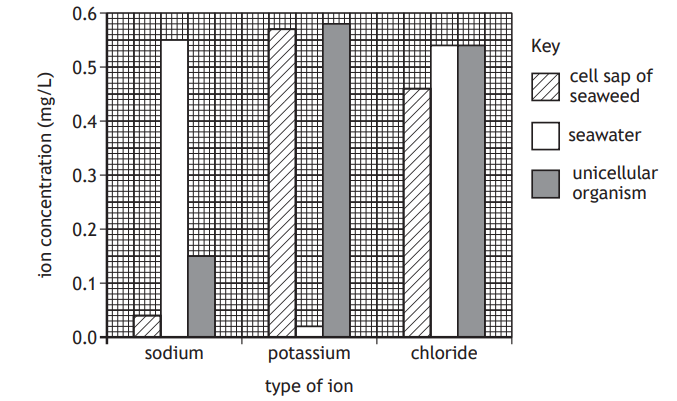
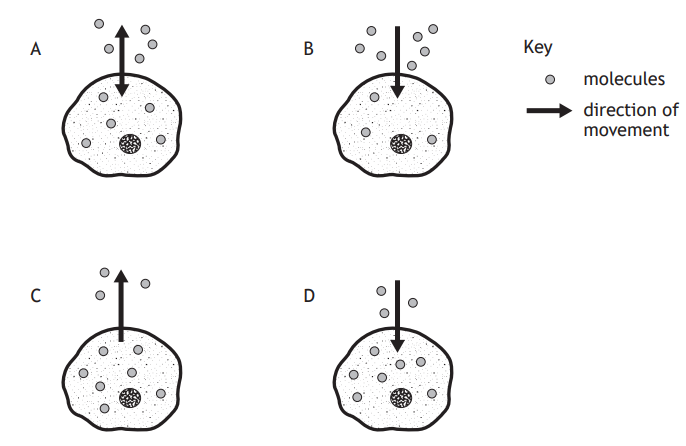
Potato cylinders were placed into different concentrations of sucrose solution and any change in mass was recorded.
The table shows the initial sucrose concentrations inside the potato cells and the concentrations of the solutions they were placed in.
Which potato cylinder will gain the most mass?
Initial sucrose concentration inside potato cells (mol/dm3 ) | Sucrose concentration of solution | |
A | 0.31 | 0.45 |
B | 0.35 | 0.35 |
C | 0.31 | 0.25 |
D | 0.35 | 0.21 |
Was this exam question helpful?