The UK’s Role in the Rest of the World (Edexcel GCSE Citizenship Studies): Revision Note
Exam code: 1CS0
The United Nations
The United Nations (UN) was created in 1945 after the Second World War to help prevent future conflict and encourage cooperation between countries
The United Kingdom was a founding member
It is based in New York and today has 193 member states
The four main goals of the UN

The UN Security Council
The UK is one of five permanent members of the UN Security Council, alongside
the USA
Russia
France
China
Each of these countries has a veto, meaning they can block any Security Council resolution
This gives the UK significant influence in international decision-making.
The UK’s influence at the UN
As it has a permanent seat on the Security Council, the UK has significant diplomatic influence, even though it has less military and economic power than other leading members
This influence, gained through cooperation, diplomacy and reputation, is an example of soft power
UK civil servants, experts and non-governmental organisations (NGOs) also contribute to the work of many UN agencies, such as
the World Health Organisation (WHO)
UNESCO (United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organisation)
UNRWA, the UN agency supporting Palestinian refugees, which is currently in the news because of its work in Gaza
North Atlantic Treaty Organisation (NATO)
NATO (the North Atlantic Treaty Organisation) was created in 1949 as a mutual defence alliance
The UK was a founding member
It was originally formed to protect Western countries from the Soviet Union and other communist states in Europe, which were part of the Warsaw Pact
Membership and defence commitment
Today, NATO has 32 member countries
Finland joined in 2023
Sweden joined in 2024
All members agree to support each other if one is attacked
This is known as Article 5, the core of the NATO treaty
NATO organisation
NATO’s headquarters are in Belgium
It has both a military structure and a political structure that work together to coordinate defence and decision-making
In October 2024, Mark Rutte, former Prime Minister of the Netherlands, became the Secretary General, the organisation’s senior political leader
NATO and recent events
In recent years, the USA has pushed NATO members, including the UK, to increase their defence spending
Many NATO countries have recently supported Ukraine in its conflict with Russia by providing
military equipment
financial assistance
training for Ukrainian forces
The Commonwealth
The Commonwealth of Nations was created after the Second World War as countries that had once been part of the British Empire became independent
Today it has 56 countries, and some of them have no past connection with the UK
The Commonwealth contains about 30% of the world’s population
Its members include both very rich and very poor countries, and more than 30 of them have populations below 1.5 million
Membership is voluntary, so countries can choose whether to join
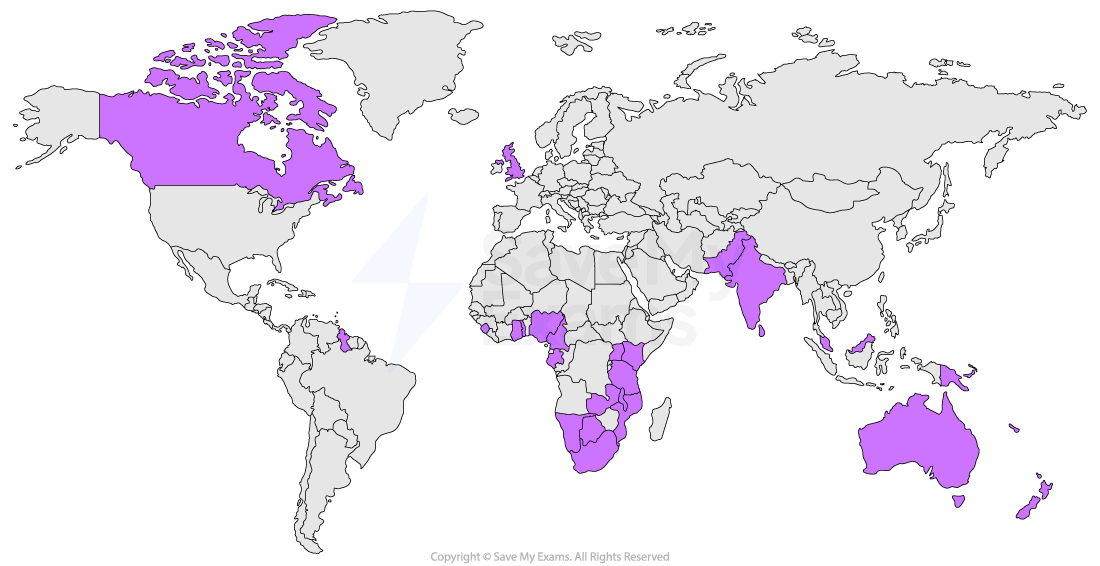
The Commonwealth is guided by a charter, which sets out shared values such as democracy, human rights, equality and development
The organisation also provides education, technical support and economic help to its members
The UK Monarch is the Head of the Commonwealth,
Leading the Commonwealth gives the UK a strong international role and helps it maintain influence across many different parts of the world
This leadership also strengthens the UK’s soft power
It can build positive relationships, support development projects and increase its global reputation with member countries
Examiner Tips and Tricks
A common mistake is assuming the Commonwealth is controlled by the UK
Remember that membership is voluntary and decisions are made collectively. Showing that the organisation operates through cooperation, not UK control, helps you avoid over-simplified answers and gain marks
The World Trade Organisation
The World Trade Organisation (WTO) was created as the General Agreement on Tariffs and Trade (GATT) after the Second World War to help countries trade fairly
Today the WTO has 166 member countries and is based in Geneva, Switzerland.
The UK first joined GATT in 1948
What the WTO Does
Role | Explanation |
|---|---|
Administers international trade agreements |
|
Provides a forum for trade negotiations |
|
Settles trade disputes between countries |
|
Monitors national trade policies |
|
Gives training and support to developing countries |
|
Works with other international organisations |
|
The UK helps agree global trade rules and uses the WTO to resolve trade disputes with other countries
WTO membership allows the UK to trade with countries worldwide on agreed terms

Unlock more, it's free!
Was this revision note helpful?
