Structure Diagrams (SQA National 5 Computing Science): Revision Note
Exam code: X816 75
Structure diagrams
What are structure diagrams?
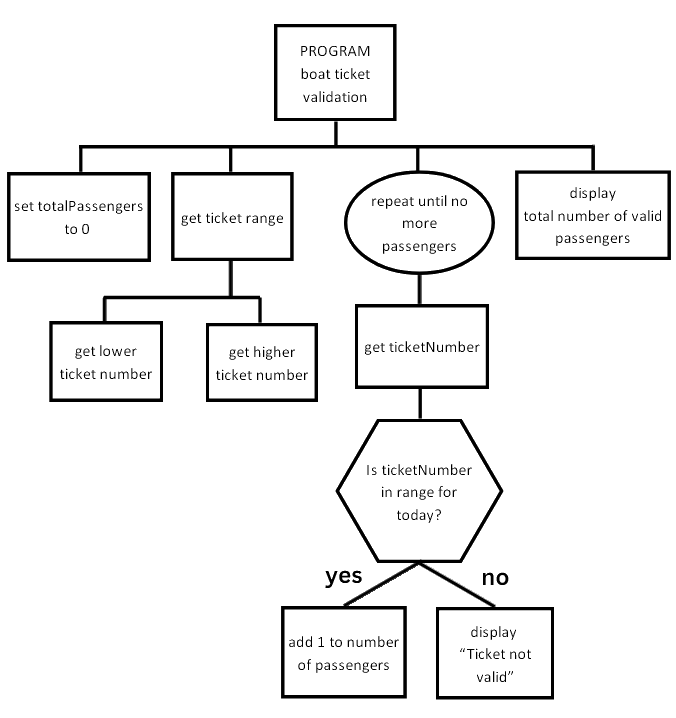
A structure diagram is a design technique used during the design stage of the software development process
It shows the overall structure of a program before any code is written
The diagram represents the main steps needed to solve a problem
Each step can be broken down into sub-tasks, helping to plan the program in a clear and logical way
Structure diagrams are read from top to bottom and left to right
Why use structure diagrams?
They help visualise the program’s structure before implementation
They make programs easier to understand, test, and maintain
They allow programmers to identify where loops, decisions, and processes are needed
They help to spot repetition or inefficient steps in a design before coding starts
Key components of structure diagrams
Symbol | Name | Meaning | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
Process | Shows an action or calculation | set totalPassengers to 0 | |
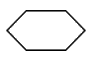 | Selection | Shows a decision or condition | Is ticketNumber in range for today? |
Loop | Shows repetition of a process | repeat until no more passengers | |
Predefined process | Refers to a separate subprogram or function | CalculateAverage() |
Examiner Tips and Tricks
Questions may ask you to identify the type of construct (e.g. loop, conditional, arithmetic operation) used in a diagram
Always read the diagram from top to bottom and look for repetition or branching to decide how the logic flows

Unlock more, it's free!
Was this revision note helpful?
