How Did Nazi's Consolidate Power Between 1934-35 (WJEC Eduqas GCSE History): Revision Note
Exam code: C100
Summary & Timeline

When Hitler was appointed Chancellor by Hindenburg in January 1933, he was just like any other politician. But in a matter of months, Hitler had completely dismantled democracy and ruthlessly removed all threats to his power.
First, he used the Reichstag fire to pass emergency laws that allowed him to arrest thousands of political opponents. He then forced through the Enabling Act, which allowed him to rule without having to answer to the Reichstag. He used these powers to ban all other political parties and make trade unions illegal. Those who opposed the changes were sent to the newly opened concentration camps.
The Night of the Long Knives removed the threat of the SA leader Ernst Rohm and brought the Army Generals on his side. When President Hindenburg died in August 1934, the Army swore a personal oath of allegiance to Adolf Hitler, their new Führer.
Hitler as Chancellor
Hitler became Chancellor of Germany on 30th January 1933, but he still did not have complete control of Germany
The Nazi Party only controlled one-third of the Reichstag
Hindenburg was the president of Germany
The Weimar Constitution limited the power of the chancellor
Just like any other elected politician, he could be voted out of power
There was also the possibility that the army could launch a coup d’etat and remove Hitler by force
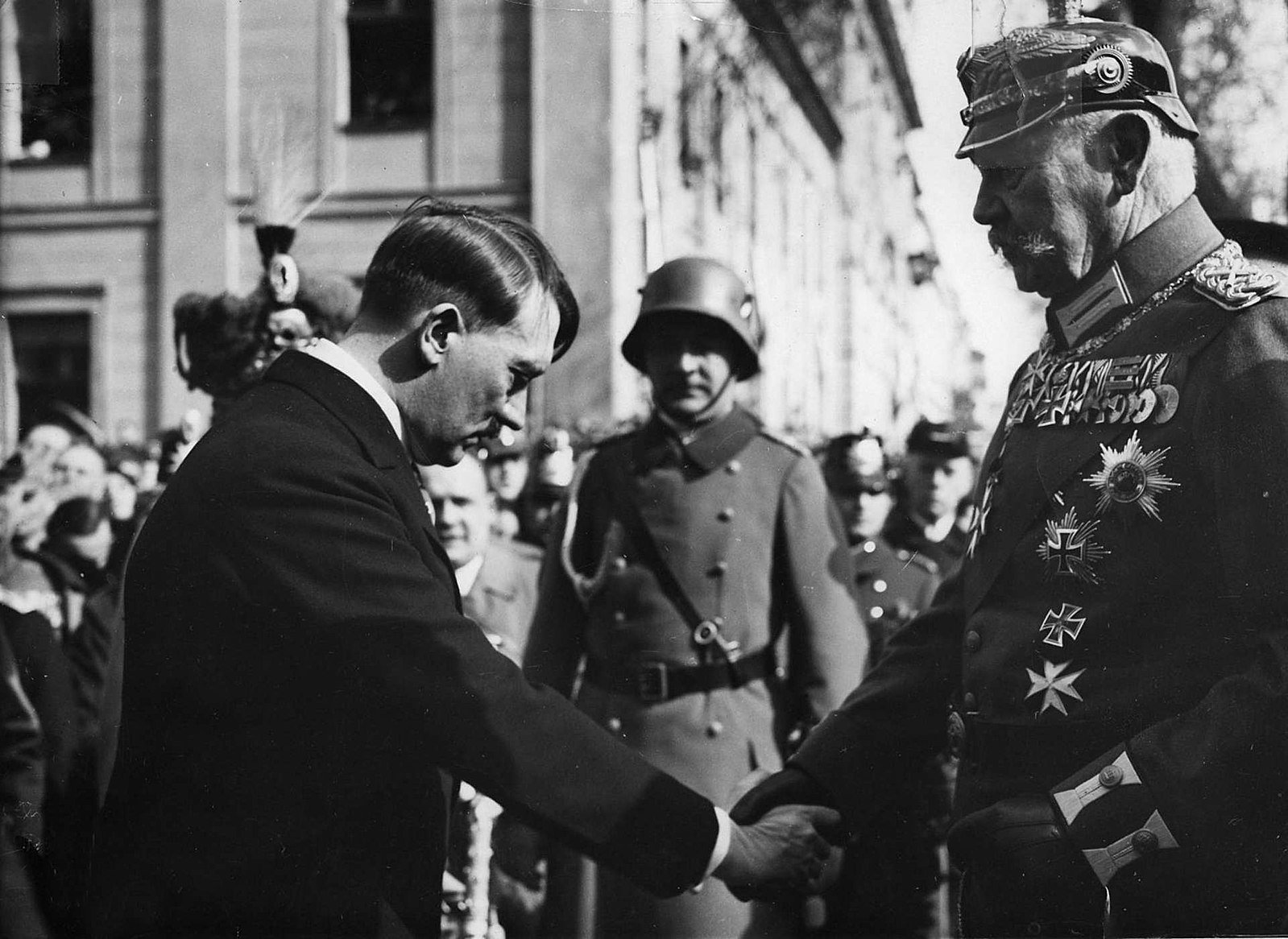

The Reichstag Fire
The Reichstag building was destroyed by fire on 27th February 1933, just weeks after Hitler came to power
A Dutch communist was arrested at the scene, convicted and executed for starting the fire
The fire enabled Hitler to convince Hindenburg that Germany was under threat from a communist revolution
Hindenburg passed the ‘Decree for the Protection of the People and the State’, which gave Hitler emergency powers and suspended civil rights
Many of Hitler’s political opponents were arrested and imprisoned and communist newspapers were shut down

The 1933 Elections and the Enabling Act
New elections were held whilst many of the communists were still imprisoned
The Nazi Party increased their seats to 288 in the March 1933 election
This gave them a majority but not the two-thirds majority they needed to change the constitution
Frustrated by his failure to get a two-thirds majority, Hitler decided to try and pass the Enabling Act
This would suspend democracy for four years and enable Hitler to pass any laws he wanted without needing the Reichstag’s permission
Hitler used devious means to ensure the Enabling Act was passed on 23 March 1933. These included:
Not allowing communists into the chamber to vote
Surrounding the chamber with armed SA men
Counting absentees as being present and voting in favour
Making false promises to the Catholic Centre Party members that the Nazis would not interfere with Churches or Catholic schools
Impact of the Enabling Act
The passing of the Enabling Act marked the end of democracy in Germany
The Enabling Act provided Hitler and the Nazi Party with the power to pass laws without the consent of the Reichstag
The Enabling Act allowed Hitler to censor anything he did not agree with and take full control of the media
Hitler then set about using the powers to remove all forms of political opposition
Trade unions and political parties
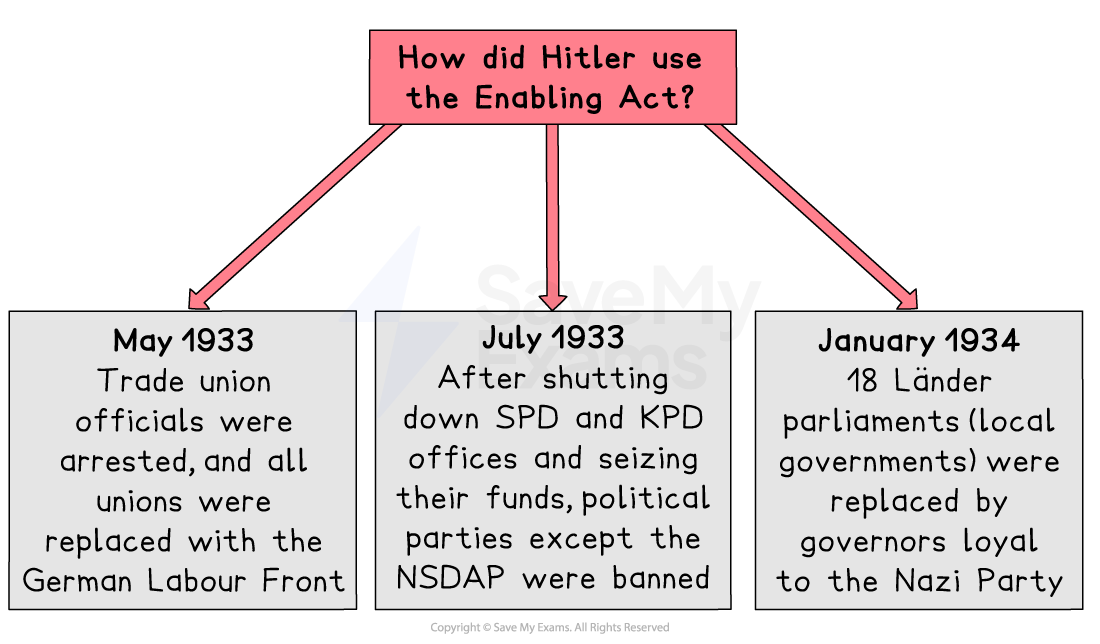
By banning trade unions and making strikes illegal, Hitler was no longer vulnerable to the kind of industrial action that had brought the Kapp Putsch to an end
The shutting down of the SPD and KPD offices was followed by the passing of the Law Against the Formation of Parties in July 1933
This made the Nazi Party the only legal political party in Germany
Union leaders and rival politicians who broke these new laws soon found themselves in Dachau, the first concentration camp, which was opened in March 1933
Night of the Long Knives
The Enabling Act had removed all political opposition
The Night of the Long Knives allowed Hitler to remove two more threats to his power:
The Army
The SA
Why was the Army a Threat to Hitler?
When the Nazis had been campaigning to be elected, Hitler had often promised to destroy the Army and replace it with the SA
The Army Generals had not forgotten this and were wary of Hitler
They could stage a coup d’etat that would remove him from power or even kill him
Why was the SA a Threat to Hitler?
The Sturmabteilung, or SA, had been a great help to Hitler on his path to power and hundreds of thousands of working-class men had joined the ‘Brownshirts’
However, its leader, Ernst Rohm, was growing impatient with Hitler
He wanted some of the more socialist parts of the 25-point programme, like profit sharing from big businesses, to be enacted
He thought Hitler was becoming too close to the army generals and the wealthy industrialists
There was a danger that Rohm could try to topple Hitler as the leader
There were other reasons for Hitler wanting to eliminate Rohm
Rohm was widely known to be homosexual, which was an embarrassment, knowing that the Nazis were in power and sending homosexuals to concentration camps
The ambitious leader of the SS, Heinrich Himmler, saw Rohm as a rival and an opponent and encouraged Hitler to act
30th June 1934
Hitler arranged a meeting with Röhm and other SA leaders on 30th June 1934
Röhm and around 400 SA members were arrested and later shot
Other opponents, such as von Schleicher, Gregor Strasser and von Kahr, who had nothing to do with the SA, were also murdered
The public was informed that Röhm had been planning to replace Hitler, and therefore, his death served the interests of the country
Hitler becomes Führer
Paul von Hindenburg had been the President of Germany since 1925
On 2nd August 1934, he died of lung cancer aged 86
Hitler combined the positions of president and chancellor to make himself Führer, which literally means leader
Over 90% of the public voted in favour of Hitler becoming Führer, although the elections were not free or fair
Hitler forced every soldier to swear an oath of allegiance to him
The period of German history known as the Third Reich had begun

Unlock more, it's free!
Was this revision note helpful?
