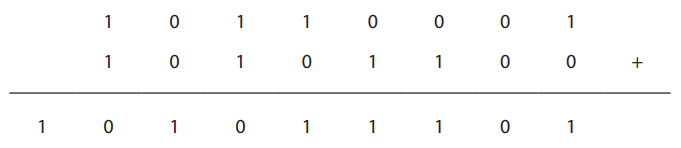
Computers manipulate binary patterns.
Complete the table with the result of applying the shift to the binary pattern.
Binary pattern | Shift | 8-bit binary result |
|---|---|---|
1010 0011 | Logical shift left by 3 | |
1100 1010 | Arithmetic shift right by 2 |
Identify the correct statement about overflow.
Causing the program to crash during an arithmetic operation
Requiring more bits to store a result than are available to store it
Switching between binary and hexadecimal number systems
Using an index less than 0 or greater than the length of an array
Convert the denary value +112 to 8‑bit binary representation.
Give the 8‑bit binary two’s complement representation of denary –73
The number of bits determines the number of patterns that can be represented.
Identify the number of symbols available in the hexadecimal system.
2
8
10
16
Was this exam question helpful?