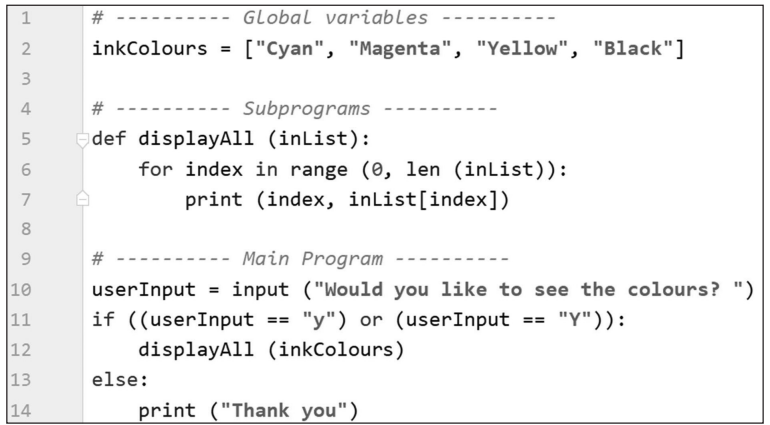
Here is an algorithm that uses colours.

(i) Give the first line number of a condition‑controlled loop.
[1]
(ii) Give the first line number of iteration over every item in a data structure.
[1]
(iii) Give the line numbers of a selection.
[1]
Programs can have syntax errors and runtime errors.
(i) Define the term ‘syntax error’.
[1]
(ii) Runtime errors happen when a program is executing.
Explain a runtime error.
[2]
Algorithms use relational and arithmetic operators.
(i) Here is a relational operator used in a conditional test.
count > index
State the two different results of evaluating a conditional test.
[2]
(ii) Identify the result of 5 // 2
[1]
A. 0.5
B. 1
C. 2
D. 2.5
Programmers consider algorithm efficiency when they write code.
(i) Sorting and searching use algorithms.
Complete the table with the name of a search algorithm and a sort algorithm.
[2]
Algorithm type | Characteristic | Algorithm name |
|---|---|---|
Search | Is a divide and conquer algorithm | |
Sort | Is not a divide and conquer algorithm |
(ii) Explain one effect the number of comparisons has on the execution time of a sorting algorithm.
[2]
Was this exam question helpful?