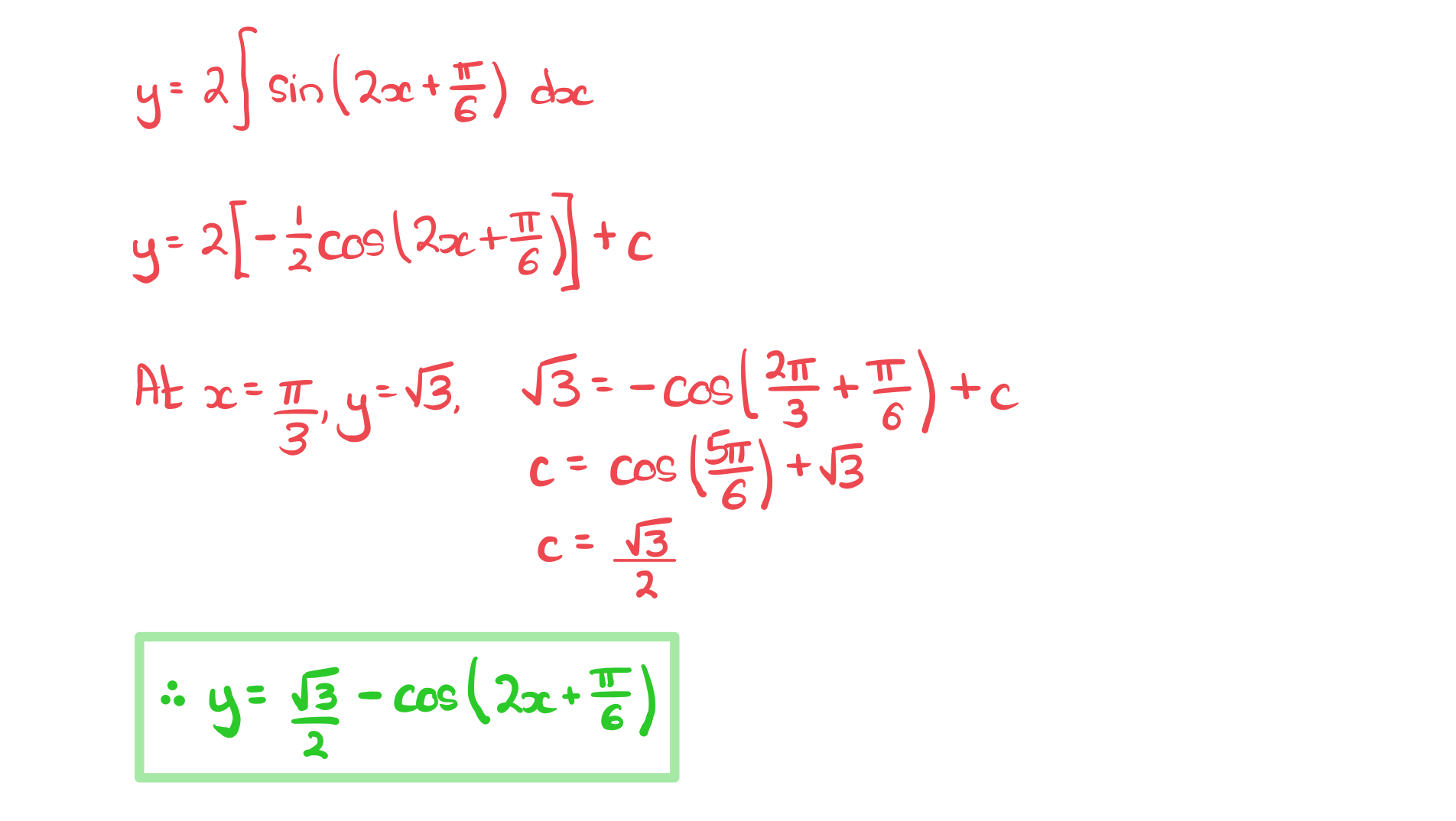
Did this video help you?
Integrating e^x & 1/x
How do I integrate exponentials and 1/x?
The antiderivatives involving
and
are
where is the constant of integration
Examiner Tips and Tricks
Both of the standard integrals above are in the exam formula booklet.
For the linear function
, where
and
are constants,
It follows from the last result (by using the using the reverse chain rule) that
Examiner Tips and Tricks
With ln, it can sometimes be useful to write the constant of integration,, as a logarithm. I.e., by letting
for some (positive) constant
.
Using the laws of logarithms, the answer can then be written as a single term. For example:
Worked Example
A curve has the gradient function.
Given the exact value of is
find an expression for
.
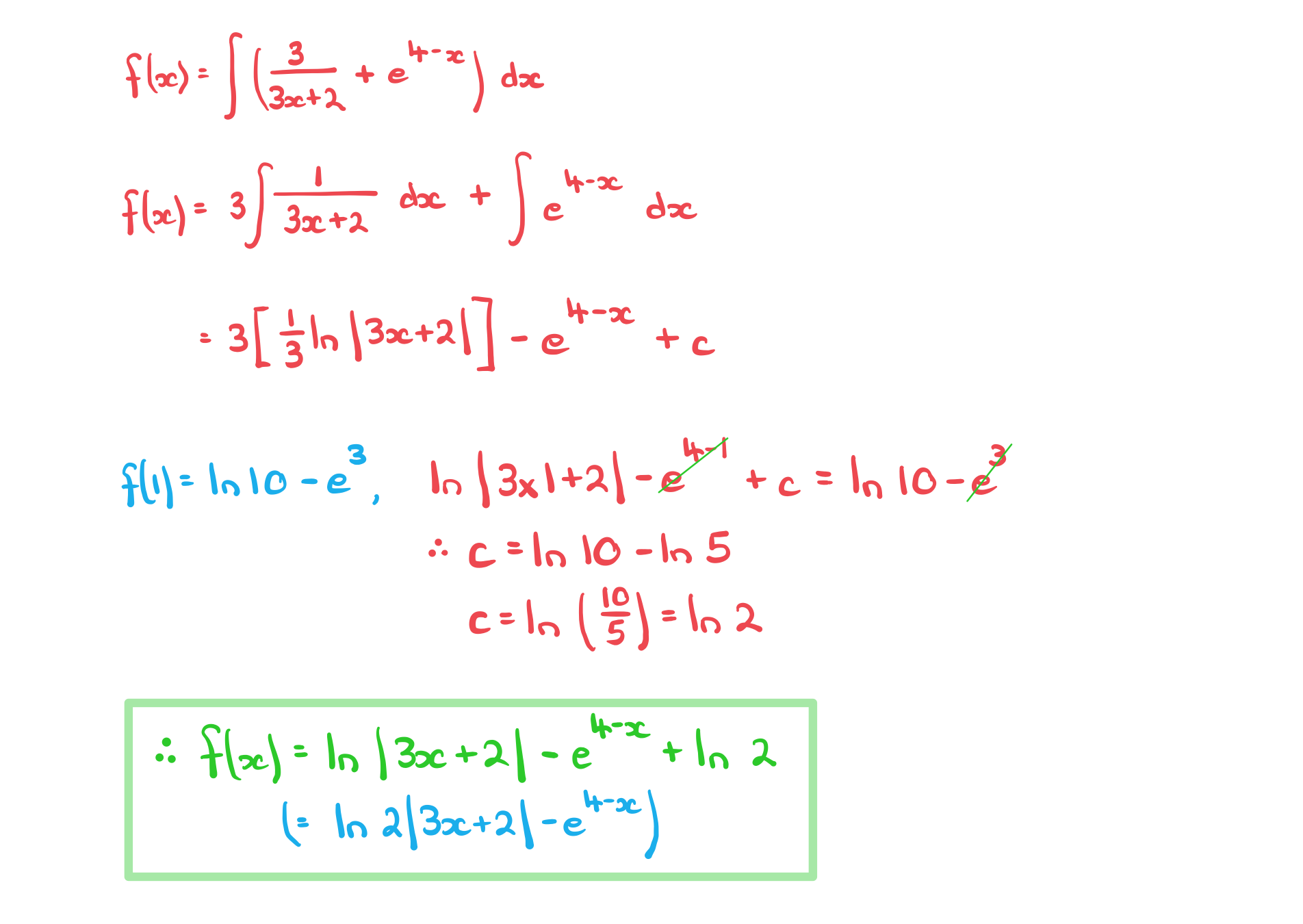

You've read 0 of your 5 free revision notes this week
Unlock more, it's free!
Did this page help you?