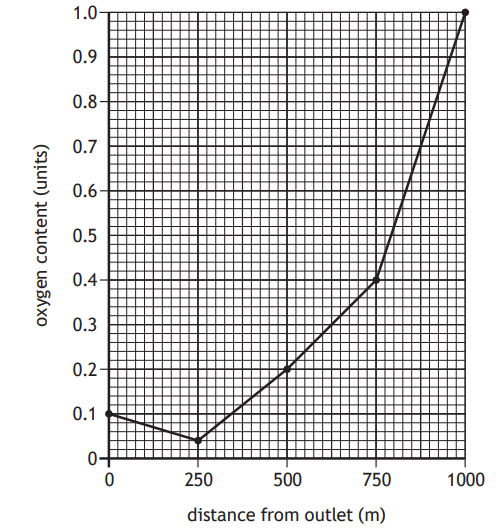
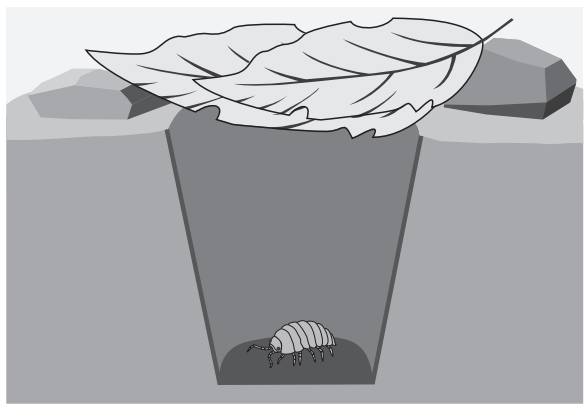
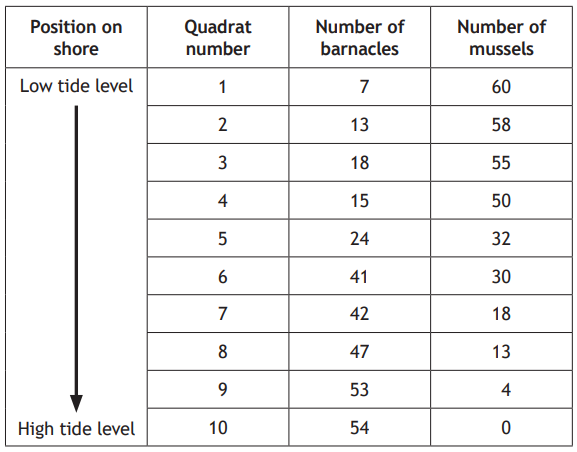
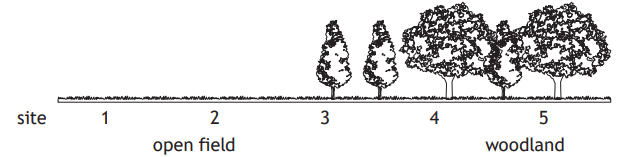
The following paired statement key can be used to identify some birds.
1. Has webbed feet .............................................go to 2
Does not have webbed feet.............................go to 3
2. Has a black head ..............................................puffin
Has a white head...............................................swan
3. Has a curved beak ...........................................go to 4
Has a straight beak ..........................................rook
4. Has a brown head............................................curlew
Has a black head .............................................avocet
Use the information in the key to identify two features of a curlew.