Which of the following compounds can be prepared by precipitation?
You may wish to use the data booklet to help you.
Lithium sulfate
Sodium sulfate
Barium sulfate
Magnesium sulfate
Was this exam question helpful?
Exam code: X813 75
Which of the following compounds can be prepared by precipitation?
You may wish to use the data booklet to help you.
Lithium sulfate
Sodium sulfate
Barium sulfate
Magnesium sulfate
Choose your answer
Was this exam question helpful?
A student was reading the volume of liquid in a piece of apparatus.
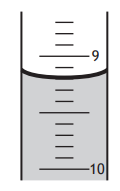
The correct volume, in cm3 , that the student should record is
8.8
9.1
9.2
10.8
Choose your answer
Was this exam question helpful?
A titration was performed using hydrochloric acid and a 10 cm3 solution of sodium hydroxide.
The results are shown in the table.
Titration | Initial reading (cm3 ) | Final reading (cm3 ) | Titre (cm3 ) |
1 | 0.0 | 11.0 | 11.0 |
2 | 11.0 | 21.1 | 10.1 |
3 | 22.0 | 32.6 | 10.6 |
4 | 33.0 | 43.3 | 10.3 |
The average of the concordant titre values, in cm3 , is
10.8
10.5
10.3
10.2
Choose your answer
Was this exam question helpful?
A titration was performed using hydrochloric acid and a 10 cm3 solution of sodium hydroxide.
The results are shown in the table.
Titration | Initial reading (cm3 ) | Final reading (cm3 ) | Titre (cm3 ) |
1 | 0.0 | 11.0 | 11.0 |
2 | 11.0 | 21.1 | 10.1 |
3 | 22.0 | 32.6 | 10.6 |
4 | 33.0 | 43.3 | 10.3 |
Which piece of apparatus is the most appropriate to measure and transfer the 10 cm3 of sodium hydroxide solution?
Burette
Pipette
Conical flask
Measuring cylinder
Choose your answer
Was this exam question helpful?
The apparatus shown was used to measure the energy released when four different fuels were burned.
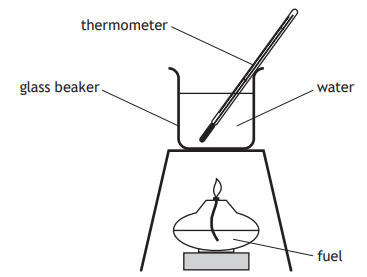
Which of the following changes would not improve the experimental results?
Increasing the distance between the burner and the beaker
Placing a lid on the beaker
Using a copper beaker
Using a heat shield/draft shield
Choose your answer
Was this exam question helpful?
The table shows the colours of ions in solution.
Ion | Colour in solution |
Sodium | colourless |
Calcium | colourless |
Copper(II) | blue |
Chloride | colourless |
Chromate | yellow |
Dichromate | orange |
Which line in the table is correct for the colour in solution and the flame colour when copper(II) chloride is burned?
You may wish to use the data booklet to help you.
Colour in solution | Flame colour | |
A | colourless | blue |
B | blue-green | blue |
C | colourless | blue-green |
D | blue | blue-green |
Choose your answer
Was this exam question helpful?
Which salt cannot be prepared by a precipitation reaction?
You may wish to use the data booklet to help you.
Barium sulfate
Lead(II) sulfate
Calcium chloride
Silver chloride
Choose your answer
Was this exam question helpful?
The Benedict’s test and the iodine test are commonly used to identify the presence of glucose and starch.
The results of these tests are shown.
Test | Result for glucose | Result for starch |
Benedict’s test | blue to orange | no change |
Iodine test | no change | brown to blue/black |
Flame tests can be used to identify the presence of some metal ions.
An unknown mixture was tested and the following results obtained.
Test | Result for unknown mixture |
Benedict’s test | blue to orange |
Iodine test | no change |
Flame test | yellow flame |
Which of the following mixtures could give the results shown?
You may wish to use the data booklet to help you.
Glucose and sodium chloride
Starch and sodium chloride
Glucose and strontium chloride
Starch and strontium chloride
Choose your answer
Was this exam question helpful?
The apparatus shown can be used to identify the products of combustion.
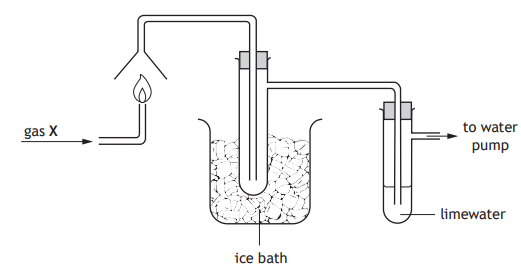
When gas X was burned, a colourless liquid collected in the cooled test tube but there was no change in the limewater.
Gas X could be:
methane
carbon monoxide
hydrogen
ethane.
Choose your answer
Was this exam question helpful?
A student measured 25 cm3 of sodium hydroxide for a titration experiment using a 100 cm3 measuring cylinder. Their teacher suggested that there was a more accurate piece of apparatus to measure this volume.
Which piece of apparatus should the student have used to more accurately measure out the 25 cm3 volume of sodium hydroxide?
100 cm3 beaker
25 cm3 measuring cylinder
25 cm3 pipette
100 cm3 conical flask
Choose your answer
Was this exam question helpful?
Nitrogen dioxide is a brown coloured gas that is soluble in water and more dense than air.
Which of the following diagrams shows the most appropriate method for collecting and measuring the volume of nitrogen dioxide?
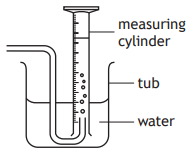
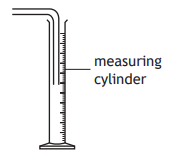
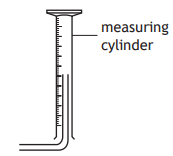
Choose your answer
Was this exam question helpful?
A solution of a metal chloride burns with a green flame.
Which of the following metal ions could be present in the metal chloride?
You may wish to use the data booklet to help you.
Ba2+
Ca2+
K+
Na+
Choose your answer
Was this exam question helpful?
Identify the gas that turns limewater cloudy.
Oxygen
Nitrogen
Hydrogen
Carbon dioxide
Choose your answer
Was this exam question helpful?
AgNO3 (aq) + NaBr(aq) NaNO3 (aq) + AgBr(s)
The reaction shown by the equation is an example of
addition
combustion
precipitation
neutralisation.
Choose your answer
Was this exam question helpful?
2K+ (aq) + 2I– (aq) + Pb2+ (aq) + 2NO3 - (aq) PbI2 (s) + 2K+ (aq) + 2NO3 - (aq)
The type of reaction represented by this equation is
neutralisation
precipitation
addition
redox.
Choose your answer
Was this exam question helpful?
A student prepared a sample of copper sulfate crystals by reacting excess copper carbonate with acid.
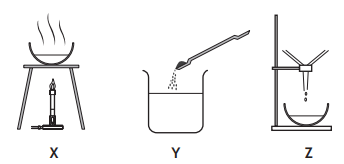
Which line in the table shows the correct order in which this experiment would be carried out?
Y, X, Z
X, Y, Z
Z, Y, X
Y, Z, X
Choose your answer
Was this exam question helpful?