The water intake of a female athlete was monitored before and after completing a marathon. In the 24 hours before the marathon her water intake was 2.70 litres. On the day of the marathon her water intake was 10.4 litres.
Calculate the percentage increase in water intake on the day of the marathon compared to the 24 hours before the marathon. Give your answer to three significant figures.
Increase in water intake = .........................................%
During a marathon, an athlete is at risk of becoming dehydrated.
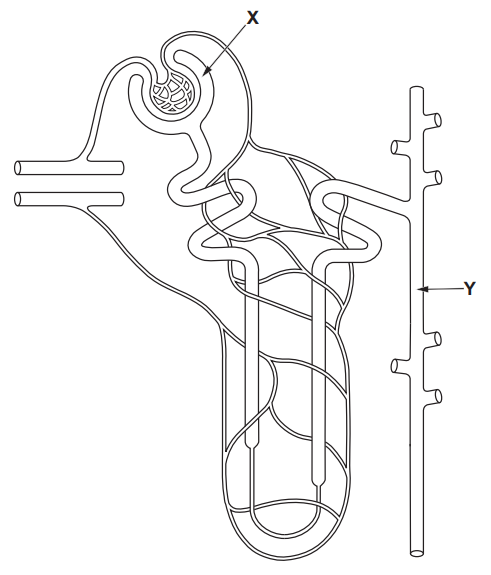
Explain how the brain and kidneys control the level of water in blood during the race to reduce the risk of dehydration.
Was this exam question helpful?