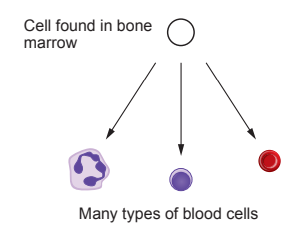
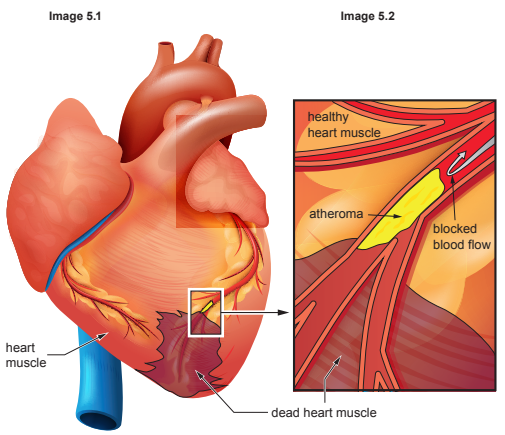
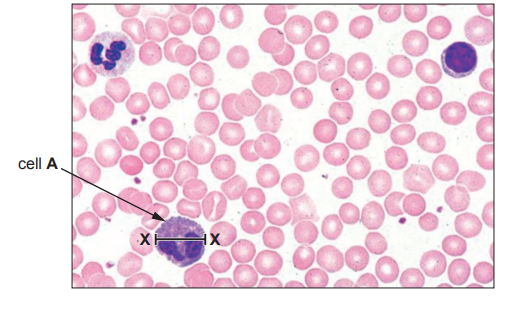
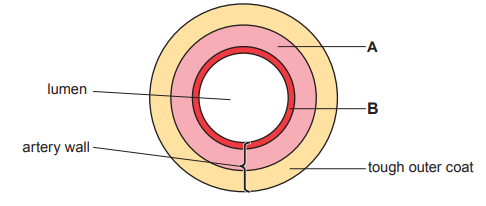
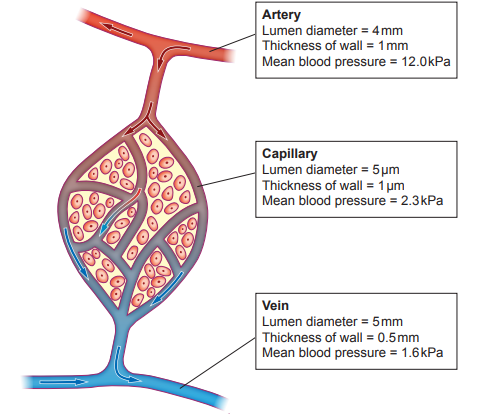
Image 1 shows a section through the heart.
Image 1
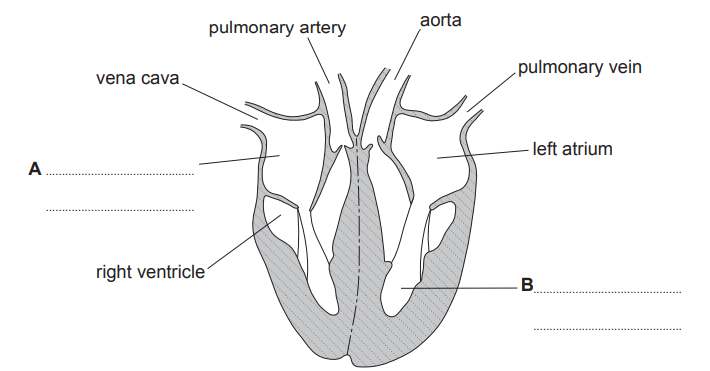
Complete Image 1 by adding the two missing labels (A and B) for the chambers of the heart.
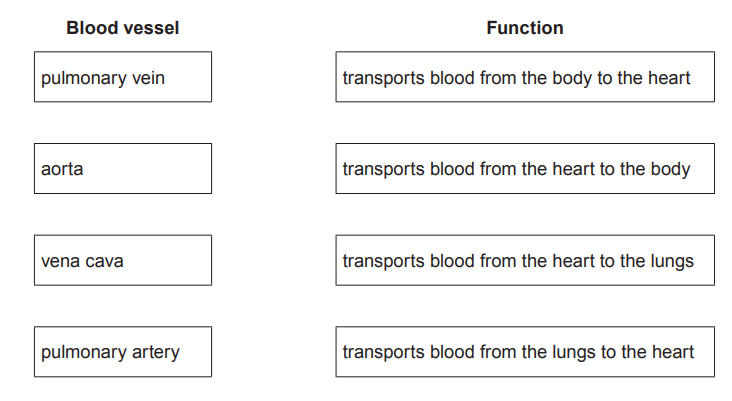
There are four main blood vessels connected to the heart.
Use a ruler to draw lines to match up each blood vessel with the correct function.
There are valves in the heart.
Underline the statement below that describes the function of the valves.
Stop blood from clotting
Push blood through the heart
Prevent the backflow of blood
Complete the following sentences, using the correct words from the list below.
pump muscle pulmonary carbon dioxide coronary
The heart is made of ……..................................………………. . The function of the heart is to ……..................................………………. blood around the body. The heart has its own blood supply provided by the ……..................................………………. arteries.
Was this exam question helpful?