Institutions of the British Constitution: Citizens, the Police and the Civil Service (AQA GCSE Citizenship Studies): Revision Note
Exam code: 8100
Citizens
Citizens are the foundation of the nation state
A nation state exists because citizens belong to it and recognise its authority
Citizen roles
In a democracy, citizens have the power to hold elected representatives to account
This is mainly done through the electoral process, such as voting in elections
Referendums give citizens a direct say in major political decisions
Every citizen’s vote carries equal weight, regardless of background
They play an important part in the justice system
They can serve as jurors, witnesses or magistrates
Citizens help maintain the social fabric of society
This includes involvement in community groups and volunteering
Voter apathy is a concern for politicians
Some citizens choose not to vote or take part in politics
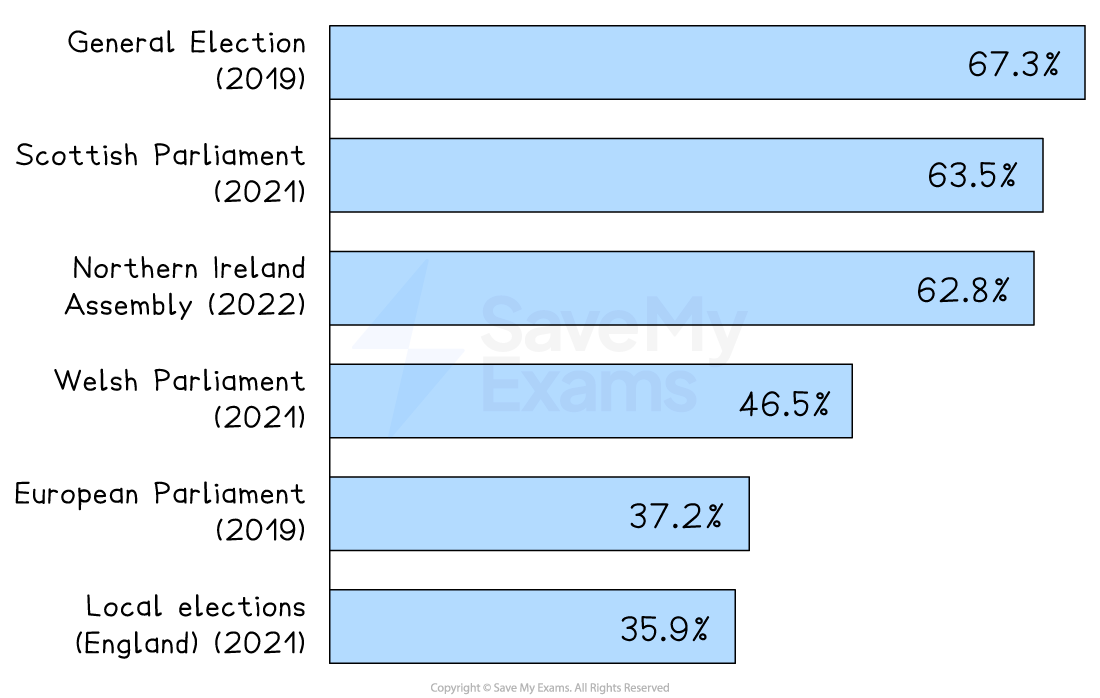
Turnout has been especially low in Police and Crime Commissioner (PCC) elections
As a result, in 2025 the government announced their abolition
In some countries, voting is compulsory
Citizens can be fined for not voting, which increases turnout
The police
The police are responsible for upholding the law, preventing crime and protecting the public
The UK has a number of regional police forces
Over time, smaller forces have been merged into larger ones for efficiency
Case Study
Police forces merge in the Midlands

In 1974, several small police forces, including Birmingham City Police, Coventry Police, and parts of Staffordshire, Worcestershire and Warwickshire Constabularies, were merged following local government reorganisation
The merger was intended to improve efficiency, coordination and consistency in policing a large urban area
West Midlands Police is now one of the largest police forces in the UK
Since 2012, police forces in England and Wales have been overseen by elected Police and Crime Commissioners (PCCs)
PCCs were designed to improve public accountability.
This role is now being abolished, and police forces will instead be overseen by directly elected mayors
The Metropolitan Police in London is different
It is partly under the authority of the Home Secretary
It is also overseen by the Mayor of London
The civil service
The civil service is made up of people who work for and advise the government
They help implement government policies and run public services
The UK civil service is based on three key principles:
Impartiality
Civil servants serve the government of the day, regardless of political party
They are not allowed to take part in political campaigning.
Anonymity
Civil servants work behind the scenes
They are not publicly identified with specific decisions or policies.
Permanence
Civil servants are part of a long-term career structure
They usually remain in their roles when governments change
Case Study
The role of a senior civil servant
Sir Simon Case is the Cabinet Secretary and Head of the Civil Service

He was appointed in 2020 under a Conservative government and continued in his role when the Labour government took office in 2024
This demonstrates the key civil service principle of impartiality
He remained in post to advise and support the government of the day, regardless of which political party was in power
In recent years, more temporary adviser roles have been created
These advisers are political appointments and usually leave when the government changes
Senior civil servants are publicly accountable
They regularly appear before parliamentary select committees, where their work is questioned in public
Examiner Tips and Tricks
When answering questions on citizens and public roles, avoid writing general statements
Examiners reward specific examples, such as jury service, PCCs, or civil service impartiality
Showing how citizens, police and civil servants each contribute in different ways helps you access higher marks

Unlock more, it's free!
Was this revision note helpful?
