The structural formula for a compound is shown.
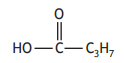
The name of this compound is
propanoic acid
propan-1-ol
butanoic acid
butan-1-ol.
Was this exam question helpful?
Exam code: X813 75
The structural formula for a compound is shown.
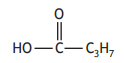
The name of this compound is
propanoic acid
propan-1-ol
butanoic acid
butan-1-ol.
Choose your answer
Was this exam question helpful?
Hydrogen bonds are a type of intermolecular force that exists between some molecules.
Hydrogen bonds will exist between molecules that contain a hydrogen atom directly bonded to an atom of either nitrogen, oxygen or fluorine.
Which of the following substances will have hydrogen bonds between its molecules?
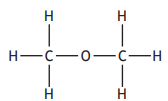
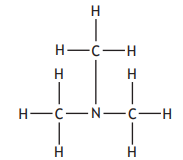
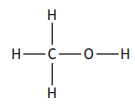
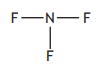
Choose your answer
Was this exam question helpful?
Carboxylic acids can react to form compounds known as ketones.
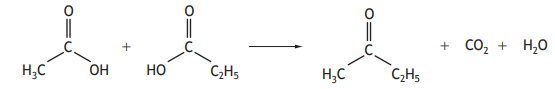
Identify the ketone that can be formed by reacting the two carboxylic acids below.
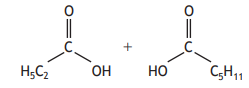
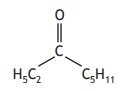
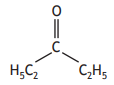
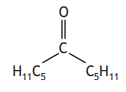
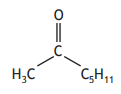
Choose your answer
Was this exam question helpful?
Which line in the table correctly describes methanol compared to octan-1-ol?
Formula mass | Solubility in water | |
A | higher | lower |
B | lower | lower |
C | higher | higher |
D | lower | higher |
Choose your answer
Was this exam question helpful?
Sodium methanoate is produced in the reaction of
sodium oxide and methanol
sodium chloride and methanoic acid
sodium oxide and methanoic acid
sodium and methanol.
Choose your answer
Was this exam question helpful?
Which of the following compounds has the highest boiling point?
You may wish to use the data booklet to help you.
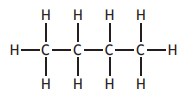
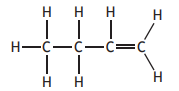
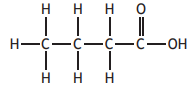
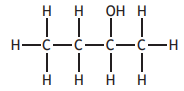
Choose your answer
Was this exam question helpful?
Which line in the table correctly describes the trends going from hexanoic acid to butanoic acid?
Formula mass | Solubility in water | |
A | increasing | decreasing |
B | decreasing | increasing |
C | decreasing | decreasing |
D | increasing | increasing |
Choose your answer
Was this exam question helpful?
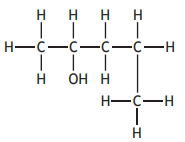
The systematic name for the above compound is
pentan-2-ol
pentan-4-ol
1-methylbutan-3-ol
4-methylbutan-2-ol.
Choose your answer
Was this exam question helpful?
Which of the following alcohols is the least soluble in water?
Butan-1-ol
Hexan-1-ol
Pentan-1-ol
Propan-1-ol
Choose your answer
Was this exam question helpful?