The Nature of Good & Evil (WJEC Eduqas GCSE Religious Studies): Revision Note
Exam code: C120
Moral decisions
Morality refers to the principles and standards determining whether actions are right or wrong
Moral decisions are decisions people must make about the right or wrong approaches to take in a situation
Several factors can help people make moral decisions
Image
Conscience is a key factor in making moral decisions. It is an inner voice that guides people and helps them make the right choices
Some religious believers think that God gives us the instinct to make the right choices
We then choose which actions to take. It is our free will that enables us to make such choices. This means that humans can make moral choices independently and voluntarily. Nothing is predetermined
Types of morality
There are two common forms of morality
Absolute morality occurs when a person has a moral principle that they stick to in all situations, regardless of the context or circumstance
For example, they hold the principle “it is wrong to kill”. They will not take part in war, even if it is for a good cause
Several religious groups, such as Roman Catholics, take this absolute moralist approach
Relative morality occurs when a person has a moral principle but is prepared to adapt it in certain situations
For example, they hold the principle “it is wrong to kill”. However, if it reduces future suffering, killing in warfare may be deemed justifiable
Several religious groups, such as Buddhists and many Protestant Christians, take this relative moralist approach
Humanists follow a relative moral approach to judging situations
What is a crime?
A crime is an action that breaks the law of the state
The causes of crime are complex, and several factors often contribute to criminal acts
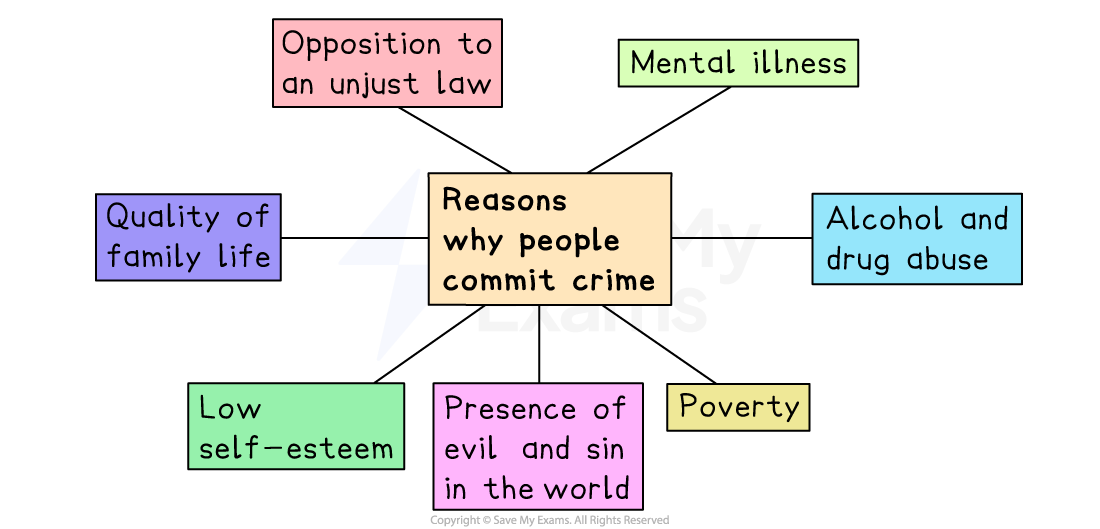
It is important that people are brought up with a strong sense of good and bad and know the difference between the two
All people have a duty to follow the laws of the country and keep order in society
All major religions agree on the importance of law and the role it plays in protecting citizens
Parents and schools have a duty to teach young people the difference between right and wrong, so that they grow up to obey the law and be respectful of others
Christians believe that the Bible teaches people the difference between right and wrong, for example, in the Ten Commandments.
Committing a crime goes against these teachings
Following these teachings can lead people to be good and to be a “child of God” according to the New Testament writer John (John 3:10)
However, sin is part of human nature; therefore, everyone has the potential to commit a crime
When someone is wronged, they should forgive rather than take revenge. This is because God forgave them their sins
Muslims believe that Allah, who is Al ‘Adl (the Just), expects Muslims to act fairly and justly, which means committing no crimes
If people avoid crime, they can advance to do further good in the world
They will be accountable for every action on the Day of Judgment, which should make them conscious about avoiding crime
Muslims should avoid anything that distracts them from focusing on Allah and their faith and which may lead to crime
Worked Example
Define what is meant by morality.
[2 marks]
Answer:
Morality means the principles or standards that help people decide what is right and wrong.
Examiner Tips and Tricks
These beliefs about morality influence how people make decisions about good and evil across all of the themes covered in this course.
Therefore, make sure you are comfortable with the meaning and use of these specialist terms:
Morality
Absolute morality
Relative morality
Conscience
Free will
You can use them throughout your answers on themes, not just when answering questions about good and evil.

Unlock more, it's free!
Was this revision note helpful?
