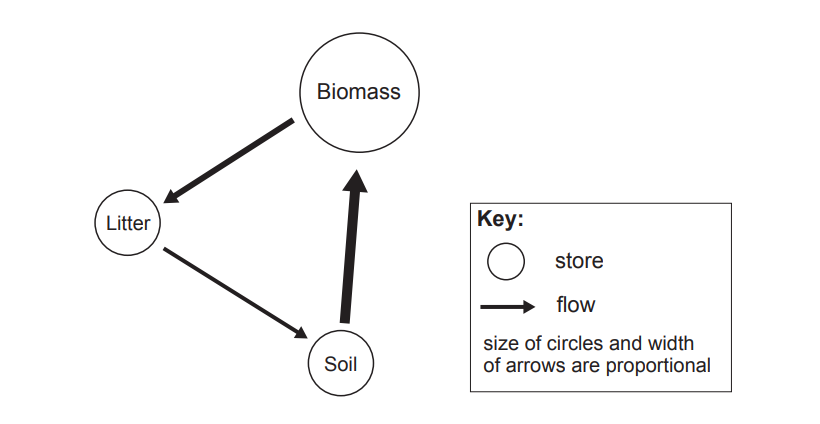
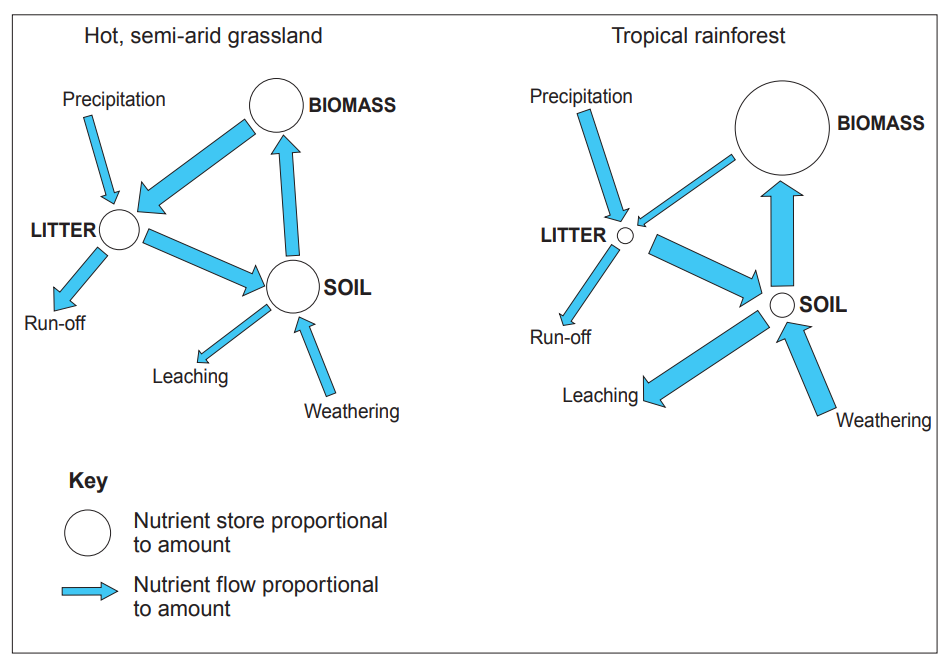
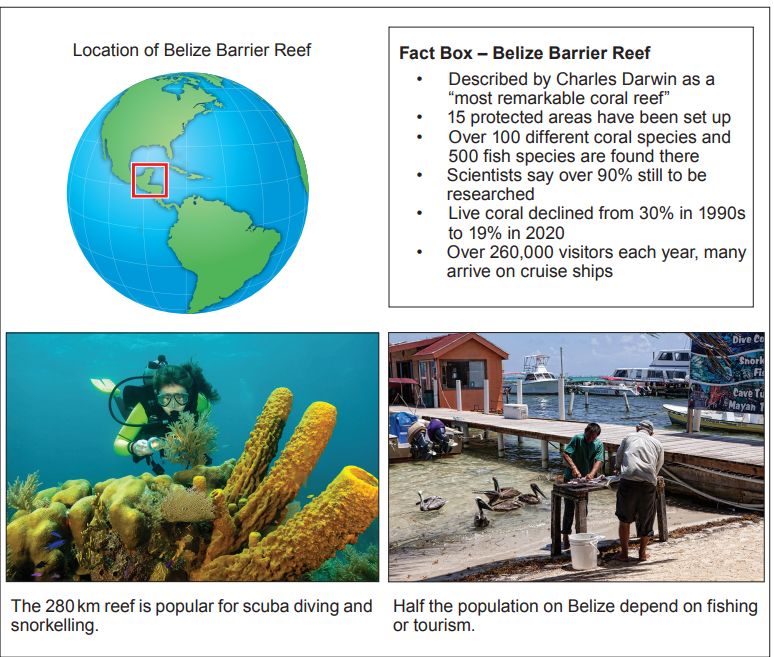
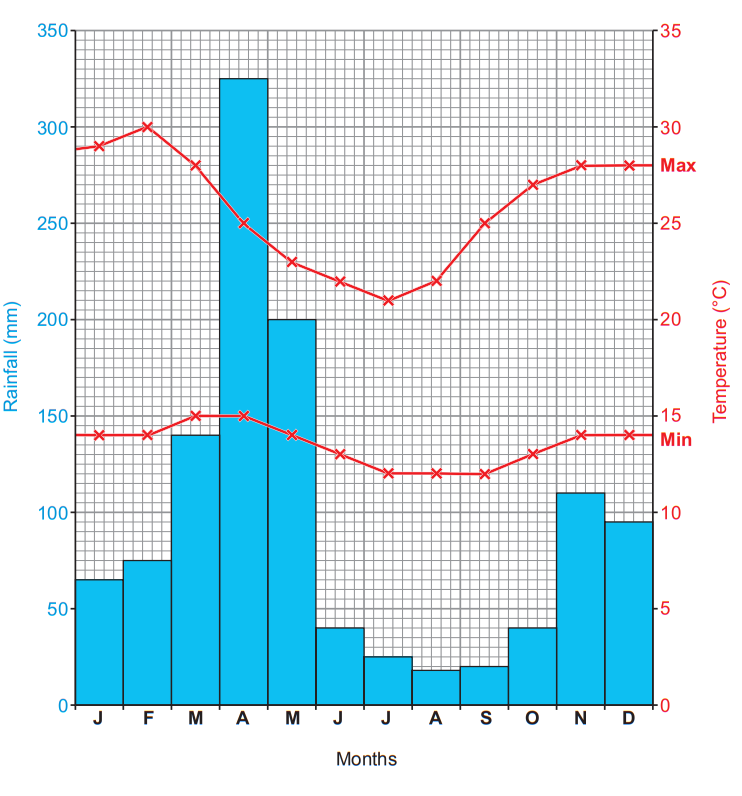
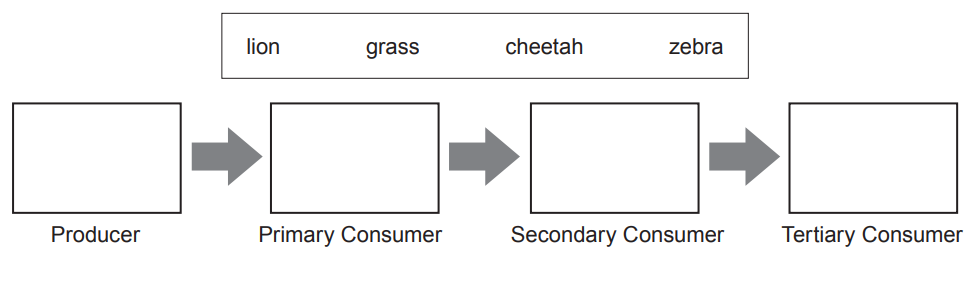
Complete the sentences that follow using three words from the text box below.
rocks photosynthesis biodiversity plants weathering decomposers soil leaching water |
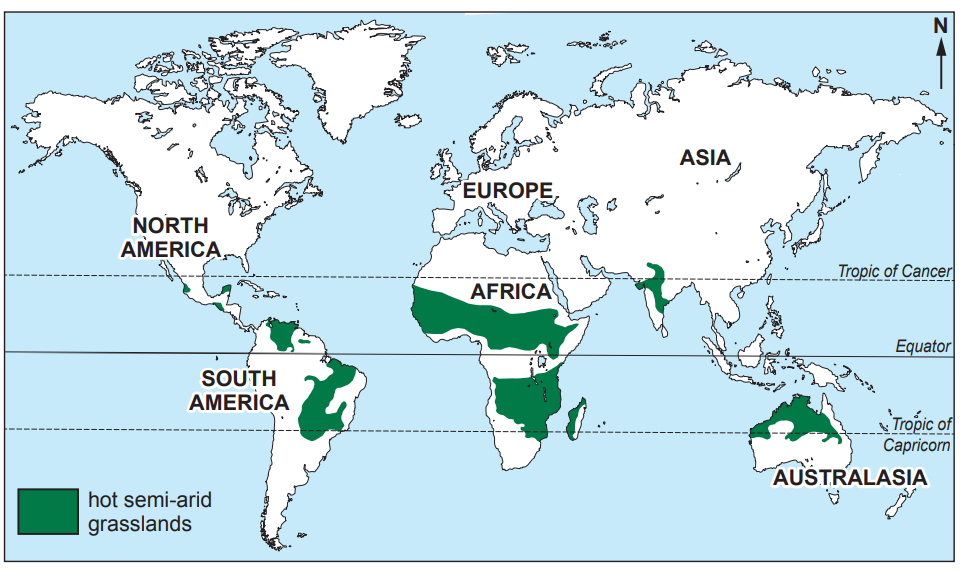
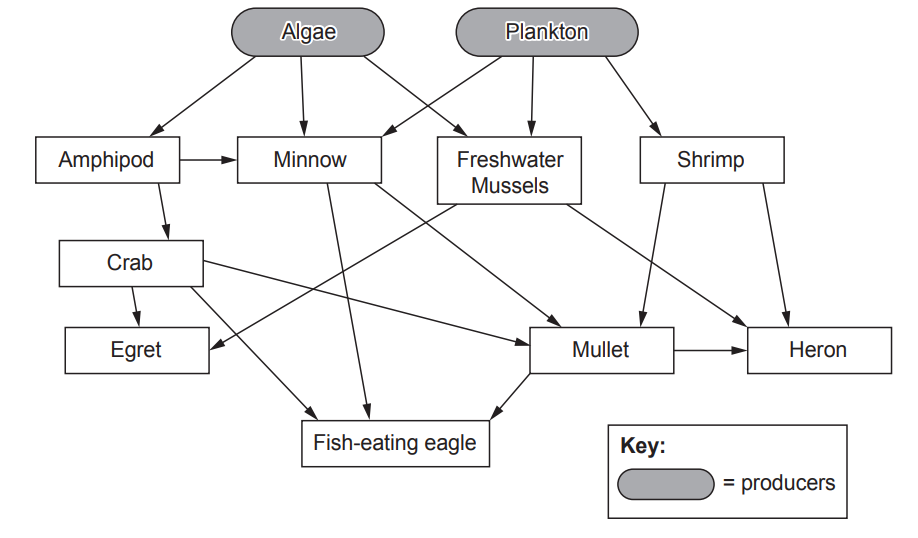
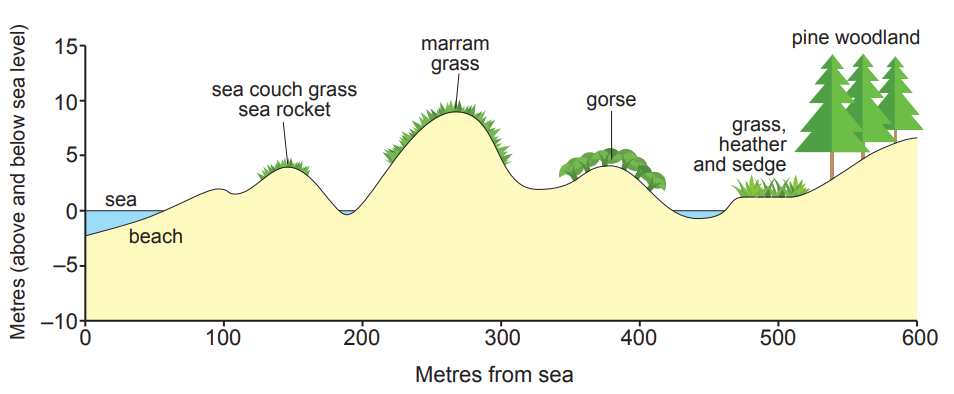
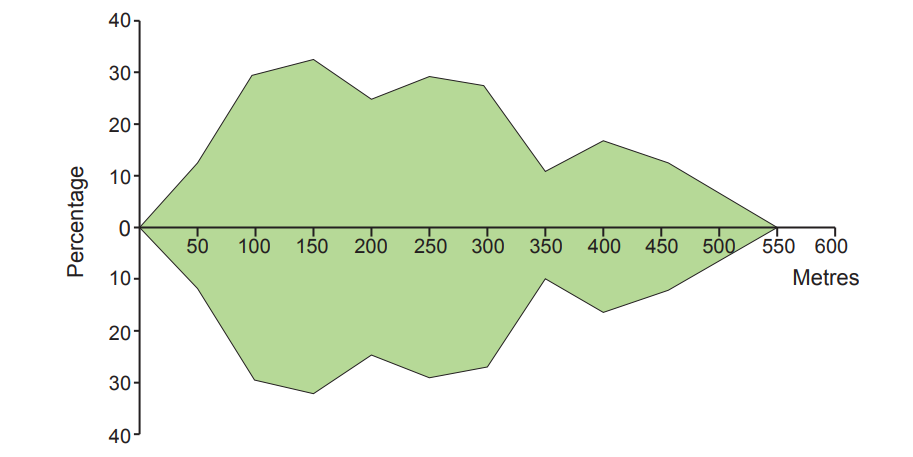
Ecosystems include both living and non-living components.
The living parts include ........................................................ and ........................................................ .
The non-living parts include solar energy, which is taken in by plants through the process of ............................................................................ .