US Relations with the USSR & China (WJEC Eduqas GCSE History): Revision Note
Exam code: C100
Timeline & Summary
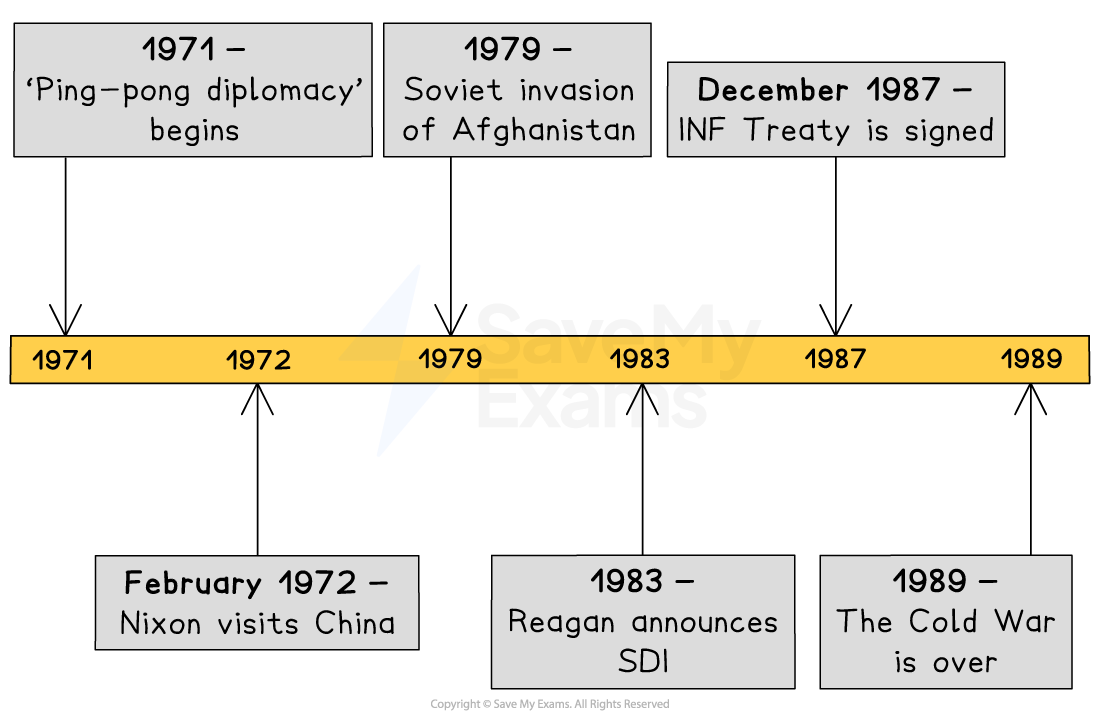
During the 1970s and 1980s, relations between the USA, the USSR and China changed dramatically as Cold War tensions shifted. President Richard Nixon recognised that improving relations with China could strengthen America’s position in the world. China’s criticism of the Soviet invasion of Czechoslovakia and the easing of trade restrictions created an opportunity for cooperation. ‘Ping-pong’ diplomacy in 1971 symbolised this new relationship, eventually leading to Nixon’s historic meeting with Chairman Mao and China’s return to the United Nations.
At the same time, relations between the USA and the USSR rose and fell sharply. The Soviet invasion of Afghanistan in 1979 brought détente to an end. The USA condemned Soviet actions, imposed economic sanctions, and boycotted the 1980 Moscow Olympics. Under President Reagan, tensions escalated during the ‘Second Cold War’. Reagan increased military spending, supported anti-communist groups abroad, and announced the Strategic Defence Initiative (SDI), which the USSR could not afford to match.
Relations improved again in the mid-1980s when Mikhail Gorbachev introduced new policies such as perestroika and glasnost. These reforms reduced Cold War hostility and led to major arms reduction treaties, including the INF Treaty in 1987 and START 1 in 1991. By the end of 1991, both countries publicly declared that the Cold War was over.
Changing Relations with China
President Nixon wanted to improve the state of international relations with China as
China denounced the 1968 Soviet invasion of Czechoslovakia
This was an opportunity for Nixon to exploit their poor relations
Nixon wanted to end the Vietnam War
The USA ended its 21-year trade embargo with China
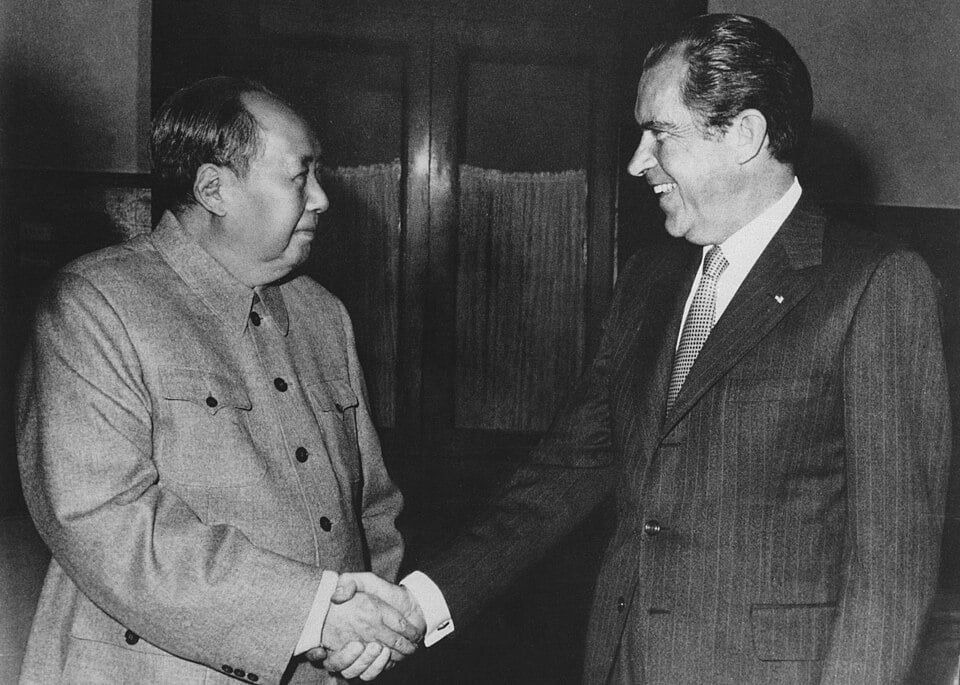
How important was ‘ping-pong’ diplomacy?
It started in 1971, when the Chinese ping-pong team invited the US team to play in China
This was an all-expenses-paid trip to China
They were the first group of US citizens to visit China since 1949
Relations also improved when Chinese ping-pong player Zhuang Zedong offered a ride to American player Glenn Cowan, who missed the bus after a game
This gained a lot of attention from the public
After the trade embargo was lifted, top government officials from the US and China held meetings to help improve relations
This eventually led to the meeting of Nixon and China’s leader, Mao Zedong,
Reducing tensions between the two countries
Economic benefits of the end of the embargo were slow, as it took a while for American products to be introduced into Chinese markets
‘Ping-pong diplomacy’ resulted in:
The restoration of China’s legitimate rights in the United Nations in October 1971
The establishment of diplomatic relations between China and other countries
China put pressure on North Vietnam to hold talks with the US
Which contributed towards the withdrawal from Vietnam

Examiner Tips and Tricks
Some students overestimate how important ‘Ping-Pong diplomacy’ was. Remember that the table-tennis visit in 1971 was mainly symbolic, as it showed a change in attitude, not a major political breakthrough.
The real turning points came after this moment, such as ending the trade embargo, China gaining its seat at the UN, and Nixon meeting Mao. When explaining improved US–China relations, use ‘Ping-Pong diplomacy’ as evidence of a warming in tensions, not the key reason policy changed.
Changing Relations with the USSR
Relations between the USSR and the US increased as
The USSR invaded Afghanistan in 1979
A new arms race began
Soon after President Ronald Reagan became president in 1981
The Soviet invasion of Afghanistan
In 1978, a communist group called the People's Democratic Party of Afghanistan (PDPA) killed the Muslim leaders and took over the government in Afghanistan
By 1979, the Mujahedin, a Muslim guerrilla movement, started a jihad against the government
From December 1979 to January 1880, 50,000 Soviet troops were sent to Afghanistan to restore order and protect the PDPA
This event shocked the US, as relations between the two countries had been improving
The US condemned Soviet actions in Afghanistan
Along with China and the United Nations
The reaction of US President Carter
President Carter adopted the Carter Doctrine, which stated that the US would
Use military force to protect national interests in the Persian Gulf
Provide military aid to all countries surrounding Afghanistan
The US acted against the Soviet Union by
Delaying the SALT II Treaty
Cancelling shipments of grain to the Soviet Union
US companies were not allowed to sell high-tech goods in the Soviet Union
Including computers and oil drilling equipment
Boycotting the 1980 Moscow Olympic Games
This resulted in 61 other countries boycotting the games
Provided funding to the Mujahideen to fight against the Soviet Union
In 1989, the Soviet Union withdrew from Afghanistan
As the Soviet casualties and costs increased
The ‘Second Cold War’ and SDI
During the early 1980s, relations between the USSR and the USA had deteriorated
This period has been referred to as the ‘Second Cold War’
Reagan believed that communism posed a significant threat to the USA
Reagan persuaded the US Congress to increase military spending
In 1982, the USA spent almost 7% of its GDP on the defence budget
Reagan encouraged the development of new weapons such as Trident and stealth bombers
The Reagan Doctrine aimed to:
Give support to anti-communist groups attempting to overthrow communist governments
The US government financed the efforts of anti-communist groups in El Salvador
The US army invaded and overthrew the communist government in Grenada
'Rollback' communism
Reagan wanted to remove the influence of communism from other parts of the world. This would keep communism in the Soviet Union
Reagan made a key speech stating his opinions on communism and the Soviet Union
On 8th March 1983, Reagan made a speech to the National Association of Evangelicals

Reagan introduced the Strategic Defense Initiative (SDI) in 1983
A popular nickname for the SDI was 'Star Wars'
The SDI involved:
Sending satellites into orbit
These satellites would have the capability of shooting down Soviet missiles by laser
Reagan announced the SDI to the US public on 23rd March 1983
At this point, the US scientists had not developed the technology to implement the SDI
Reagan did not inform the US public that the technology did not exist
In the next decade, the US government spent $30 billion attempting to create the SDI
The Soviet Union knew it could not compete with SDI, as it lacked
The money needed to spend on such an initiative
The technology to create the weaponry
The Cold War Reagan & Gorbachev
In the mid-1980s, relations between the USA and USSR improved due to Gorbachev’s policies and his relationship with Reagan
Gorbachev introduced the following policies in the USSR that affected Cold War relations,
Perestroika
A set of economic reforms was created to make the Soviet economy more efficient
Glasnost
A policy of openness, which ended things like censorship of the press and criticism of the government
The end of the arms race
Stopped Soviet interference in Soviet Satellite States
Gorbachev believed that these reforms would strengthen the Soviet Union; however, they led to the collapse of the Soviet Union in 1991 as
Glasnost provided the people with more freedom and the ability to criticise the government
Undermining Gorbachev and the Communist Party
It also showed the people how far behind the Soviet Union was, in terms of technology and wealth, in comparison to the West
The reforms in Perestroika did not really improve the economy
It undermined key systems and parts of the communist system in the USSR, such as centralisation, which was eventually removed
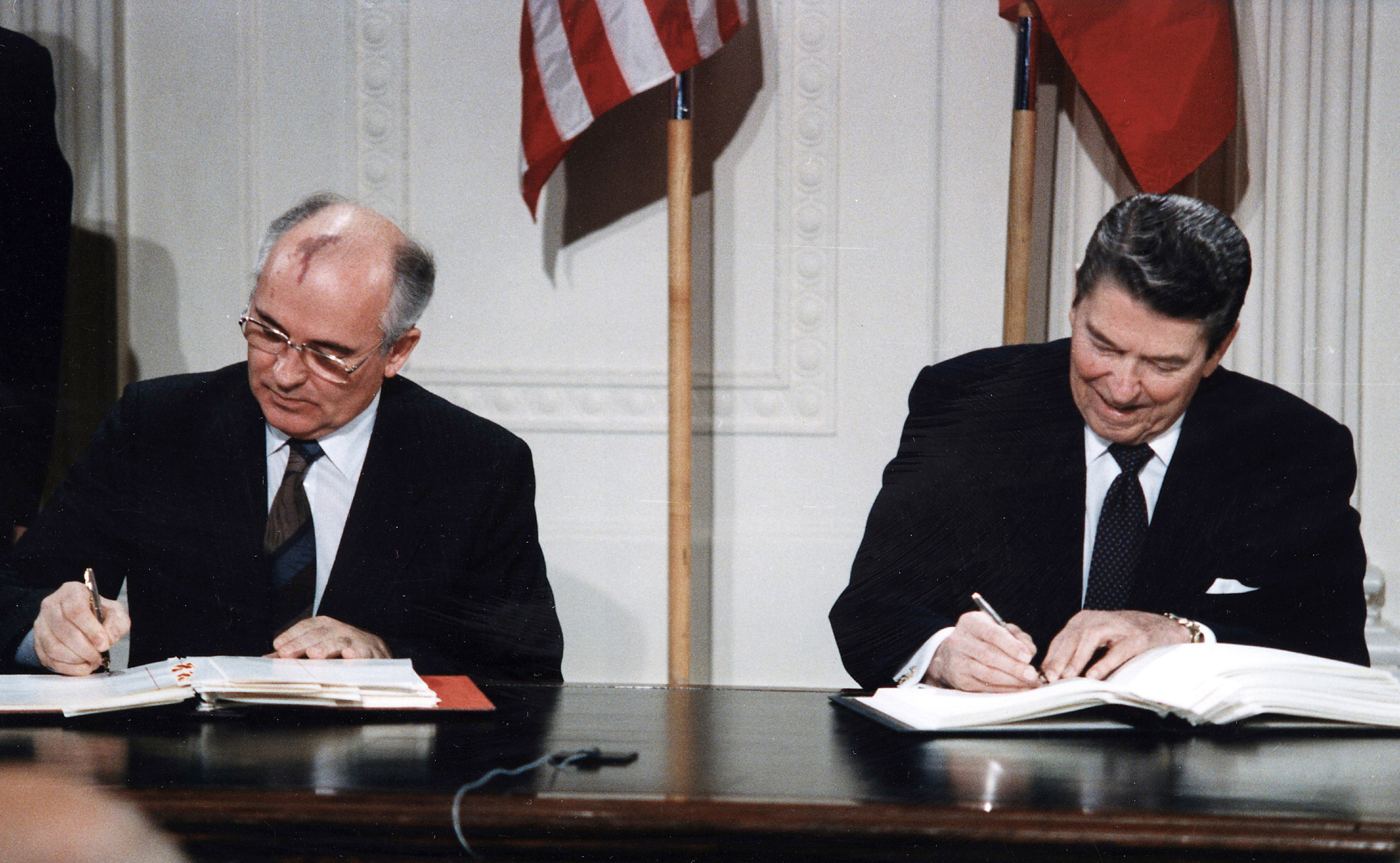
In December 1987, the Intermediate Nuclear Forces Treaty (INF) were signed
Eliminating the use of nuclear and ground-launched missiles and cruise missiles
By Jun 1991, both the USA and USSR honoured this treaty and destroyed a total of 2,692 weapons between them
This was the first treaty to reduce the number of nuclear missiles
Therefore, limiting the growth of both Soviet and American stockpiles
The INF treaty was followed by the Conventional Forces in Europe Treaty, signed by NATO and the Warsaw Pact representatives in November 1990
This reduced the number of tanks, missiles and aircraft held by all nations

Relations continued to improve in the 1990s under President George Bush Snr and Gorbachev
They announced the Cold War was older in Malta, 1989
The Reduction and Limitation of Strategic Arms (START 1) was signed on 31 July 1991
Both sides agreed to reduce strategic nuclear arms over the next seven years

Unlock more, it's free!
Was this revision note helpful?
